It is possible for an attacker to compromise an RPM repository and add a malicious key. An attacker could compromise an RPM repository by compromising a system that hosts RPM repositories via XSS or other vectors. Alternatively, an attacker could compromise an RPM repository by compromising the RPM signing key. An attacker could compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the system on which the signing key is stored. An attacker could also compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the RPM repository itself. An attacker could compromise the RPM repository by compromising the system that hosts the RPM signing key. A compromised repository could then be used to install malicious keys. Further, an attacker could compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the system on which the signing key is stored. An attacker could compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the system on which the signing key is stored. An attacker could compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the system on which the signing key is stored. An attacker could compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the system on which the signing key is stored. An attacker could compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the system on which the signing key is stored. An attacker could compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the system on which the signing key is stored.
Vulnerability Finding Tips
Search for the CVE-2021-3521 vulnerability on Shodan. This vulnerability has been confirmed in the following releases of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.
Search for the CVE-2021-3521 vulnerability on Shodan. This vulnerability has been confirmed in the following releases of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.
Installment
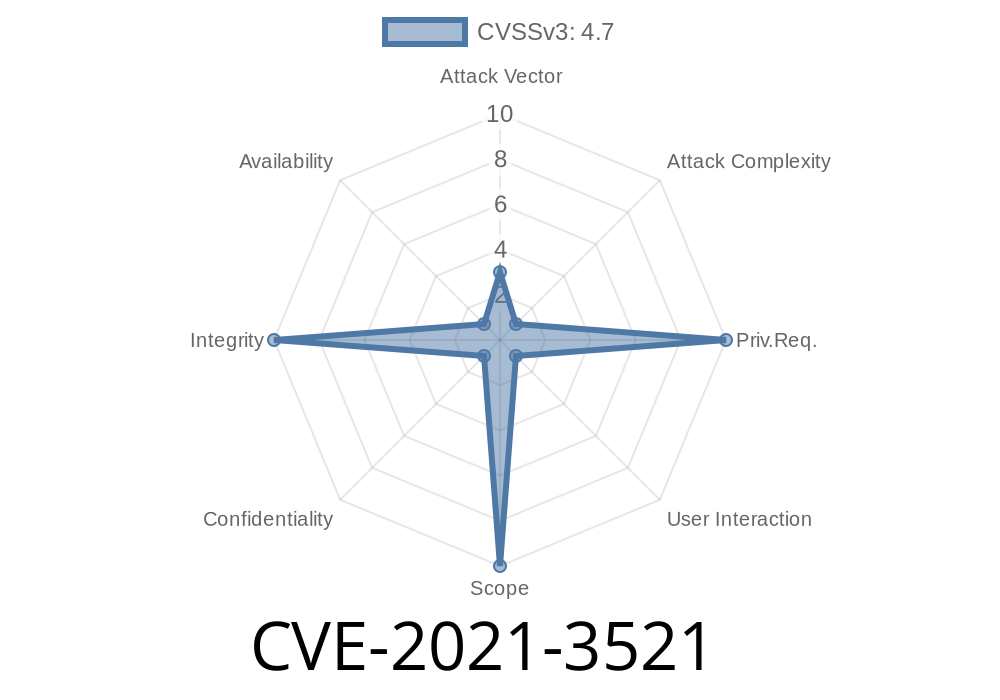
The vulnerability, CVE-2021-3521, is a local privilege escalation vulnerability in an RPM repository.
Potential Impact of CVE-2021-3521
A malicious RPM that uses this vulnerability could allow attackers to install keyless RSA keys on the affected system. This would allow attackers to impersonate the legitimate key. In addition, a malicious RPM that uses this vulnerability could allow an attacker to install a keyless RSA key on the affected system. This would allow the attacker to impersonate any user who possesses a key signed by the compromised signing key and use their credentials to access and manipulate web servers running on the affected system.
CVE-2022-3533
It is possible for an attacker to compromise a repository and add malicious keys. An attacker could compromise a repository by compromising a system that hosts repositories via XSS or other vectors. Alternatively, an attacker could compromise a repository by compromising the RPM signing key. An attacker could also compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the repository itself. A compromised repository could then be used to install malicious keys. Further, an attacker could compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the system on which it is stored. An attacker could even compromise the RPM signing key by compromising the system on which it is stored.
Timeline
Published on: 08/22/2022 15:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 08/26/2022 15:36:00 UTC
References
- https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2021-3521
- https://github.com/rpm-software-management/rpm/pull/1795/
- https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1941098
- https://github.com/rpm-software-management/rpm/commit/bd36c5dc9fb6d90c46fbfed8c2d67516fc571ec8
- https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2021-3521