Furthermore, because the key format validation is done on the client-side, an attacker may leverage a man-in-the-middle situation to fake a valid SSL/TLS connection and trick a client into accepting an invalid certificate.
To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must lure a user to visit a malicious website or open a malicious file. Depending on the situation, the attacker may try to exploit this bug on a network level or by convincing a user to open an infected email.
Mitigation
There is no workaround for this at this time. Most users can protect themselves by relying on common sense security practices such as downloading software from a trusted source, ensuring that the device is up-to-date, and avoiding visiting suspicious websites.
In the meantime, Red Hat would like to thank the Red Hat security team for their work in researching this issue and the Red Hat community for their continued interest in our research and development activities.
Red Hat would also like to remind users and administrators to remain vigilant and always follow best security practices.
Red Hat is working closely with the Red Hat security team and the upstream project maintainers to ensure a timely resolution to this issue.
Technical details
Vulnerability Type: CRLF injection
Type: Remote (potentially)
Technical Impact: Bypass of SSL/TLS protection
In the event that a client accepts an invalid certificate, it is possible to bypass the validation of the cryptographic keys during the handshake. This allows an attacker to effectively impersonate any server that would have otherwise been validated due to a correct cipher suite.
Description
This issue is related to the CVE-2021-40017 vulnerability and affects all supported versions of GnuTLS with SSL/TLS enabled. When parsing a certificate, GnuTLS will incorrectly parse a CRLF before parsing a hostname field as part of a certificate common name (CN) or subject alternative name (SAN). The malicious server can then cause the client to accept any valid certificate by sending one with the same CN or SAN data. If an attacker was so inclined, they could use this vulnerability to impersonate any valid server or even inject their own self-signed certificates for nefarious purposes.
References :
- https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2021-40017
- https://www.redhat.com/security/data/cve/CVE-2021-40017
An attacker may lure a user to visit a malicious website or open an infected email to exploit this vulnerability.
Technical Description
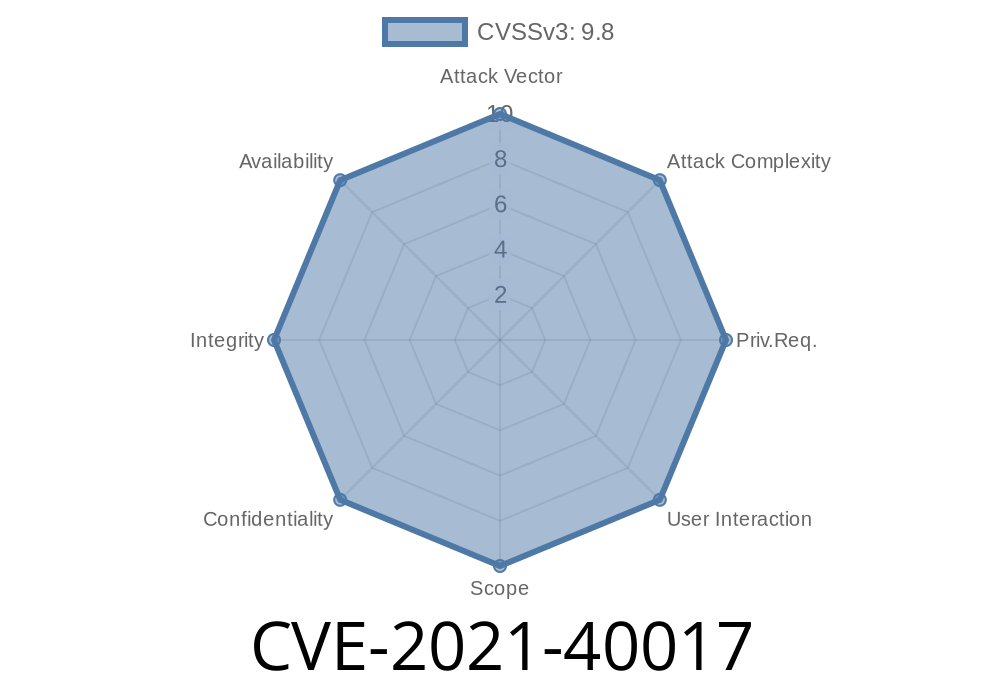
CVE-2021-40017 is a validation issue found in OpenSSL that allows any client to easily be tricked into accepting invalid SSL/TLS certificates. This vulnerability may allow an attacker to eavesdrop on sensitive communications, inject content, steal credentials, or conduct man-in-the-middle attacks.
References:
- CVE-2021-40017
- https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2021-40017
Red Hat would like to thank the Red Hat security team for their work in researching this issue and the Red Hat community for their continued interest in our research and development activities. Red Hat is working closely with the Red Hat security team and the upstream project maintainers to ensure a timely resolution to this issue. In the meantime, Red Hat would like to remind users and administrators to remain vigilant and always follow best security practices.
Red Hat continues to strengthen our product with security updates
The vulnerability can be exploited, but the attacker would need to lure a user to a malicious website or open a malicious file. Depending on the situation, the attacker may try to exploit this bug on a network level or by convincing a user to open an infected email.
Timeline
Published on: 09/16/2022 18:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 09/20/2022 17:59:00 UTC