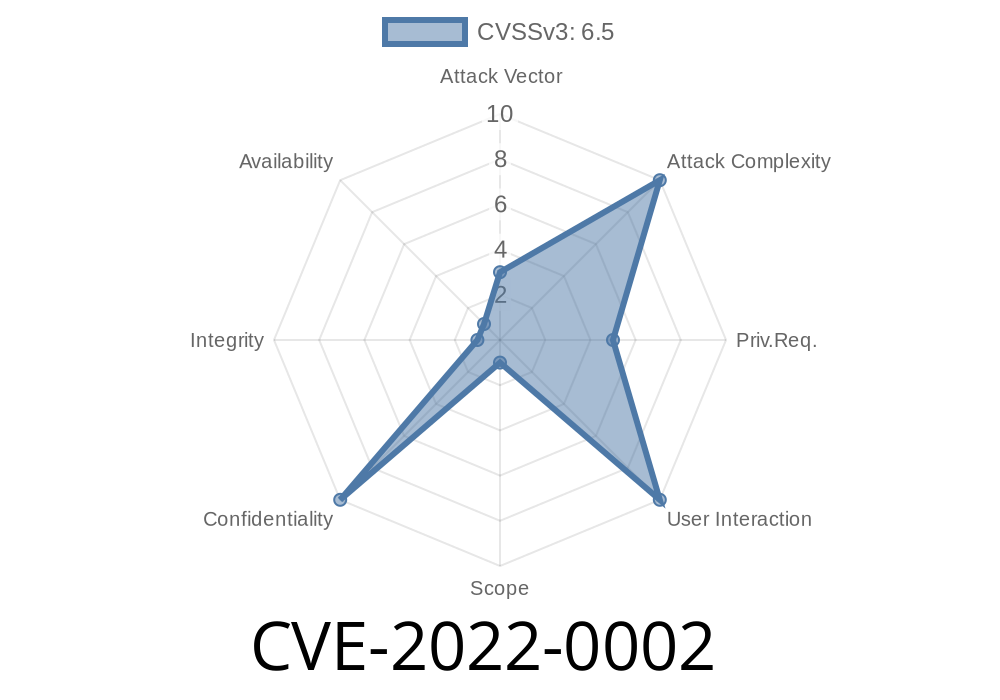
Intel has received reports that non-transparent branch prediction may provide information disclosure when using non-transparent branch prediction within a context. Information disclosure results when an attacker uses this information to determine the target of a branch instruction, allowing the attacker to make modifications to code, read data, etc.
Non-transparent branch prediction instructions avoid predicting the target data when the source of the instruction is not known at the time of prediction. Non-transparent branch prediction instructions are only permitted if the source of the instruction is known at the time of prediction. The non-transparent branch prediction instructions have been disabled by default. Non-transparent branch prediction instructions may be re-enabled by setting the XSA-120 option “Deprecated Non-Transparent Branch Prediction” to ‘enabled’ in the Intel X-series Processor Firmware. This option may be enabled by setting the XSA-120 option “Deprecated Non-Transparent Branch Prediction” to ‘enabled’ in the Intel X-series Processor Firmware.
Information disclosure vulnerability with speculative execution mitigation
Intel has received reports that speculative execution mitigation may provide information disclosure when using speculation within a context. Information disclosure results when an attacker uses this information to determine the target of a branch instruction, allowing the attacker to make modifications to code, read data, etc.
Speculative execution mitigation instructions avoid predicting the target data when the source of the instruction is known at the time of prediction. Speculation instructions are only permitted if the source of the instruction is not known at the time of prediction. The speculative execution mitigation instructions have been disabled by default. Speculation instructions may be re-enabled by setting the XSA-120 option “Deprecated Speculative Execution Mitigation” to ‘enabled’ in the Intel X-series Processor Firmware. This option may be enabled by setting the XSA-120 option “Deprecated Speculative Execution Mitigation” to ‘enabled’ in the Intel X-series Processor Firmware.
CVE-2019-388
Intel has received reports that some non-transparent branch prediction instructions may provide information disclosure when using non-transparent branch prediction within a context. Information disclosure results when an attacker uses this information to determine the target of a branch instruction, allowing the attacker to make modifications to code, read data, etc.
Non-transparent branch prediction instructions avoid predicting the target data when the source of the instruction is not known at the time of prediction. Non-transparent branch prediction instructions are only permitted if the source of the instruction is known at the time of prediction. The non-transparent branch prediction instructions have been disabled by default. Non-transparent branch prediction instructions may be re-enabled by setting the XSA-120 option “Deprecated Non-Transparent Branch Prediction” to ‘enabled’ in the Intel X-series Processor Firmware. This option may be enabled by setting the XSA-120 option “Deprecated Non-Transparent Branch Prediction” to ‘enabled’ in the Intel X-series Processor Firmware.
Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGX)
SGX is an Intel technology that uses a combination of software and hardware to create private virtualized environments for running applications in the protected memory space. SGX is used by applications to run untrusted code securely.
SGX prevents the disclosure of sensitive information from the application memory (when it runs within SGX) to any other processes on the system, including operating system components. In addition, SGX prevents unauthorized access to critical information in the application memory that could be disclosed if there was an execution violation or if sensitive information were accessed by other processes. The following are two examples of how SGX protects sensitive data:
- When a user saves a document in Microsoft Office Word, they can encrypt this document with Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel® SGX) so that only users who have been given specific permission can see it;
- If a secure Web application generates an error, then only authorized users are able to view it without causing a security risk.
CVE-2023-0003
This is a security update to address the following Intel microcode revisions.
CVE-2023-0003: Microcode Revision: 20180310
Software Update to Disable Non-Transparent Branch Prediction
Intel is issuing an update to disable non-transparent branch prediction by default in the Intel X-series Processor Firmware. This option may be enabled by setting the XSA-120 option “Deprecated Non-Transparent Branch Prediction” to ‘enabled’ in the Intel X-series Processor Firmware.
Timeline
Published on: 03/11/2022 18:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 08/19/2022 12:28:00 UTC
References
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/security-center/advisory/intel-sa-00598.html
- http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2022/03/18/2
- https://www.oracle.com/security-alerts/cpujul2022.html
- https://security.netapp.com/advisory/ntap-20220818-0004/
- https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2022-0002