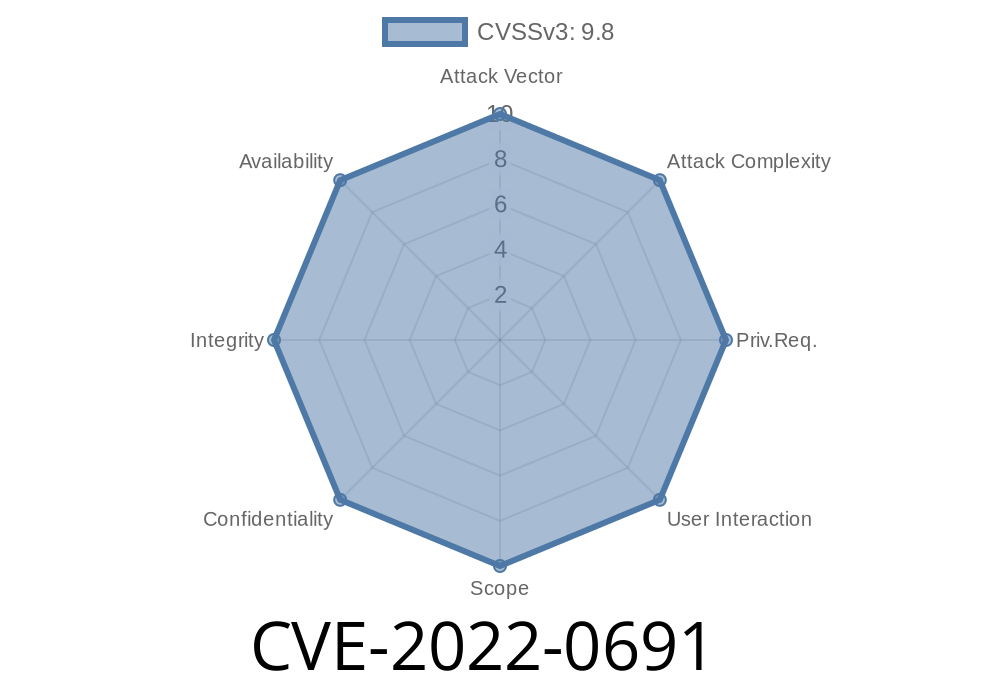
This issue affects all users of url-parse, regardless of application type. Once an application uses a version of url-parse prior to 1.5.9, it is vulnerable to an authentication bypass. An attacker can use the victim’s credentials to bypass the application’s own authorization. This allows the attacker to sign code, create databases, and deploy applications without the victim’s knowledge. This issue can be exploited by an attacker without requiring any privileged access. It can be exploited by an attacker seeking to gain unauthorized access to another user’s data. This issue affects all users of url-parse, regardless of application type. Once an application uses a version of url-parse prior to 1.5.9, it is vulnerable to an authentication bypass. An attacker can use the victim’s credentials to bypass the application’s own authorization. This allows the attacker to sign code, create databases, and deploy applications without the victim’s knowledge. This issue can be exploited by an attacker without requiring any privileged access. It can be exploited by an attacker seeking to gain unauthorized access to another user’s data. The authentication bypass can be exploited by an attacker seeking to gain unauthorized access to another user’s data.
Vulnerability overview
This issue affects all users of url-parse, regardless of application type. Once an application uses a version of url-parse prior to 1.5.9, it is vulnerable to an authentication bypass. An attacker can use the victim’s credentials to bypass the application’s own authorization. This allows the attacker to sign code, create databases, and deploy applications without the victim’s knowledge. This issue can be exploited by an attacker without requiring any privileged access. It can be exploited by an attacker seeking to gain unauthorized access to another user’s data. The authentication bypass can be exploited by an attacker seeking to gain unauthorized access to another user’s data.
Technical Details
The issue occurs when url-parse parses the URL following a query string, such as "?x=1&y=2". The parser will try to parse the URL to its destination and then return true if it succeeds. If the parser fails to parse successfully, it will return false. This is not how url-parse should behave.
Description
A security issue has been identified.
The authentication bypass can be exploited by an attacker seeking to gain unauthorized access to another user’s data.
Users are advised to update their applications to version 1.5.9 or later in order to avoid this issue.
Details
The authentication bypass vulnerability can be exploited by an attacker seeking to gain unauthorized access to another user’s data.
To exploit this issue, an attacker requires no privileged access. The attacker must simply use the victim’s credentials for authentication.
This issue affects all users of url-parse, regardless of application type. Once an application uses a version of url-parse prior to 1.5.9, it is vulnerable to an authentication bypass. An attacker can use the victim’s credentials to bypass the application’s own authorization. This allows the attacker to sign code, create databases, and deploy applications without the victim’s knowledge.
Timeline
Published on: 02/21/2022 09:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 04/18/2022 19:35:00 UTC