This vulnerability was fixed in GitLab 14.7.5 and 14.8.2 releases. Users can update their GitLab installations by going to Settings > Updates and clicking on “Check for updates now”. A security issue has been identified with Quick actions that might allow an unauthorised user to access sensitive data and potentially steal the login tokens of the runner. This has been fixed in GitLab 14.7.5 and 14.8.2 releases. If you are using a pre-14.7.5 or pre-14.8.1 version, you need to update as soon as possible. Users can update their GitLab installations by going to Settings > Updates and clicking on “Check for updates now”.
GitLab Single Sign-On
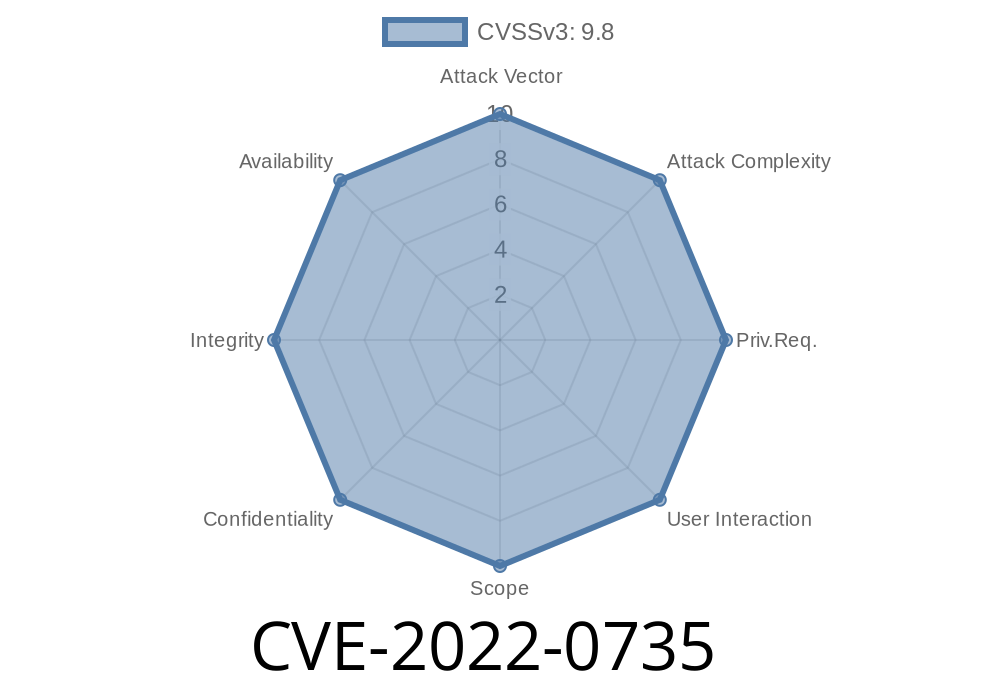
(SSO) vulnerability
The vulnerability is related to GitLab single sign-on (SSO). An unauthorised user might be able to access sensitive information and steal the login tokens of the runner.
GitLab Vulnerability Summary
GitLab is an open-source, web-based repository for working with Git and other version control systems. It provides a web interface that integrates closely with the Git command line tool.
The vulnerability allowed an unauthorised user to access sensitive data and potentially steal the login tokens of the runner.
This issue has been fixed in the 14.7.5 and 14.8.2 releases of GitLab CE/EE/EEH and EE Core (all versions). All users should upgrade as soon as possible to ensure they are protected against this security risk.
GitLab version and build number check
If you are using the default GitLab installer, and have not run the update yet after upgrading to 14.7.5 or 14.8.2, please check your GitLab version and build number by running gitlab-ctl version and gitlab-ctl build . If they do not match the current release and build number, you need to either check for updates manually or use the installation instructions below to install from scratch:
* Install from scratch:
If your GitLab installation was upgraded by a package manager or through an upgrade script (such as apt) on Debian-based distributions, then it is likely that your packages have been removed by the upgrade script and you may need to reinstall them again manually. The following commands will help you with this:
Debian/Ubuntu: apt remove gitlab && apt install gitlab-gitlab-shell && apt install --only-upgrade gitlab-gitlab-runner
Arch Linux: pacman -R gitlab && pacman -Sp gitlab
Fedora, CentOS/RHEL: dnf remove --purge gitlab && dnf reinstall --only=latest gitlab*
Gentoo: emerge app-admin/gitlab*
Oracle Linux: yum remove --exclude=gitlab*
GitLab Instances Experiencing High CPU and Disk Utilization
GitLab instances experiencing high CPU and disk utilization can be identified by the following:
* The instance is taking unusually long to start.
* Memory usage is high.
* A significant number of core processes are running.
* High memory usage for a user with a small number of repositories.
Timeline
Published on: 03/28/2022 19:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 04/04/2022 19:23:00 UTC