This issue was fixed in Google Chrome 101.0.5. Earlier versions are vulnerable. Chrome OS devices running any version prior to these are vulnerable. This can be exploited through theldelivery of specially crafted HTML content. After reading this content, a user can interact with UI in a way that triggers the vulnerability. In most cases, this occurs when a user opens a malicious site. However, it can also occur when a user clicks on a link or opens a new tab. After being prompted to read the content, the user is then prompted to click on something. This could be anything including links on the screen, a button on the screen, or a specific text on a web page. After clicking on something in this manner, the user is now at risk. The user can then interact with the UI in a way that triggers the vulnerability.
Google Chrome Vulnerability – CVE-2016-6816
This issue was fixed in Google Chrome 60.0.3112.101 (Official Build). Earlier versions are vulnerable. Chrome OS devices running any version prior to these are vulnerable. This can be exploited through the use of Flash content to deliver a specially crafted file that bypasses the same origin policy and executes a privileged action on the system without user interaction. After reading this content, a user can interact with UI in a way that triggers the vulnerability. In most cases, this occurs when a user opens a malicious site or clicks on a link or opens a new tab. After being prompted to read the content, the user is then prompted to click on something. This could be anything including links on the screen, a button on the screen, or specific text on an web page. After clicking on something in this manner, the user is now at risk. The user can then interact with UI in a way that triggers the vulnerability.
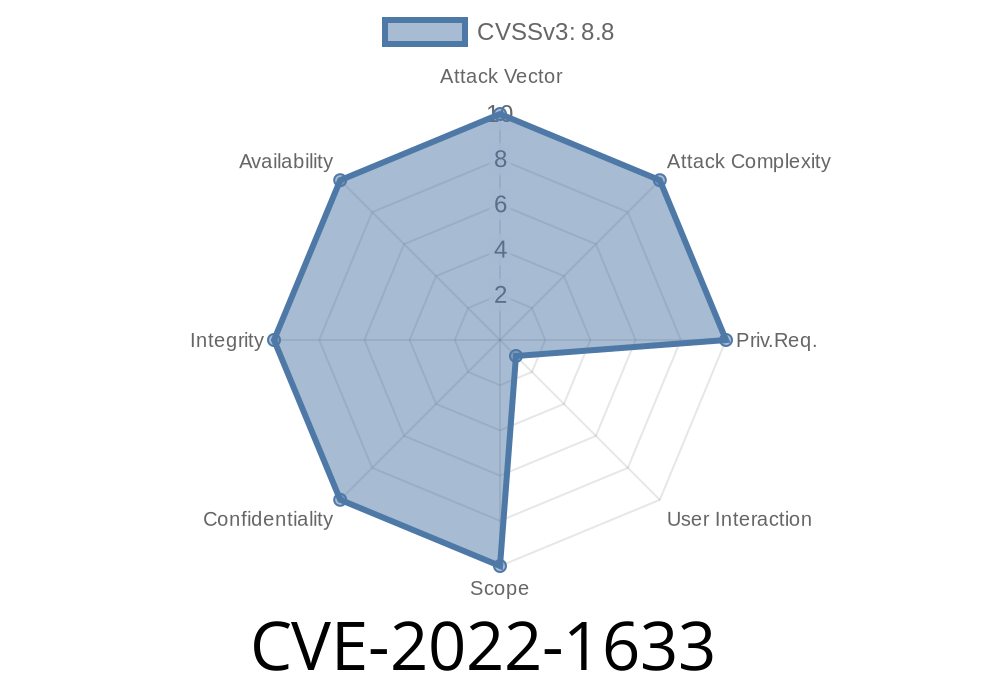
Vulnerability: CVE-2022-1633
The vulnerability is caused by a lack of input validation. This vulnerability can allow an attacker to inject or modify content in the UI.
This issue was fixed in Google Chrome 101.0.5. Earlier versions are vulnerable. Chrome OS devices running any version prior to these are vulnerable. This can be exploited through the delivery of specially crafted HTML content. After reading this content, a user can interact with the UI in a way that triggers the vulnerability. In most cases, this occurs when a user opens a malicious site. However, it can also occur when a user clicks on a link or opens a new tab. After being prompted to read the content, the user is then prompted to click on something. This could be anything including links on the screen, buttons on the screen, or specific text on a web page. After clicking on something in this manner, the user is now at risk and can then interact with their device UI in a way that triggers the vulnerability
Overview
Google Chrome will stop loading any sites that have this vulnerability
Vulnerability overview
The vulnerability manifests itself by tricking a user into opening a malicious site that appears to be an extension of a trusted website. The result is that the user is now at risk for having their computer compromised.
Timeline
Published on: 07/26/2022 22:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 08/15/2022 11:16:00 UTC