In January 2022, Oracle disclosed a notable bug affecting MySQL Server, identified as CVE-2022-21344. This vulnerability, found in the Replication component, impacts widely used versions—5.7.36 and earlier and 8..27 and earlier. According to Oracle’s advisory, it is easily exploitable by high-privileged users with access via multiple protocols, potentially resulting in a hang or crash (DoS) of the MySQL process.
Let’s break down what this means, how it could be exploited, and what you can do to stay secure—all in plain language, with code samples and real context.
Vulnerability Details
CVE-2022-21344 resides in MySQL’s Replication logic. While it cannot be exploited remotely without proper user rights, any attacker with SUPER or equivalent privileges and network access to your MySQL server can easily crash the whole database instance.
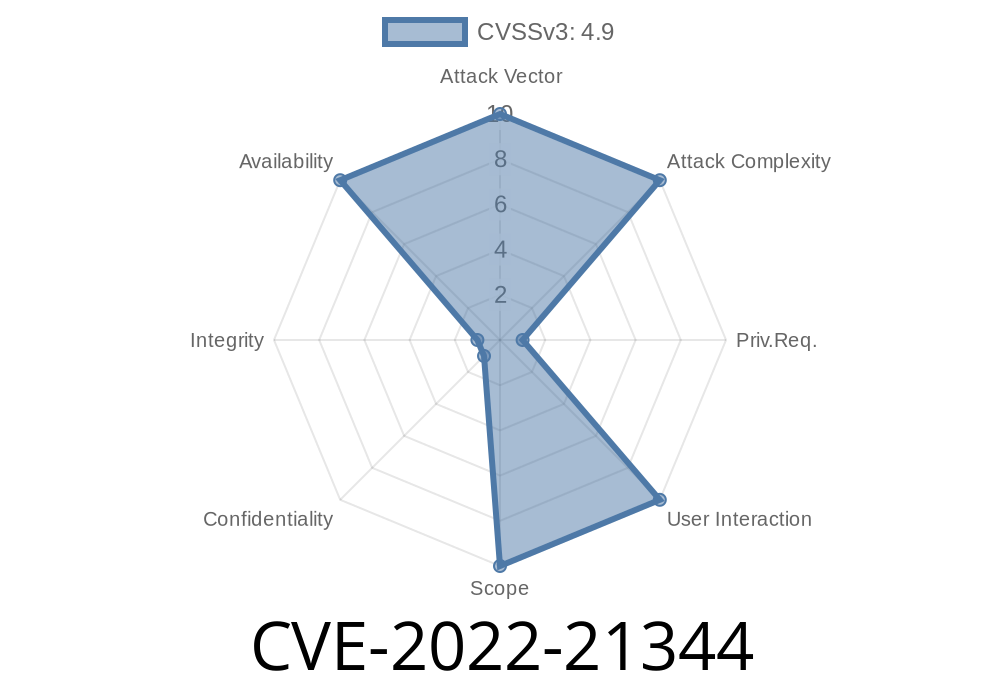
4.9 (medium availability impact)
- Vector: CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:N/A:H
References:
- Oracle CPU January 2022 advisory
- NVD Entry for CVE-2022-21344
Here is a step-by-step scenario for a potential exploit
1. Attacker acquires high-privilege access (e.g., the repl or root account, or any account with SUPER/REPLICATION CLIENT privileges).
Via network, attacker connects to the MySQL server.
3. Attacker submits malformed or specially crafted statements to the Replication subsystem, causing buffer corruption, assertion failure, or a hang.
MySQL server crashes, resulting in total loss of service (DoS) until manually restarted.
While Oracle did not publish a detailed technical description, analysis of patch diffs and community discussions give us a hint about the vectors.
Example Exploit (Hypothetical)
Note: There are no readily-available public exploits, but based on the patch and replication bugs, typical attacks involve creating master/slave replication setups and sending malformed binlog events.
Suppose you have a replication account
-- On the master, attacker has access as 'repl_user'@'%'
CREATE USER 'repl_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'repl_user'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Now, using a crafted client or by abusing existing MySQL tools, an attacker may attempt to set up replication with malicious input or binlog manipulation, causing crash conditions.
Pseudo Code: Crash via Replication
import mysql.connector
# Attacker connects with high-privileged account
conn = mysql.connector.connect(
host='target-mysql-server',
user='repl_user',
password='password'
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Send crafted statement (this is a generic example)
# The actual statement would require knowledge of replication internal bins, possibly crafted GTID or binlog events
cursor.execute("START SLAVE;") # Starts replication
# Potentially send malformed requests or chain of replication commands
cursor.execute("CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_LOG_FILE='corrupt-log.000001', MASTER_LOG_POS=12345;")
cursor.close()
conn.close()
Note: The real exploit would require deep understanding of MySQL's replication protocol and possibly tools to send invalid events directly—not achievable just with SQL statements.
Update MySQL to a safe version as soon as possible.
- MySQL 5.7.37 Release Notes
- MySQL 8..28 Release Notes
Official Descriptions
> "Easily exploitable vulnerability allows high privileged attacker with network access via multiple protocols to compromise MySQL Server. Successful attacks of this vulnerability can result in unauthorized ability to cause a hang or frequently repeatable crash (complete DOS) of MySQL Server."
> – Oracle CPU Jan 2022
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|-------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------|
| CVE | CVE-2022-21344 |
| Score | 4.9 (CVSS 3.1, Availability Impact) |
| Component | MySQL Server: Replication |
| Affected | 5.7.36 and earlier, 8..27 and earlier |
| Attackers Need| High Privilege, Network Access |
| Impact | Hang/Crash (DoS) |
| Fix | Update to 5.7.37+ or 8..28+ |
| References | Oracle, NVD |
Conclusion
CVE-2022-21344 is a critical reminder that internal misuse and misconfigurations are as serious as remote attacks. If your MySQL server is accessible to users with high privileges, and you run an affected version, this bug could let them cause a Denial of Service—shutting down your business until you restart your DB. Patch immediately, audit user rights, and never expose DBs on open networks.
Further Reading
1. Oracle Security Alerts
2. How to secure MySQL replication
3. What’s new in MySQL 8..28
Stay safe—always patch early and audit those privileged accounts!
Timeline
Published on: 01/19/2022 12:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 01/24/2022 19:23:00 UTC