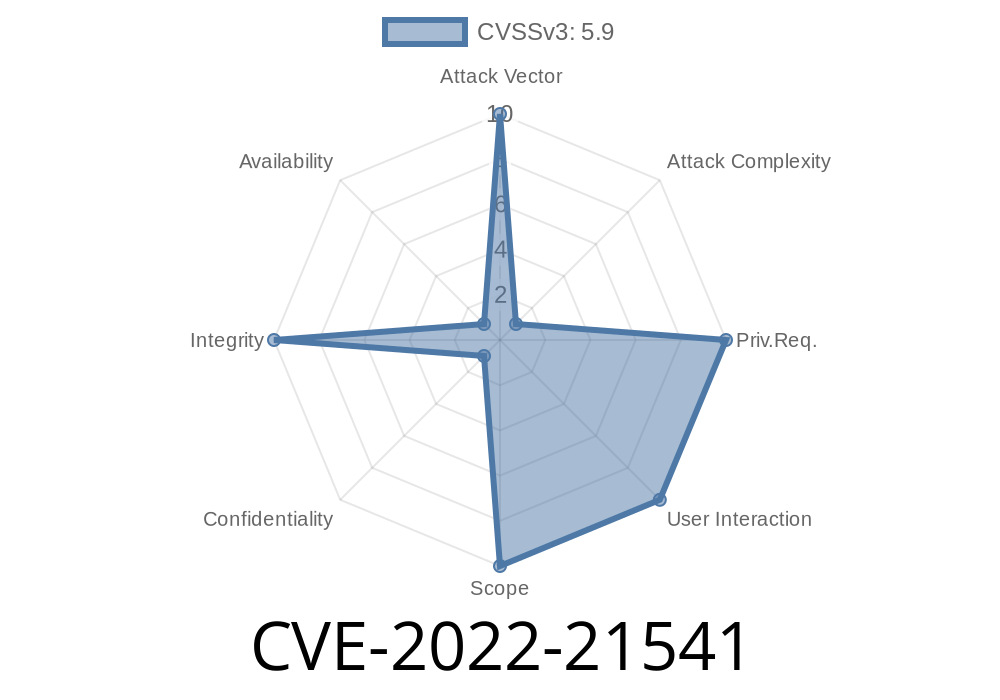
- The attacker must compromise the Java Security Manager to exploit this vulnerability. An attacker must have access to the network to compromise Oracle Java SE, Oracle GraalVM Enterprise Edition. An attacker cannot directly exploit this vulnerability. Instead, they would likely attempt to persuade users to visit a malicious site or lure them into clicking a malicious link. - Exploitation of this vulnerability is likely unintended, given the nature of the Java sandbox. However, if user code does run in a sandboxed Java applet or sandboxed Java Web Start application, and this code triggers this vulnerability, an attacker could execute arbitrary code with the privileges of the applet or Web Start application. - This vulnerability can also be exploited by Java clients using HTTP protocol. - Java clients running on OS that do not support TCP/UDP connection, such as Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, are not vulnerable to this issue. - For Java clients running on Windows, the default port number for TCP/UDP connection is 8888. - This issue can also be exploited by Java clients running on UNIX. - The default port number for UNIX UDP connection is 1215. - We recommend that you change the client port number to some other unused port number. - This vulnerability can be exploited by Java clients running on a Windows operating system. - The default port number for TCP/UDR connection is 5985. - We recommend that you change the client port number to some other unused port number
Vulnerability Scenario
The vulnerability is a weakness in the Java Security Manager that results in the execution of arbitrary code with the privileges of the applet or Web Start application.
Timeline
Published on: 07/19/2022 22:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 08/22/2022 15:09:00 UTC
References
- https://www.oracle.com/security-alerts/cpujul2022.html
- https://www.debian.org/security/2022/dsa-5188
- https://www.debian.org/security/2022/dsa-5192
- https://security.netapp.com/advisory/ntap-20220729-0009/
- https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/package-announce@lists.fedoraproject.org/message/KO3DXNKZ4EU3UZBT6AAR4XRKCD73KLMO/
- https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/package-announce@lists.fedoraproject.org/message/JN3EVGR7FD3ZLV5SBTJXUIDCMSK4QUE2/
- https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2022-21541