This issue was fixed in Google Chrome 103.0.5060.53. Users can protect themselves from this risk by updating to the latest version of Google Chrome. In addition, users can avoid installing extensions from untrusted sources and by updating to the latest version of Chrome.
Redundant code in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass access checking via a crafted HTML page.
This issue was fixed in Google Chrome 103.0.5060.53. Users can protect themselves from this risk by updating to the latest version of Google Chrome. In addition, users can avoid installing extensions from untrusted sources and by updating to the latest version of Chrome. Redundant code in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass access checking via a crafted HTML page. This issue was fixed in Google Chrome 103.0.5060.53. Users can protect themselves from this risk by updating to the latest version of Google Chrome. In addition, users can avoid installing extensions from untrusted sources and by updating to the latest version of Chrome. Redundant code in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass access checking via a crafted HTML page. This issue was fixed
Vulnerability Summary
Redundant code in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass access checking via a crafted HTML page.
This bug was fixed in Google Chrome 103.0.5060.53
Users can protect themselves from this risk by updating to the latest version of Google Chrome and making sure they don't install extensions from untrusted sources, or update to the latest version of Chrome
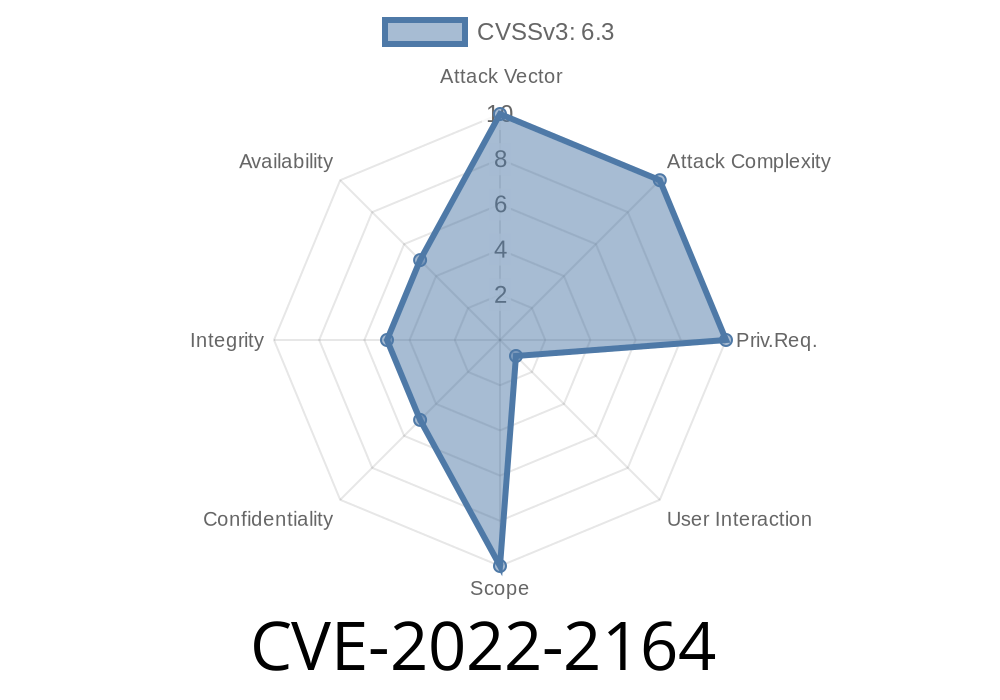
Summary CVE-2022-2164
This issue was fixed in Google Chrome 103.0.5060.53. Users can protect themselves from this risk by updating to the latest version of Google Chrome. In addition, users can avoid installing extensions from untrusted sources and by updating to the latest version of Chrome. Redundant code in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass access checking via a crafted HTML page
Overview
This post explains the risk of CVE-2022-2164. This is a vulnerability in Google Chrome extensions that can be used to bypass access restrictions.
Critical Issues (Risk of Loss of Critical Data)
Google Chrome has published a new Critical Issues report. This report is intended to make users aware of the most critical vulnerabilities and threats that exist in the latest version of Google Chrome.
The purpose of this report is to inform users about any critical issues that exist in Google Chrome, as well as how these issues can be mitigated or resolved.
Timeline
Published on: 07/28/2022 01:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 08/19/2022 12:06:00 UTC
References
- https://chromereleases.googleblog.com/2022/06/stable-channel-update-for-desktop_21.html
- https://crbug.com/1268445
- https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/package-announce@lists.fedoraproject.org/message/5BQRTR4SIUNIHLLPWTGYSDNQK7DYCRSB/
- https://lists.fedoraproject.org/archives/list/package-announce@lists.fedoraproject.org/message/H2C4XOJVIILDXTOSMWJXHSQNEXFWSOD7/
- https://security.gentoo.org/glsa/202208-25
- https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2022-2164