In early 2022, Microsoft patched a critical security issue in its Chromium-based Edge browser known as CVE-2022-21970. This vulnerability made it possible for attackers to gain higher privileges than intended – essentially, giving them more power inside your Windows system if you were tricked into running malicious code. If you use Edge, especially in business environments, you should know what happened.
Let's dig into what CVE-2022-21970 is, how it can be exploited, and what you (or your IT team) need to do to stay safe. I’ll also provide code snippets to illustrate the risk, reference links, and plain-English explanations.
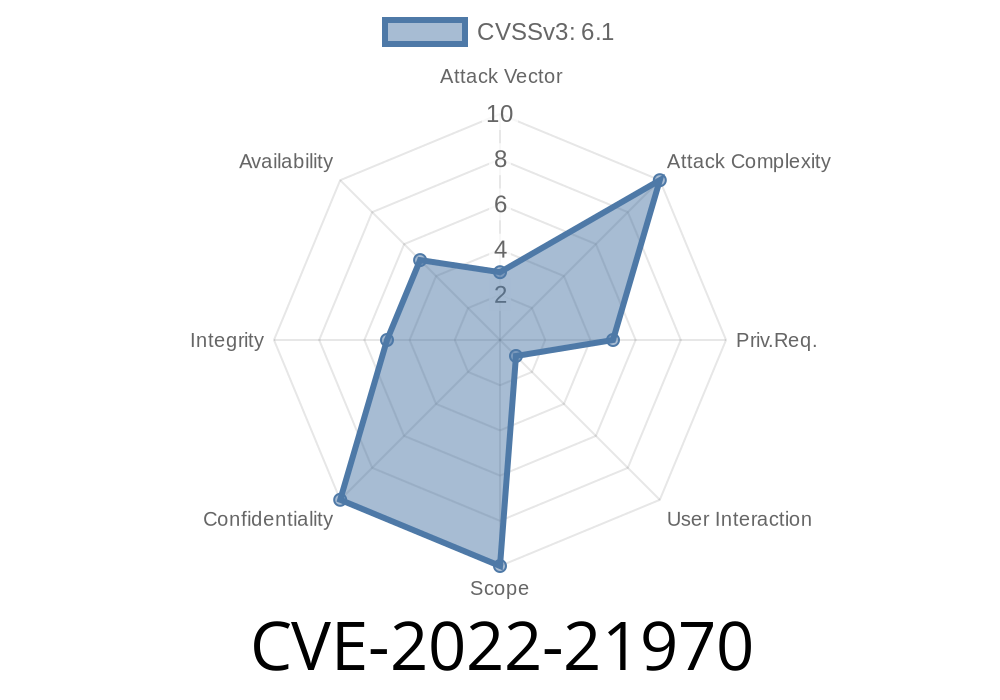
What Is CVE-2022-21970?
CVE-2022-21970 is an Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerability that affects Microsoft Edge built on Chromium (not the legacy Edge). If exploited, it allows an attacker to execute code with higher privileges than the current user should have.
Vector: Malicious web pages or exploited sites.
- CVE Uniqueness: This is *not* the same as CVE-2022-21954, though both are Edge browser vulnerabilities.
How Does It Work?
Like many browser bugs, this problem comes from how Edge processes certain objects, browser frames, or permissions in memory. A smart attacker could exploit a weakness and break out of the browser sandbox.
In Plain Terms: Edge is supposed to keep web content in a tightly controlled box (“sandbox”). Because of this bug, an attacker could jump the fence.
Hypothetical Exploitation Steps
Here’s an *imagination* of how an attacker might exploit this (based on available public technical details):
Lure: They get the user to visit a booby-trapped website or open a malicious ad.
2. Exploit: Malicious JavaScript or crafted HTML takes advantage of the vulnerability, causing unexpected memory changes or privilege validation bypass.
3. Privilege Jump: Evil code runs with system or higher-level account permissions (far more powerful than a regular webpage).
Example Exploit Scenario
Based on Chromium’s typical elevation bugs (note: Microsoft did not publish full PoC code for CVE-2022-21970), here’s a simplified, hypothetical code snippet:
// This is a *theoretical* example for illustrative purposes only
// Vulnerable function triggers improper privilege check
window.open("edge://vulnerable_internal_resource");
// Attacker tries to inject code or access restricted browser APIs
fetch("file:///C:/Windows/System32/config/SAM")
.then(response => response.text())
.then(data => {
// With successful exploit, attacker could steal local secrets
console.log("Stolen file contents: " + data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.log("Exploit failed or patched.");
});
What this shows: If the EoP bypass worked, evil JavaScript could access system files normally blocked by the browser’s security model.
How Was It Fixed?
Microsoft silently patched this issue in their regular Edge security updates. Fixes typically involve:
Blocking unexpected API calls from web content
Always update Edge when prompted – these silent security fixes protect you from issues like CVE-2022-21970.
Stay Cautious Online: Don’t click strange links or download odd browser extensions.
4. IT Admins: Consider deploying browser security policies (block risky sites, enable SmartScreen, etc.).
## More Reading / Original References
Microsoft Security Update Guide:
CVE-2022-21970 | Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Edge Release Notes (2022):
Edge Stable Channel Update for Windows (2022)
Chromium Security Overview:
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is CVE-2022-21970 the same as CVE-2022-21954?
A: No, these are separate bugs, even though both affect Edge.
Q: Was there malware exploiting this in the wild?
A: Microsoft did not disclose reports of “active exploitation,” but the risk was high enough to warrant a quick patch.
Q: What if I’m using Chrome, not Edge?
A: This CVE is specific to Microsoft Edge, but many Chromium bugs are cross-browser. Always keep all browsers up to date.
Summary
CVE-2022-21970 was a serious Elevation of Privilege vulnerability in Microsoft Edge (Chromium). If left unpatched, it could let attackers run code with more privileges than intended – possibly infecting your whole system.
Bottom line:
Update your browsers
- Stay alert for phishing/malicious webpages
Stay safe online!
> Disclaimer: This post is for educational purposes only. The code sample is a simplified, generic illustration; do not attempt to exploit or attack any system. Always follow ethical security practices.
Timeline
Published on: 01/11/2022 21:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 08/10/2022 20:15:00 UTC