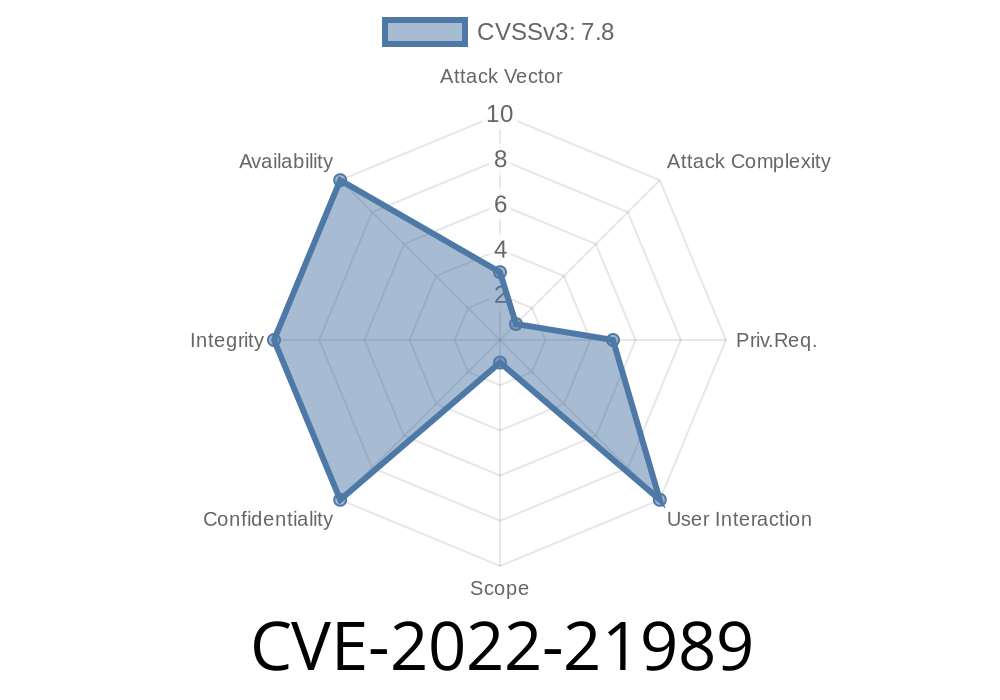
A remote unauthenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability to gain kernel level access on the targeted system.
This hW kernel vulnerability is a result of a combination of two factors.
First, in the Linux kernel, vDSO is a high-speed D-Bus-based virtual method that is used by the system calls to resolve the address of a memory location.
Second, Linux kernel includes a cgroup virtual filesystem that provides a mechanism to organize the Linux system into virtual groups. Each virtual group is assigned a process id.
It is possible to elevate privileges on the targeted system by accessing the vDSO of the target process and then injecting malicious code in the kernel.
For example, a user who has “System V-style” privileges and has access to the /etc/passwd file would be able to elevate privileges and then access the vDSO of another process to gain access to the target system.
To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must be in a position where they have control over user-level processes.
In order to exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must have user-level access to the system.
In order to exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must be in a position where they have control over user-level processes.
On Linux systems, a privileged user such as “nobody” or “root” can use su, sudo, or another privileged process to gain system
Vulnerability Information and Detection
Security vulnerabilities are important to detect and mitigate. This hW kernel vulnerability is a result of a combination of two factors. The first factor is that in the Linux kernel, vDSO is a high-speed D-Bus-based virtual method that is used by the system calls to resolve the address of a memory location. The second factor is that Linux kernel includes a cgroup virtual filesystem that provides a mechanism to organize the Linux system into virtual groups. Each virtual group is assigned a process id. It is possible to elevate privileges on the targeted system by accessing the vDSO of the target process and then injecting malicious code in the kernel.
For example, if an attacker can run user-level processes such as su, sudo, or another privileged process, they will be able to elevate their privileges and then access the vDSO of another process to gain access to the target system.
Timeline
Published on: 02/09/2022 17:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 05/23/2022 17:29:00 UTC