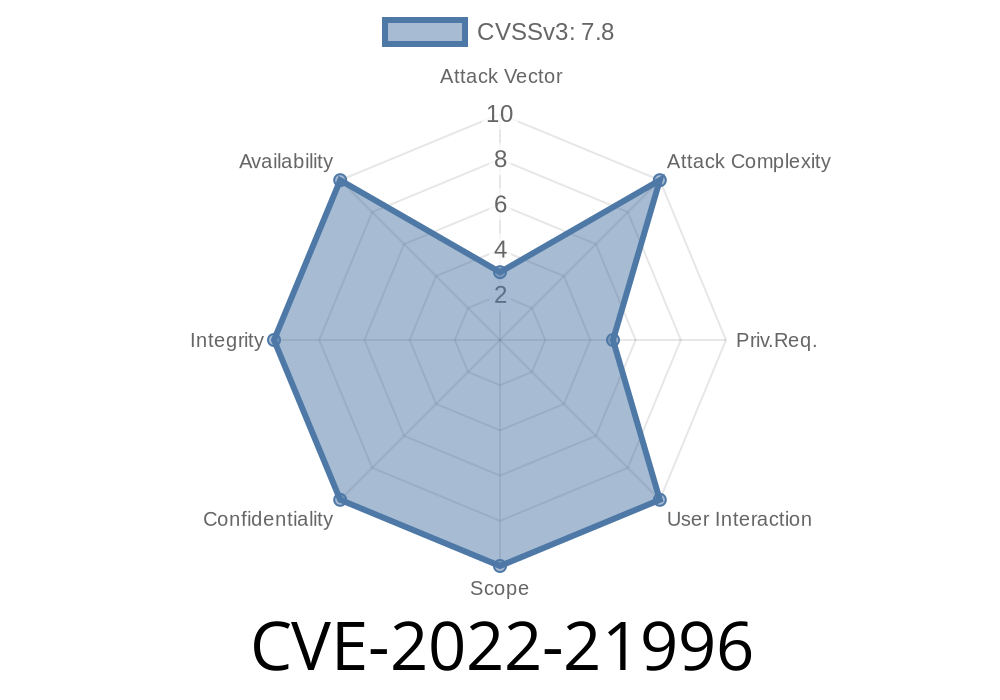
This vulnerability allows attackers to elevate their privileges on an affected system.
An attacker must trick the user into opening a specially crafted file or web page, possibly by sending them a link.
There are several ways an attacker can exploit this vulnerability, such as: In the context of a man-in-the-middle attack. As a drive-by-download attack. By using a compromised website or host that has a malicious file. An attacker may also deliver malicious software through other vectors, such as email, or by using remote access tools. In the context of a man-in-the-middle attack. An attacker may also deliver malicious software through other vectors, such as email, or by using remote access tools. By sending a user a link to a file that has been specifically crafted to exploit this vulnerability. In the context of a drive-by-download attack. An attacker may also deliver malicious software through other vectors, such as by exploiting weaknesses in software that manages file installation, such as inadequately protected software distribution systems. By using a compromised website or host that has a malicious file. An attacker may also deliver malicious software through other vectors, such as by exploiting weaknesses in software that manages file installation, such as inadequately protected software distribution systems. By sending a user a link to a file that has been specifically crafted to exploit this vulnerability. In the context of a remote access attack
Examples of how an attacker could exploit this vulnerability
In the context of a remote access attack. An attacker may also deliver malicious software through other vectors, such as by exploiting weaknesses in software that manages file installation, such as inadequately protected software distribution systems.
Important Tips:
You should consider the following:
Who would be the target of an attack?
What are their habits or what type of system are they using?
What is their physical location?
How much information do you know about them?
Vulnerability Scenario
If a user visits an attacker-controlled website, the attacker may be able to exploit this vulnerability and take control of their computer.
The attacker could then install malicious software on the system to gain access to sensitive information or install software with other capabilities.
Examples of how the vulnerability can be exploited
An attacker can exploit the vulnerability by sending a user a link to a specially crafted file or web page. This could be done with an email, instant message, or in another way, such as through social media. The specially crafted file could also come from a compromised website on the Internet. The link can be sent as part of an attack that might include spam campaigns, drive-by downloads, man-in-the-middle attacks, or other types of cybercrime activities. A remote access tool may also be used to exploit this vulnerability.
The vulnerability is not limited to any specific software package and affects all versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems since Vista. The vulnerability is fixed in the latest version of Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016.
CVE-2022 CVE Numbering Committee
The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) is the official repository for all public vulnerabilities. The NVD assigns a unique identification number to each vulnerability, called the CVE identifier.
The vulnerability numbering process ensures that vulnerability numbers are tracked consistently across products and vendors by assigning them to a specific version of software or hardware rather than using a product-specific ID such as an "SNMPv3 packet structure memory corruption" vulnerability .
The CVE Committee assigns the CVEs in accordance with the following guidelines:
- A new vulnerability is assigned when it affects one or more pieces of software which have never been documented before.
- A new vulnerability is assigned when it affects one or more pieces of software which have been documented but not previously assigned a CVE identifier.
- A new vulnerability is assigned when it affects one or more different operating systems, both major and minor versions, or similar platforms.
- A new vulnerability is assigned if there has been no previous CVE assignment for that particular issue in any major release of OpenSSL (1.0 through 1.1.0).
- A new vulnerability is assigned if there has been no previous CVE assignment for that particular issue in any minor release of OpenSSL (0.9 through 0.9.8).
Timeline
Published on: 02/09/2022 17:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 02/14/2022 18:31:00 UTC