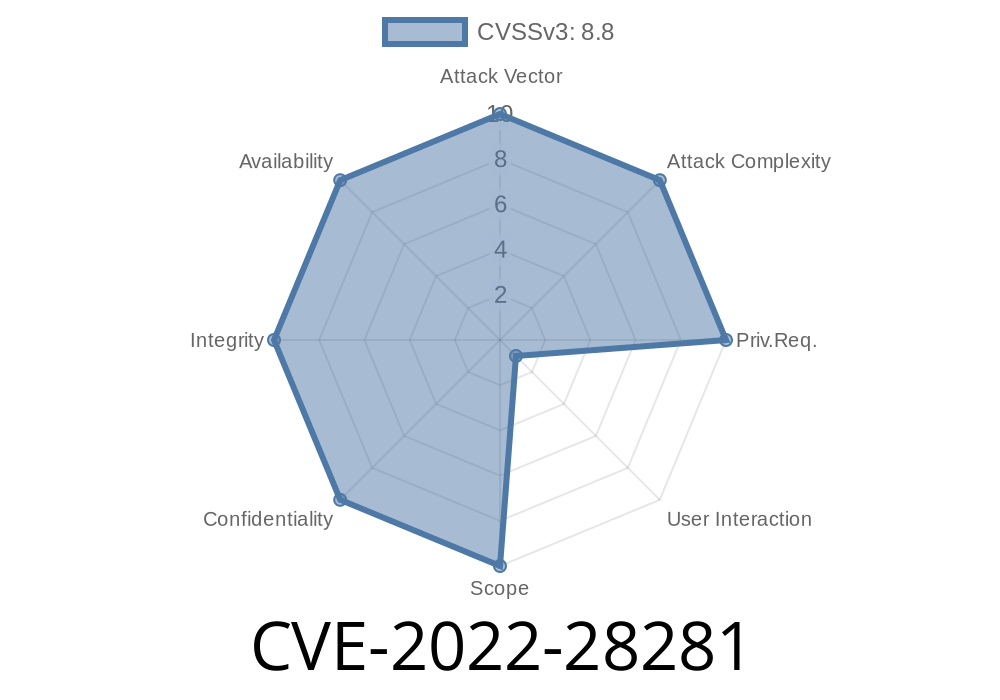
*CVE-2022-28281* is a security vulnerability found in Mozilla’s Firefox, Firefox ESR, and Thunderbird email client. This flaw is related to how these products handled certain WebAuthN (Web Authentication) commands, specifically when processing an unexpected number of "WebAuthN Extensions" during a registration command sent from a compromised content process to the parent process.
If successfully exploited, this bug allowed an attacker to cause a dangerous out-of-bounds write—a type of memory corruption—which could lead to crashing the application or potentially executing arbitrary code.
> Affected versions:
> - Thunderbird < 91.8
> - Firefox < 99
> - Firefox ESR < 91.8
Understanding the Vulnerability
WebAuthN is a web standard for secure authentication, often used with hardware security keys (like YubiKey). When a website wants you to register a token, your browser handles commands and passes messages between various processes.
Here’s the issue:
If a malicious website or extension could compromise a web content process, it could send a crafted message to the parent (main) browser process with more WebAuthN extensions than expected. The parent process did not properly check the number of extensions and wrote past the end of memory buffers—a classic *out-of-bounds (OOB) write*.
This means an attacker exploiting this flaw could corrupt browser memory, resulting in a crash or—if chained with other vulnerabilities—possibly run code of their choice.
A Simple Analogy
Imagine filling out a form with 5 boxes for your address, but someone sends you a form with 100 boxes. If you start writing past what was expected, you’ll spill over, possibly overwriting other important information lying next to your form—potentially letting a hacker take over.
Example Code Snippet (Pseudo-Code)
The bug happens in the code that processes the array of WebAuthN extensions in the parent process. Here’s a simplified example:
// Vulnerable: Assumes 'numExtensions' is always safe
void HandleRegisterCommand(int numExtensions, Extension* extensions) {
Extension safeExtensions[10]; // Only room for 10
for (int i = ; i < numExtensions; i++) {
safeExtensions[i] = extensions[i]; // OOB write if numExtensions > 10!
}
}
If numExtensions is too big (maybe 100), then this code writes way beyond the safeExtensions buffer, which only has space for 10.
The proper fix is to check numExtensions before copying, like this
void HandleRegisterCommand(int numExtensions, Extension* extensions) {
const int MAX_EXTENSIONS = 10;
if (numExtensions > MAX_EXTENSIONS)
return; // Error: too many extensions
Extension safeExtensions[MAX_EXTENSIONS];
for (int i = ; i < numExtensions; i++) {
safeExtensions[i] = extensions[i];
}
}
Exploit Details
A successful attacker would need to first compromise the content process—often through another browser bug, or via a malicious add-on/extension. Then, they can send a crafted Register command loaded up with too many extensions to the parent process. If the parent process isn’t expecting this, it writes data past the end of its memory buffer, causing:
- Denial-of-Service: Browser/Thunderbird crash
- Potential code execution: Corrupt memory in just the right way, and the attacker may run code (although this usually needs luck or more bugs)
In practice, this type of vulnerability is a building block for more complex attacks.
Security Patch
Mozilla fixed this by *properly checking* the number of extensions supplied in registration commands, and not letting the parent process write more data than it can safely handle.
Upgrade to the latest versions
- Firefox Download
- Thunderbird Download
Original References
- Mozilla Foundation Security Advisory 2022-14
- CVE Details Page: CVE-2022-28281
- Bugzilla: 1763252
Mitigation Advice
- Update your browser/email client. Always use the latest versions of Firefox and Thunderbird.
- Beware of suspicious add-ons or websites. This bug can be chained with others, so untrusted code is always a threat.
Summary
CVE-2022-28281 is a memory safety bug that could let an attacker crash your browser or, in a worst-case scenario, run code on your device. It was fixed quickly, but underlines the importance of input validation—especially between different processes.
If you’re using Firefox or Thunderbird, make sure you’re updated. Memory safety still matters, even in 2024.
*Stay safe—and always keep your software patched!*
Timeline
Published on: 12/22/2022 20:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 12/30/2022 20:55:00 UTC