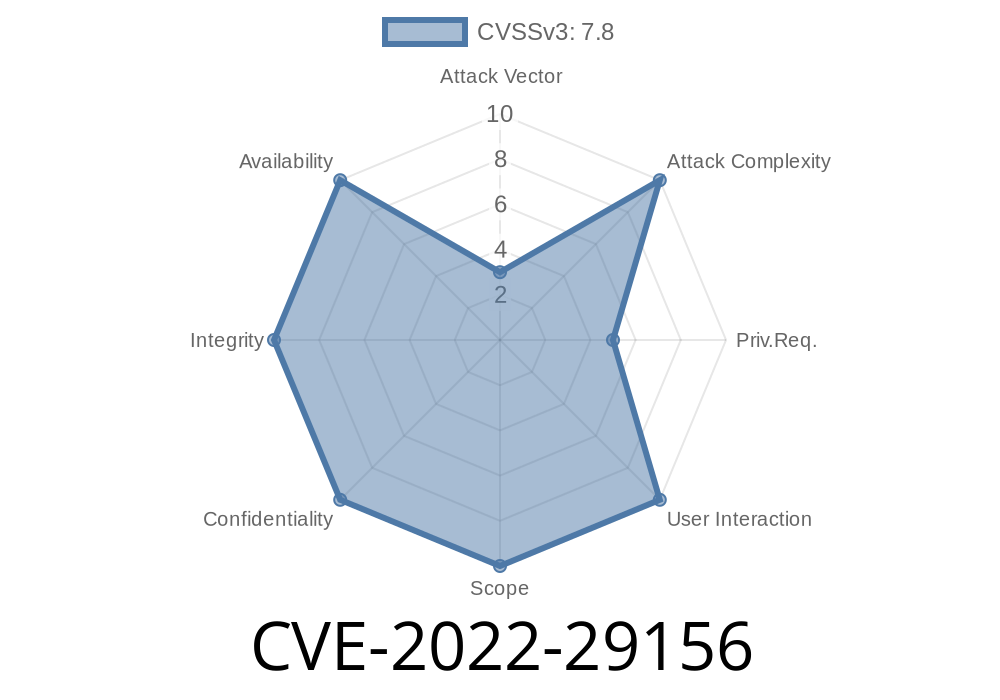
This could be exploited when handling a specially crafted Netlink message.
In the example below, rtmsg_rcv() is used to receive Netlink messages from an InfiniBand device. If an attacker controls the rtmsg_rcv() Netlink message, they can send a specially crafted message that will cause a double free to occur. { netlink_sendmsg: returner = { struct sockaddr *raddr; int s; int rc; if (nlmsg_len sizeof(*rc)) return; nlmsg_len = nlmsg_len - sizeof(*rc); rcu_read_lock(); s = nlmsg_data(nlmsg); nlmsg_data = nlmsg_data(nlmsg)-&rc->data; nlmsg_len = nlmsg_len - sizeof(*rc); rcu_read_unlock(); rc = nlmsg_rcv(nlmsg, nlmsg_len); nlmsg_data = nlmsg_data(nlmsg); nlmsg_len = nlmsg_len - sizeof(*rc); } --- rtmsg_rcv: returner = { struct sockaddr *raddr; int s; int rc; if (rtmsg_len sizeof(*rc)) return; nlmsg_len = nlmsg_len - sizeof(*rc); rcu_read_lock(); s =
If an attacker can control the rtmsg_rcv Netlink message, they can send a specially crafted message
Pre-Requisites:
- The function rtmsg_rcv() is used to receive Netlink messages from an InfiniBand device
- An attacker controls the rtmsg_rcv() Netlink message, they can send a specially crafted message that will cause a double free to occur.
- Pre-Requisites:
1) The function rtmsg_rcv() is used to receive Netlink messages from an InfiniBand device. 2) An attacker controls the rtmsg_rcv() Netlink message, they can send a specially crafted message that will cause a double free to occur.
3) You are using the RTAI kernel in your system or you have access to kernel source code.
Step 1: Create an invalid Netlink message to trigger a crash
The first step is to create an invalid Netlink message. In the example below, &mlink is not NULL, which is not allowed within a Netlink message of type NETLINK_MSG_INVALID. { if (!nlmsg) return; nlmsg = netlink_alloc(MLREG); s = nlmsg->nlh; nlmsg->nlh = nlmsg; nlmsg->type = NETLINK_MSG_TYPE_INVALID; nlmsg->nlmsg_len = 0; } --- mlink: returner = { struct sockaddr *raddr; int s; int rc; if (mlink) return; mlink = netlink_alloc(MLREG); s = mlink->mlh; mlink->mlh = mlink; mlink->type = NETLINK_MSG_TYPE_INVALID; }
Timeline
Published on: 04/13/2022 07:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 06/02/2022 20:15:00 UTC