If a user visited a malicious website or opened a malicious file on Windows, an attacker could potentially exploit this vulnerability to access arbitrary system memory and cause a denial of service or escalate privileges to run arbitrary code. In the case of a user visiting a malicious website or opening a malicious file on a Linux system, an attacker would likely cause a denial of service due to the crash and potential corruption of the browser. As a user cannot typically determine whether a specific website is malicious or not, and if the user is visiting the website from a Windows system, it is recommended that administrators monitor any network traffic for signs of suspicious activity. An attacker may be able to exploit this vulnerability by convincing a user to visit a malicious website or open a malicious file on a Windows system. If a user is running a version of Thunderbird or Firefox that is older than the end-of-life (EOL) distribution, it is possible that the user has not updated to a newer release. If a user has not updated to a newer release, it is possible that the user has not updated to a newer release due to convenience or other reasons. If a user has not updated to a newer release, it is possible that the user has not updated to a newer release due to convenience or other reasons. An attacker may be able to exploit this vulnerability by convincing a user to visit a malicious website or open a malicious file on a Linux system.
About Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge is an HTML5 web browser developed by Microsoft. It's the default and recommended browser for Windows 10. While it comes with some built-in extensions, other third-party extensions require users to "enable" them in settings.
Vulnerability Severity and Scope
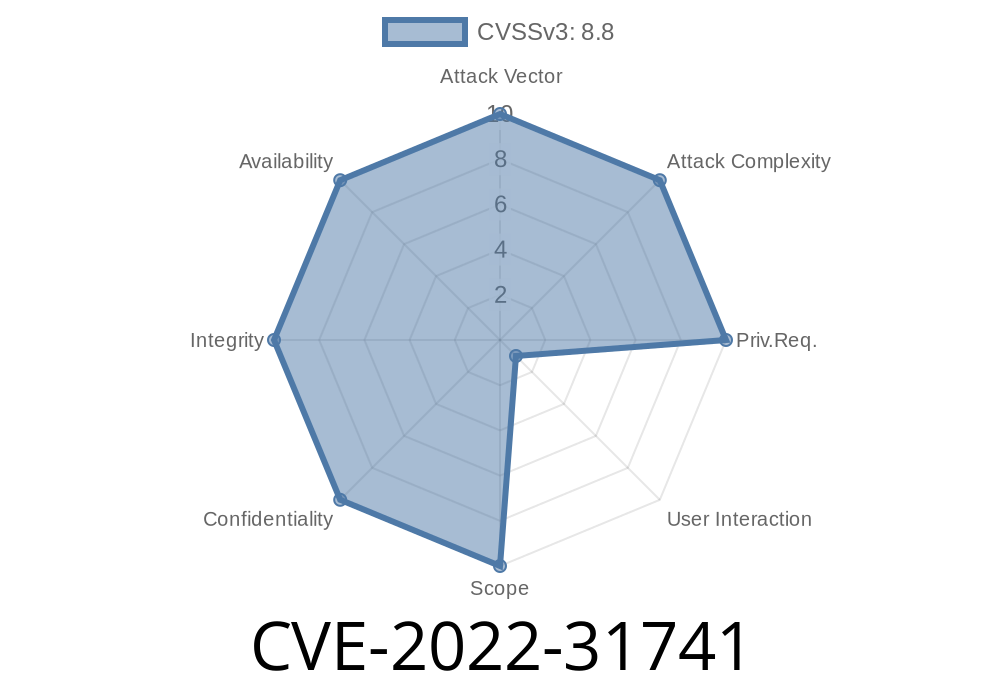
The vulnerability has a severity of 3 due to the fact that there is limited user interaction required for exploitation, which means that a low-privileged user could be exploited without significant difficulty. In addition, if exploitation occurs, it is likely to cause a denial of service or escalate privileges. The scope of the vulnerability is system-wide because it affects all versions of Thunderbird and Firefox.
Vulnerability overview
A vulnerability in the browser XULRunner has been discovered that could allow an attacker to access arbitrary system memory, resulting in a denial of service or escalation of privileges to run arbitrary code. The vulnerability exists due to improper sandboxing and access restriction checks on XULRunner. As a user cannot typically determine whether a specific website is malicious or not, and if the user is visiting the website from a Windows system, it is recommended that administrators monitor any network traffic for signs of suspicious activity.
If you have files created by CVE-2022-31741 installed on your computer, then either update your installations of Thunderbird ESR 38.1.0 and Firefox 51.0 or earlier with new releases using the instructions provided below:
Version 38.1.0 includes Firefox 52.0
Version 41 includes Firefox 56
Version 45 includes Firefox 59
Other ways to exploit the vulnerability
An attacker could also exploit this vulnerability by convincing a user to install a malicious browser extension.
Vulnerability details
Vulnerabilities are typically classified as high, medium, and low risk. The level of risk is determined by the potential impact of exploitation. For example, a vulnerability in an application such as Microsoft Office is considered low-risk. These vulnerabilities can be exploited for privilege escalation or denial of service but typically cannot be used to compromise confidentiality or integrity. However, a vulnerability in an operating system such as Windows is considered medium-risk because it can potentially lead to an attacker compromising confidentiality and integrity. These vulnerabilities can be exploited for privilege escalation or denial of service but typically cannot be used to compromise confidentiality or integrity unless the attacker has already compromised confidentiality and integrity prior to exploitation.
Timeline
Published on: 12/22/2022 20:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 01/03/2023 21:12:00 UTC