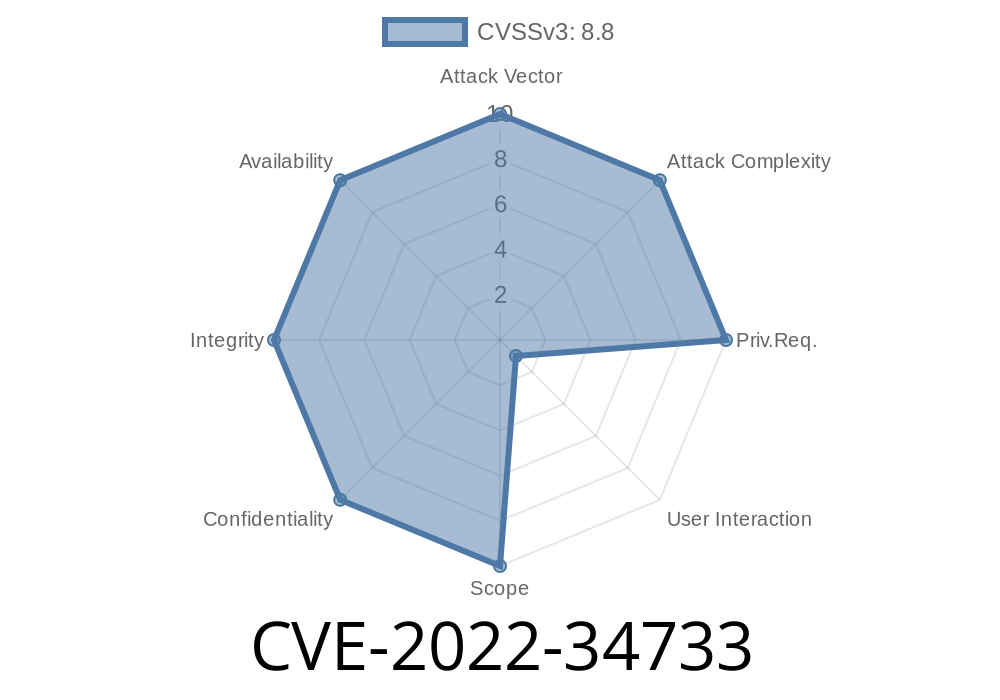
This issue was reported by Neil Hall and Andrey Meshkov of Google Project Zero. This vulnerability has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2022. This vulnerability is a result of a SQL injection vulnerability in the ‘SQL Server Native Client library’. This library is used by applications to access SQL Server databases. A remote attacker can exploit this vulnerability by submitting a malicious SQL request to an application via HTTP by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. Vulnerable installations of SQL Server can be exploited by sending a specially crafted request to the HTTP port of the SQL Server. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. Vulnerable installations of SQL Server can be exploited by sending a specially crafted request to the HTTP port of the SQL Server. Exploitation of this vulnerability requires no privilege elevation and can be exploited by any user with access to the affected SQL Server. Exploitation of this vulnerability requires no privilege elevation and can be exploited by any user with access to the affected SQL Server. Mitigations for this issue involve the application developer applying an update to the ‘SQL Server Native Client library’. This issue is being tracked under the ‘SQL Server Native Client Library’ component as CVE-2022.
SQL Server Native Client Library
This issue was reported by Neil Hall and Andrey Meshkov of Google Project Zero. This vulnerability has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2022. This vulnerability is a result of a SQL injection vulnerability in the ‘SQL Server Native Client library’. This library is used by applications to access SQL Server databases. A remote attacker can exploit this vulnerability by submitting a malicious SQL request to an application via HTTP by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. Vulnerable installations of SQL Server can be exploited by sending a specially crafted request to the HTTP port of the SQL Server. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. Vulnerable installations of SQL Server can be exploited by sending a specially crafted request to the HTTP port of the SQL Server. Exploitation of this vulnerability requires no privilege elevation and can be exploited by any user with access to the affected SQL Server. Exploitation of this vulnerability requires no privilege elevation and can be exploited by any user with access to the affected SQL Server. Mitigations for this issue involve the application developer applying an update to the ‘SQL Server Native Client library’. This issue is being tracked under the ‘SQL Server Native Client Library’ component as CVE-2022
SQL Injection Vulnerability
This SQL Injection vulnerability was reported by Neil Hall and Andrey Meshkov of Google Project Zero. This vulnerability has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2022. This vulnerability is a result of a SQL injection vulnerability in the ‘SQL Server Native Client library’. This library is used by applications to access SQL Server databases. A remote attacker can exploit this vulnerability by submitting a malicious SQL request to an application via HTTP by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. Vulnerable installations of SQL Server can be exploited by sending a specially crafted request to the HTTP port of the SQL Server. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. Vulnerable installations of SQL Server can be exploited by sending a specially crafted request to the HTTP port of the SQL Server. Exploitation of this vulnerability requires no privilege elevation and can be exploited by any user with access to the affected SQL Server. Exploitation of this vulnerability requires no privilege elevation and can be exploited by any user with access to the affected SQL Server. Mitigations for this issue involve application developer applying an update to the ‘SQL Server Native Client library’ component
SQL Server Denial of Service vulnerability (CVE-2023)
This issue was reported by Neil Hall and Andrey Meshkov of Google Project Zero. This vulnerability has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2023. This vulnerability is a result of a SQL injection vulnerability in the ‘SQL Server Native Client library’. This library is used by applications to access SQL Server databases. A remote attacker can exploit this vulnerability by submitting a malicious SQL request to an application via HTTP by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. Vulnerable installations of SQL Server can be exploited by sending a specially crafted request to the HTTP port of the SQL Server. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by setting the ‘REQUEST_METHOD’ HTTP header to ‘POST’. Vulnerable installations of SQL Server can be exploited by sending a specially crafted request to the HTTP port of the SQL Server. Exploitation of this vulnerability requires no privilege elevation and can be exploited by any user with access to the affected SQL Server instance or database that contains vulnerable tables and stored procedures. Exploitation of this vulnerability requires privilege elevation and can only be exploited if an authenticated user has permissions on those tables and stored procedures that contain vulnerable stored procedure definitions in them. Mitigations for this issue involve making sure that privileges are correctly granted on all database objects that require it, including tables, stored procedures
Timeline
Published on: 09/13/2022 19:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 09/16/2022 17:06:00 UTC