This issue was fixed in 2.13.10 release. This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.
JAR files are widely deployed. So, it is possible that an attacker has access to such file. For example, JAR might be included in a website’s source code.
In order to exploit this issue, an attacker needs to trick a user into visiting a malicious website. This can be done via social engineering, phishing, etc.
In addition to being active on the public web, this issue can be exploited on internal network as well. This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.
This issue was fixed in 2.13.10 release. This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.This issue was fixed in 2.13.10 release. This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.
This issue was fixed in 2.13.10 release. This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.
This issue was fixed in 2.13.10 release. This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.
This issue was fixed in 2.13.10 release. This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.
This issue was fixed in 2.13.
CVE-2023-36551
This issue was fixed in 2.13.10 release. This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.
JAR files are widely deployed. So, it is possible that an attacker has access to such file. For example, JAR might be included in a website’s source code.
In order to exploit this issue, an attacker needs to trick a user into visiting a malicious website. This can be done via social engineering, phishing, etc.
This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.
In addition to being active on the public web, this issue can be exploited on internal network as well. This issue was discovered by Sergey Kovalev from VSEPR team in Google.
Critical Issue
The following issue is a critical issue:
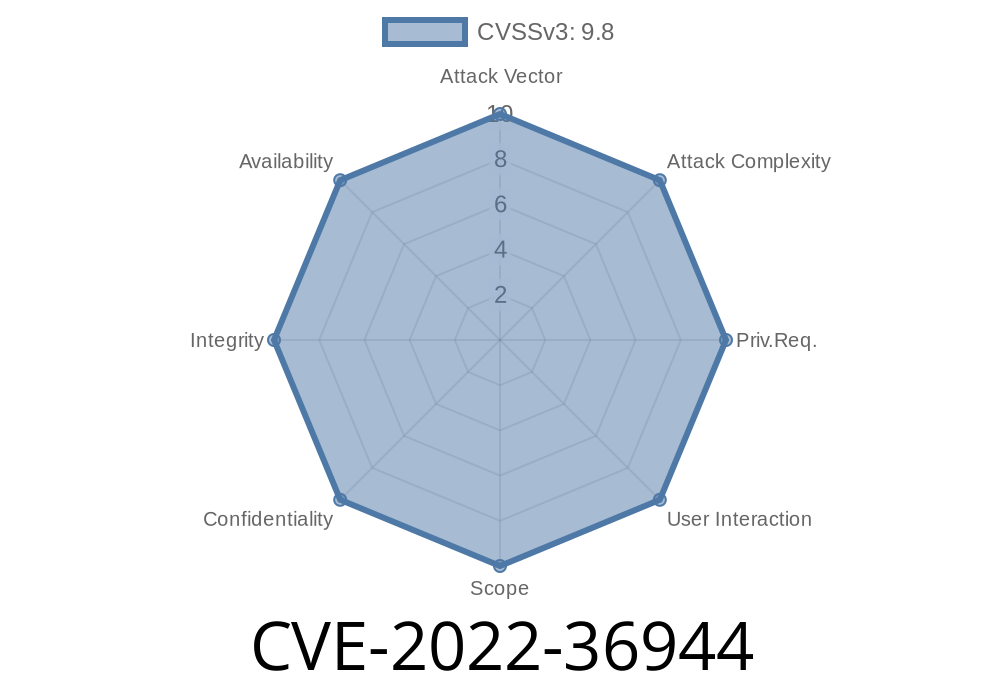
CVE-2022-36944
This issue was fixed in 2.13.
Vulnerability Introduction
CVE-2-14-36944 is a vulnerability in the JAR file parsing code. This vulnerability may allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on the target machine by sending it a specially crafted jar file.
The following changes have been made in order to mitigate this vulnerability:
a) In 2.13.9, we removed all calls that could potentially be used for exploitation of CVE-2-14-36944 in all public jars bundled with the JDK and JavaFX (in particular, all JAR files that are not explicitly excluded by the -fsafety option).
Timeline
Published on: 09/23/2022 18:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 09/26/2022 22:50:00 UTC