Microsoft has released a security bulletin for this issue. The report mentions that an elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Remote Desktop client fails to properly handle RDP packets with specially crafted PWD lengths. Remote attackers on the targeted system with access to the Remote Desktop client could exploit this vulnerability to gain elevated privileges on the remote system. In addition to this, Microsoft has also released a security advisory for this issue. Microsoft has provided the following workarounds for this issue: - Edit the RDP settings in Windows to disable the ‘PWD length’ check - Disable RDPv1 and RDPv2 on a per-service basis - Disable RDP connections to endpoints running legacy versions - Disable RDP connections to endpoints using specific ports - Disable RDP connections to specific IP addresses - Disable RDP connections at the firewall - Enable Kerberos authentication on RDP connections
RDP Vulnerability: An elevation of privilege vulnerability where an attacker could exploit the Remote Desktop client to gain elevated privileges on the remote system
Microsoft has released a security bulletin for this issue. The report mentions that an elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Remote Desktop client fails to properly handle RDP packets with specially crafted PWD lengths. Remote attackers on the targeted system with access to the Remote Desktop client could exploit this vulnerability to gain elevated privileges on the remote system. In addition to this, Microsoft has also released a security advisory for this issue. Microsoft has provided the following workarounds for this issue: - Edit the RDP settings in Windows to disable the ‘PWD length’ check - Disable RDPv1 and RDPv2 on a per-service basis - Disable RDP connections to endpoints running legacy versions - Disable RDP connections to endpoints using specific ports - Disable RDP connections to specific IP addresses - Disable RDP connections at the firewall - Enable Kerberos authentication on RDP connections
Microsoft Security Bulletin
: Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability in Remote Desktop Client
Microsoft has released a security bulletin for Windows, which mentions an elevation of privilege vulnerability. The issue is that the Remote Desktop client fails to properly validate RDP packets with specially crafted PWD lengths. This can cause remote attackers on the targeted system with access to the Remote Desktop client to exploit this vulnerability to gain elevated privileges on the remote system. Microsoft has also released a security advisory for this issue. Microsoft has provided the following workarounds for this issue:
- Edit the RDP settings in Windows to disable the ‘PWD length’ check - Disable RDPv1 and RDPv2 on a per-service basis - Disable RDP connections to endpoints running legacy versions - Disable RDP connections to endpoints using specific ports - Disable RDP connections to specific IP addresses - Disable RDP connections at the firewall - Enable Kerberos authentication on RDP connections
References ^^
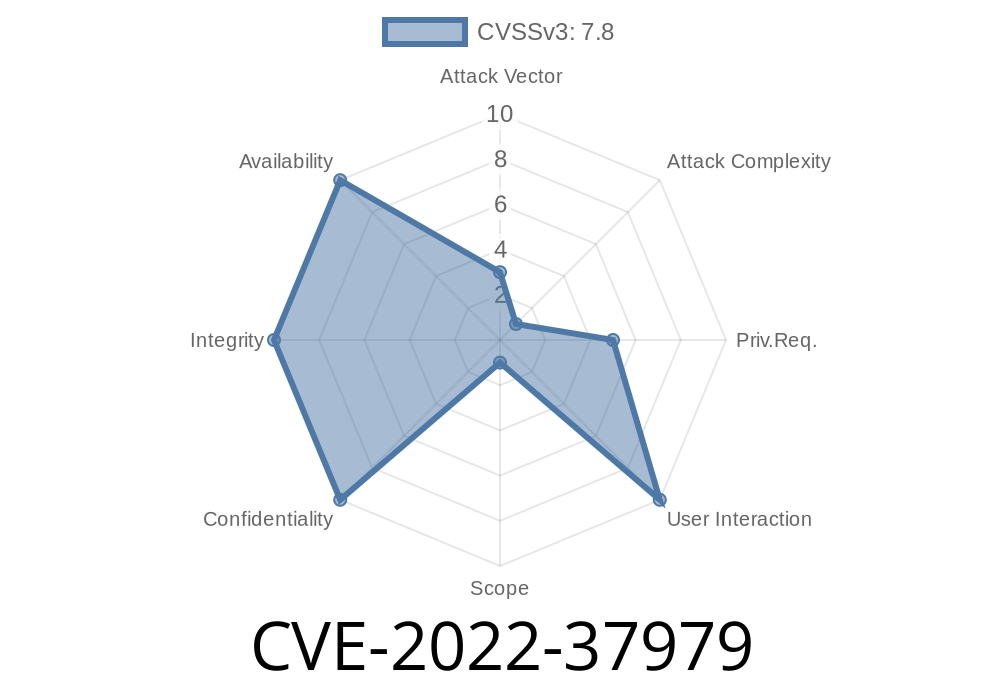
- CVE-2022-37979 - Microsoft Security Advisory
- Windows 10 Bulletin
- Microsoft's workaround for this issue
Microsoft has issued the following security update for this issue
The CVE-2022-37979 vulnerability is being exploited by hackers to gain control of computers running Windows. A security update has been released by Microsoft to help protect against this vulnerability, but how can you protect your computer?
There are a few things that you can do to prevent any kind of virus or malware from infecting your computer. These include:
- Install anti-virus software - Update your anti-virus software - Update Windows with the latest patches and updates
Microsoft has released a security bulletin for this issue and have provided workarounds for the issue.
This is a public Microsoft Security Bulletin with an associated security advisory that provides information on how to mitigate this potentially dangerous vulnerability.
Timeline
Published on: 10/11/2022 19:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 10/11/2022 19:16:00 UTC