Microsoft has released an out-of-band security update for Windows 7, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, that plugs this vulnerability.
The flaw was discovered by researchers at Cisco Systems and Tenable Network Security.
Due to the way Windows handles remote procedure call (RPC) requests, a malicious user on another system could launch a Denial of Service (DoS) attack against the vulnerable Windows machine.
The vulnerability can be exploited by sending a specially crafted RPC request to the target system.
An attacker could send malicious RPC requests to a vulnerable Windows system to crash that system and deny service to legitimate users.
This vulnerability is critical as an attacker can remotely crash a Windows system and deny service to legitimate users and administrators.
Exploiting this vulnerability requires sending a specially crafted RPC request and could be accomplished by sending RPC requests over TCP port 135 or UDP port 137.
The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
Windows 7 users and administrators are urged to install this security update as soon as possible.
Windows 8.1 users and administrators are urged to install this security update as soon as possible.
Windows 10 users and administrators are urged to install this security update as soon as possible.
End users who are running Windows 10 and have enabled the “Block incoming connections” setting are advised to leave this setting enabled.
Windows 7 security updates
Microsoft has released an out-of-band security update for Windows 7, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, that plugs this vulnerability.
The flaw was discovered by researchers at Cisco Systems and Tenable Network Security.
Due to the way Windows handles remote procedure call (RPC) requests, a malicious user on another system could launch a Denial of Service (DoS) attack against the vulnerable Windows machine.
The vulnerability can be exploited by sending a specially crafted RPC request to the target system.
An attacker could send malicious RPC requests to a vulnerable Windows system to crash that system and deny service to legitimate users.
This vulnerability is critical as an attacker can remotely crash a Windows system and deny service to legitimate users and administrators.
Exploiting this vulnerability requires sending a specially crafted RPC request and could be accomplished by sending RPC requests over TCP port 135 or UDP port 137.
The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2012 R2
Microsoft has released an out-of-band security update for Windows 7, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, that plugs this vulnerability.
The flaw was discovered by researchers at Cisco Systems and Tenable Network Security.
Due to the way Windows handles remote procedure call (RPC) requests, a malicious user on another system could launch a Denial of Service (DoS) attack against the vulnerable Windows machine.
The vulnerability can be exploited by sending a specially crafted RPC request to the target system.
An attacker could send malicious RPC requests to a vulnerable Windows system to crash that system and deny service to legitimate users.
This vulnerability is critical as an attacker can remotely crash a Windows system and deny service to legitimate users and administrators.
Exploiting this vulnerability requires sending a specially crafted RPC request and could be accomplished by sending RPC requests over TCP port 135 or UDP port 137.
The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
Windows 7 users and administrators are urged to install this security update as soon as possible.
Windows 8.1 users and administrators are urged to install this security update as soon as possible.
Windows 10 users and administrators are urged to install this security update as soon as possible.
What is TCP port 135?
TCP port 135 is used by the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) which is a connection-oriented protocol.
The TCP port 135 is associated with the Dynamic Port Range for Transmission Control Protocol (21-65535).
Windows 10 Security Update
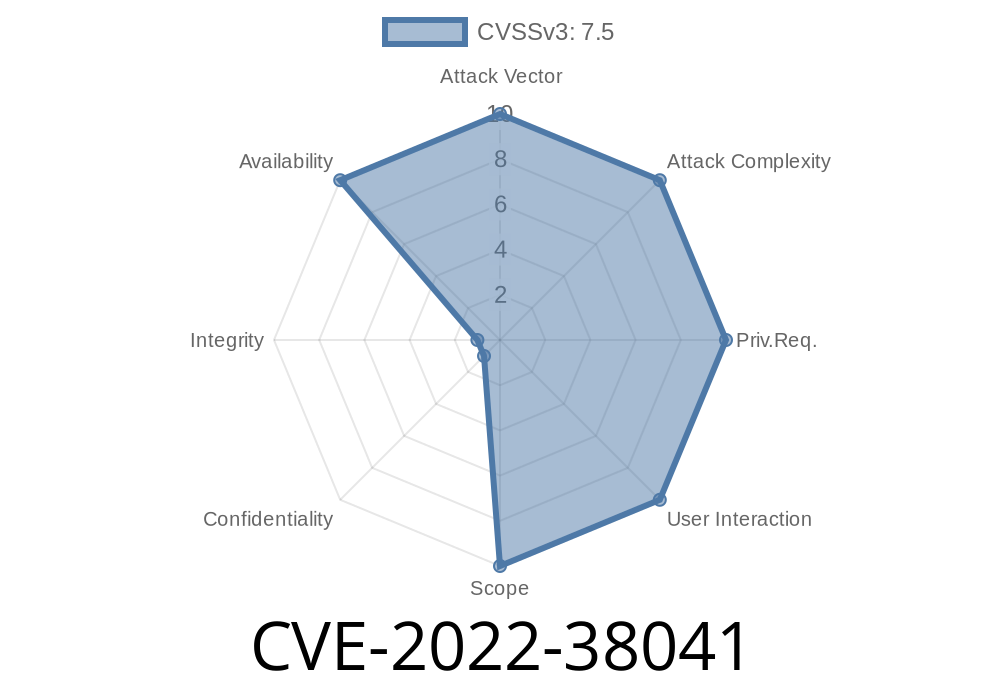
Windows 10 users are urged to install the latest security update, which fixes the vulnerability CVE-2022-38041. Microsoft has released an out-of-band security update for Windows 7, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, that plugs this vulnerability. "The flaw was discovered by researchers at Cisco Systems and Tenable Network Security." Due to the way Windows handles remote procedure call (RPC) requests, a malicious user on another system could launch a Denial of Service (DoS) attack against the vulnerable Windows machine. The vulnerability can be exploited by sending a specially crafted RPC request to the target system. An attacker could send malicious RPC requests to a vulnerable Windows system to crash that system and deny service to legitimate users. This vulnerability is critical as an attacker can remotely crash a Windows system and deny service to legitimate users and administrators. Exploiting this vulnerability requires sending a specially crafted RPC request and could be accomplished by sending RPC requests over TCP port 135 or UDP port 137. The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
Timeline
Published on: 10/11/2022 19:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 10/11/2022 19:16:00 UTC