These vulnerabilities have been assigned Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures names. A bug existed in the implementation of the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) in Microsoft Windows that allowed an attacker to inject and execute code on the system. However, this bug was only exploitable by privileged attackers, and not least of all, not by users with regular privileges. Because of the high privileged position of the attacker, this could only be exploited in a targeted attack scenario. The vulnerability was discovered by Vladk0r of the Cisco Talos team and reported to Microsoft. Microsoft has released a security bulletin to address this issue. How to determine if your operating system is vulnerable: After installing a new or upgraded Microsoft Windows operating system, log in and open the Control Panel > Device Manager > click on the arrow next to Network Adapters > click on Update Driver Software to update the driver. This will display a warning that says “Windows has detected that this driver is outdated. As soon as this driver has been updated, this security warning will no longer be displayed.” If you see this message, your operating system is vulnerable. You can update the driver manually, or obtain an updated driver from your hardware or software vendor.
Microsoft Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the implementation of the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) in Microsoft Windows. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a malicious PPTP packet to a target system via SMB, resulting in an out-of-bounds write on a stack buffer. However, this bug is only exploitable by privileged attackers, and not least of all, not by users with regular privileges. Because of the high privileged position of the attacker, this could only be exploited in a targeted attack scenario. The vulnerability was discovered by Vladk0r of the Cisco Talos team and reported to Microsoft. Microsoft has released a security bulletin to address this issue. How to determine if your operating system is vulnerable: After installing a new or upgraded Microsoft Windows operating system, log in and open the Control Panel > Device Manager > click on the arrow next to Network Adapters > click on Update Driver Software to update the driver. This will display a warning that says “Windows has detected that this driver is outdated. As soon as this driver has been updated, this security warning will no longer be displayed.” If you see this message, your operating system is vulnerable. You can update the driver manually, or obtain an updated driver from your hardware or software vendor.
Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
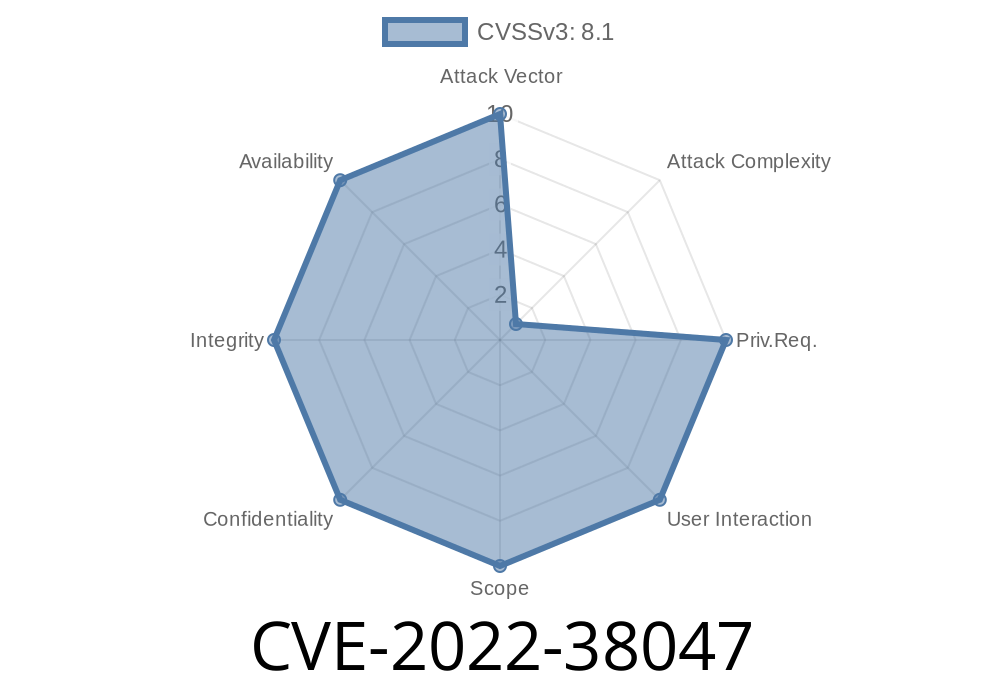
CVE-2022-38047 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft Office. This vulnerability allows an attacker to execute code on the system by tricking a user into opening a specially crafted Microsoft Office Document.
This vulnerability was discovered by Huawei's Security Team and reported to Microsoft. Microsoft has released a security bulletin to address this issue. How to determine if your operating system is vulnerable: If you are using the Office Remote Desktop Client (MRDC) then you will need to upgrade to the latest version of MRDC. This can be done by logging into your Windows account and clicking on Updates > Update Now > Update MRDC and clicking Yes when prompted.
Microsoft Office Software
Microsoft Office software is very important to the day-to-day functioning of a company. The software is used by many people on a daily basis and it is constantly updated with new features and improved security practices. However, this comes at a cost. With every update, vulnerabilities are found that need to be patched in order for the software to function properly. The speed in which these vulnerabilities are discovered can be staggering and can leave companies open to cyberattacks.
Therefore, it’s important for companies to take proactive measures such as patching their Microsoft Office software when updates are released or implementing other security practices before the vulnerability becomes exploited.
Timeline
Published on: 10/11/2022 19:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 10/13/2022 15:55:00 UTC