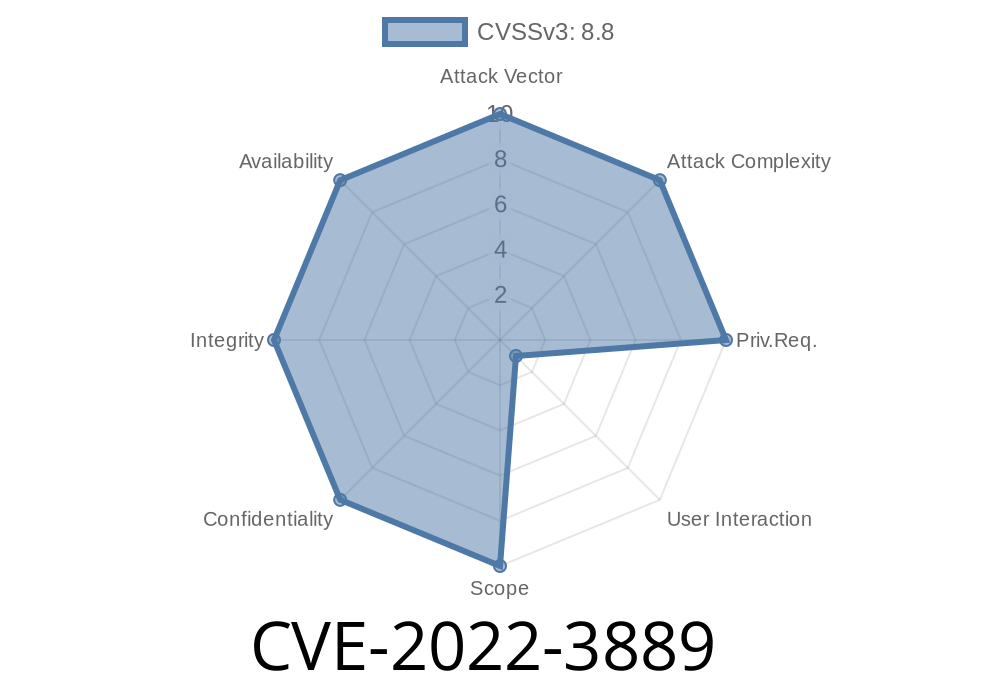
Summary:
In October 2022, security researchers discovered a high-severity vulnerability — CVE-2022-3889 — in V8, the JavaScript engine used by Google Chrome. This bug, specifically a type confusion issue, could let attackers cause heap corruption by tricking users into opening a malicious web page. Below, we’ll explain what type confusion means, how this bug works, show some code snippets, and provide details on exploitation. If you use Chrome, updating promptly is essential.
1. What is Type Confusion?
JavaScript engines like V8 often optimize code by assuming types (like ‘number’, ‘object’, ‘array’) don’t change unexpectedly. Type confusion happens when a function expects one type but gets another. This misassumption can lead to reading or writing outside the intended memory space, causing “heap corruption,” which attackers can use to run their own code.
> For a clear intro: Type Confusion in C++ (Stack Overflow)
2. How Did CVE-2022-3889 Happen?
In this vulnerability, certain optimizations in V8 affected how the engine handled objects created in JavaScript. Attackers could craft a web page with specific JavaScript, tricking V8 into treating an object as if it were a different type. The engine then writes data in the wrong place, which can corrupt the heap.
- Official bug entry: Chromium Issue 1371404 (may require permissions)
- NIST NVD entry: NVD - CVE-2022-3889
Chrome release notes:
Stable Channel Update for Desktop - November 2022
Here’s a simplified proof-of-concept (PoC) showing how you might trigger a type confusion in V8
function confuse(arr, o) {
arr[] = 1.1;
arr[1] = 2.2;
arr[2] = 3.3;
arr[3] = 4.4;
// JIT compiler may optimize and assume all elements are doubles
o.prop = 1337;
// Later, the array is modified to "object" type
}
let arr = new Array(4);
let obj = {};
for (let i = ; i < 10000; i++) {
confuse(arr, obj);
}
// Now, in a real exploit, attackers cause type confusion using crafted objects
arr[] = {}; // Changes the type unexpectedly
confuse(arr, obj);
// arr now contains "object" type, but V8 may think they're still doubles
Please note:
This PoC is for educational purposes. Real exploits are complex and require a deep understanding of V8’s internals and memory layouts.
This bug lets an attacker
- Corrupt memory (heap): By controlling what’s written and where, they can gain the ability to execute code.
- Potential remote code execution (RCE): Once attackers can execute code, they might install malware, steal data, or take over browsers.
Avoid suspicious links and pages.
6. References
- CVE-2022-3889 Detail (NVD)
- Chromium bug tracker (Issue 1371404)
- Chrome Official Release Notes
- Project Zero Blog: Exploiting Type Confusion *(general background)*
TL;DR:
CVE-2022-3889 is a serious Chrome bug that could let hackers run code on your device just by visiting a malicious web page. The fix is simple: update your browser now.
Timeline
Published on: 11/09/2022 04:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/14/2022 15:15:00 UTC