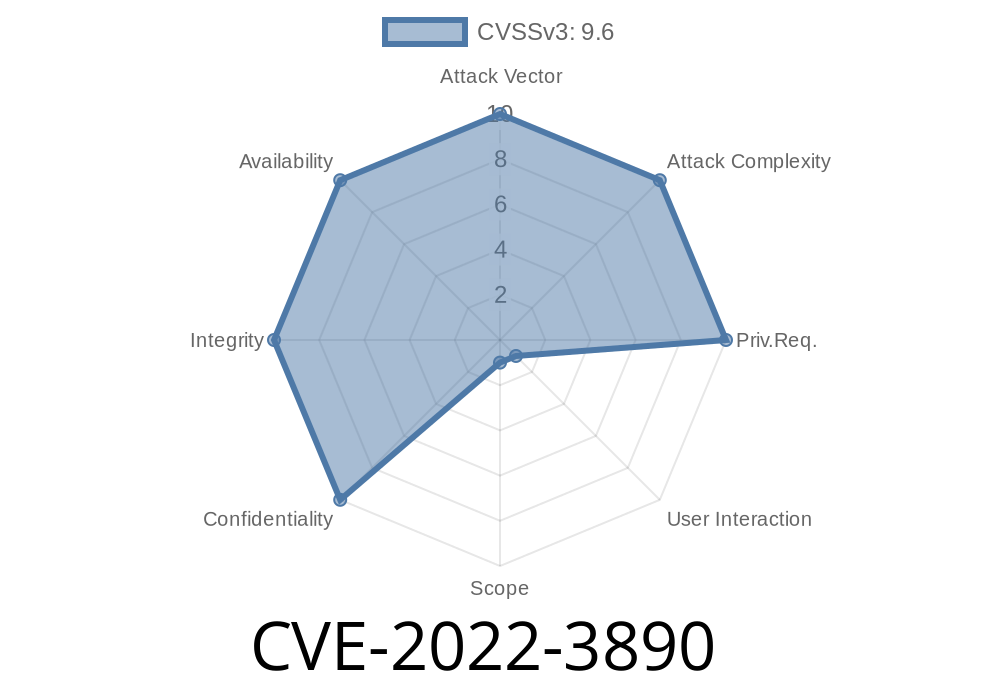
In this long-read post, we will discuss a security vulnerability with the code identifier CVE-2022-3890, which affects Google Chrome on Android versions prior to 107..5304.106. This issue is classified as a heap buffer overflow in the Crashpad module, and it could allow a remote attacker to perform a sandbox escape, potentially causing severe damage. The Chromium Security Team has classified the severity of this vulnerability as high.
First, let's take a look at what exactly a heap buffer overflow is and how it can be exploited in this specific case.
What is Heap Buffer Overflow?
Heap buffer overflow is a type of vulnerability that occurs when data is written to a buffer on the heap but exceeds the intended memory allocation. This can cause adjacent memory areas to be overwritten, leading to data corruption, program crashes, or even arbitrary code execution.
Crashpad Overview
Crashpad is an open-source crash-reporting system developed by Google that is used by Chromium-based browsers like Google Chrome. It is used to collect crash reports and other diagnostics related to software crashes. This information is essential for developers to diagnose and fix any code-related issues that lead to an application's crash.
Exploring CVE-2022-3890
CVE-2022-3890 is a heap buffer overflow vulnerability in Crashpad that affects Google Chrome on Android. A remote attacker who has compromised the renderer process of the browser can exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to visit a specifically crafted HTML page, thus allowing them to escape the sandbox and potentially execute malicious code.
The Security Advisory provided by Google Chrome can be found here: Chrome Releases: Stable Channel Update for Desktop
Let's take a look at a code snippet that shows the heap buffer overflow vulnerability in Crashpad
void CrashpadDemo::executeOverflow(char *data, size_t data_size) {
char buffer[64];
if (data_size > sizeof(buffer)) {
// Heap buffer overflow occurs here when data_size is too large
memcpy(buffer, data, data_size);
}
// Rest of the Crashpad-related code...
}
In the code snippet above, a simple memcpy() call is used to copy data from one buffer to another. However, if the data_size exceeds the size of the destination buffer, a heap buffer overflow will occur.
How Can an Attacker Exploit This Vulnerability?
To exploit the CVE-2022-3890 vulnerability, an attacker needs to create a crafted HTML page containing malicious code that would compromise the renderer process of Google Chrome on Android. Once this is achieved, the attacker can manipulate the data being processed by the Crashpad, triggering the heap buffer overflow, and potentially escaping the sandbox.
The following steps outline the exploitation of this vulnerability
1. Compromise the renderer process of Google Chrome on Android by injecting malicious code into a specifically crafted HTML page.
2. Manipulate the data being processed by the Crashpad module, causing the data size to exceed the allocated buffer size.
Conclusion
CVE-2022-3890 is a high-severity vulnerability affecting Google Chrome on Android. It is essential for users to update their browsers to the latest version (107..5304.106) to address this issue. Developers should be aware of the potential effects of heap buffer overflows in their code and take precautions to prevent such vulnerabilities.
Timeline
Published on: 11/09/2022 04:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/14/2022 15:15:00 UTC