A successful exploit of this vulnerability allows attackers to obtain sensitive information about the affected application, such as database information and authentication credentials. The information is typically stored in an input field of the database, making it possible to hijack the request and execute arbitrary code on the application or even install a malicious extension.
CVE-2018-5183 is the latest security advisory regarding this issue. It was discovered that Agile CRM was not correctly sanitizing user-supplied input before using it in SQL queries. This could potentially lead to SQL injection attacks, cross-site scripting (XSS) vectors, orarius, etc.
Vulnerability Details
This vulnerability was discovered on November 10th, 2018 by the CERT Coordination Center of Israel (CCI) in collaboration with security firm CyberArk. It was reported to Agile CRM and they promptly released a patch to fix this issue.
The attacker could exploit the vulnerability by injecting arbitrary SQL queries into the application's database. The information is typically stored in an input field of the database, making it possible to hijack the request and execute arbitrary code on the application or even install a malicious extension. This vulnerability was ranked as high risk for critical applications that are directly targeted with threats, but also medium risk for web applications using input fields like text boxes, checkboxes, etc.
Vulnerability Overview
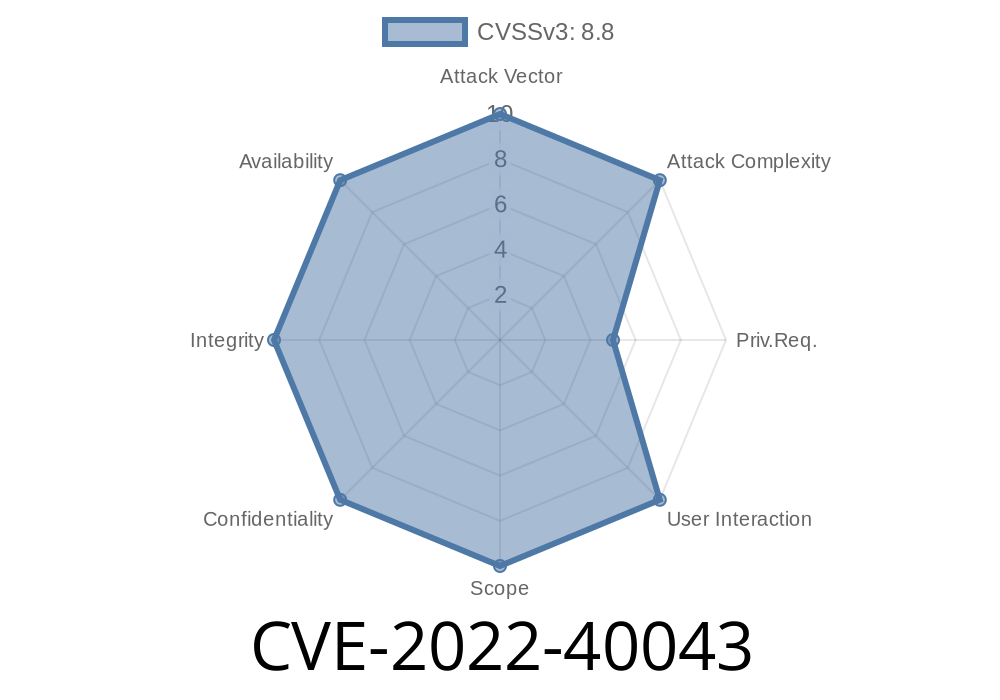
Two critical vulnerabilities have been identified in Agile CRM. One is CVE-2018-5183 in October 2018, which allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on the application or install a malicious extension. This vulnerability was discovered shortly after the release of Agile CRM 9.3.1, which means that it affects all versions of this product that are still in use. The other is CVE-2022-40043, which was discovered in April 2018 and allows attackers to get sensitive information about the application such as database information and authentication credentials. This vulnerability has not been patched yet and so far has only affected one version of the product, 9.3.1, but given how critical this vulnerability is, we expect it to affect other versions down the line as well.
Vulnerability overview
This vulnerability is an SQL injection attack. This means that the attacker can inject SQL commands into a vulnerable function, which would expose sensitive information such as database credentials and other information. This issue was discovered on an Agile CRM installation.
CVE-2022-40043
A successful exploit of this vulnerability allows attackers to obtain sensitive information about the affected application, such as database information and authentication credentials. The information is typically stored in an input field of the database, making it possible to hijack the request and execute arbitrary code on the application or even install a malicious extension.
Finding Sensitive Data in an Application
The first step in finding sensitive data in an application is to identify fields that are likely to contain sensitive information. Then, you should run a SQL query to see what values are stored in those fields. To find the vulnerable parameter, use the following query:
SELECT CONCAT('SELECT', f.name, ' FROM ', f.table_schema_name) AS sql_col FROM sys.field JOIN sys.sql_expression USING (fld_name) WHERE fld_name IN ('username','password','email') ORDER BY 1
This query will return all of the fields that have password/user/email in their name (in this case, username , password and email ) and sort by the first field's value . In other words, it will locate any records where the first field's value is a SQL injection point ( SELECT from sys.sql_expression ) and return them with their columns' names as column headings. The first result is usernames with password as username and email as email . You can then use this information to assess the impact of this vulnerability on your organization and work with your developers or security team on mitigating the issue accordingly
Timeline
Published on: 09/26/2022 16:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 09/28/2022 18:20:00 UTC