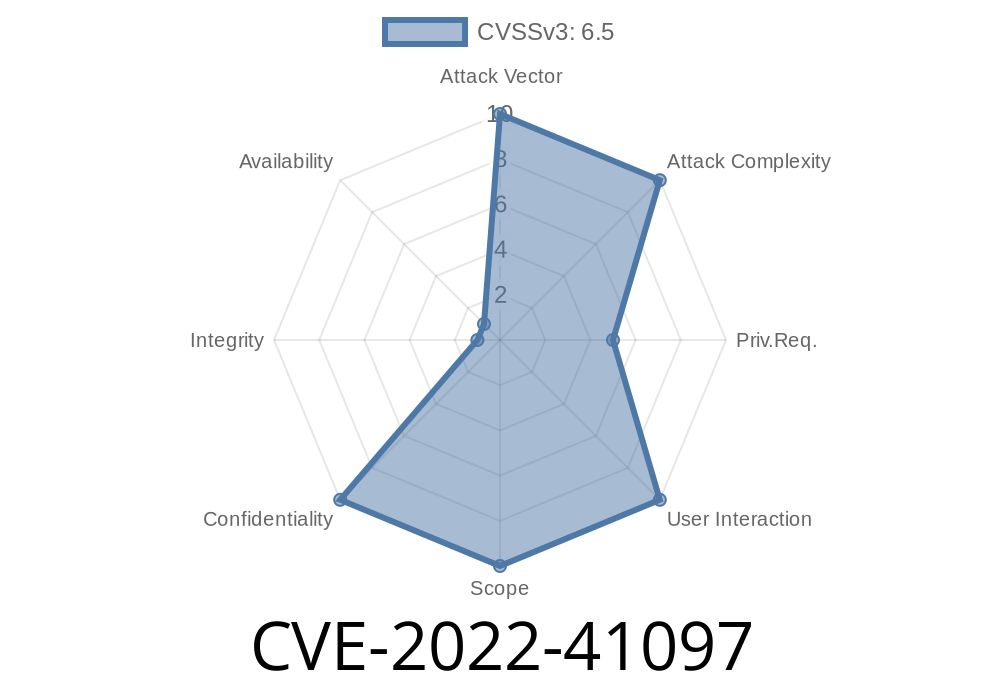
It is possible to retrieve information, such as the user’s name, e-mail address, or password, by submitting a specific packet on the NPS. This can be exploited if the service is configured to authenticate users on the RADIUS protocol. NPS is a web-based authentication server that can be used by administrators to control access to a network. By default, it is installed on the majority of Linux, Microsoft Windows, and Apple OS X systems. NPS is used in various industries for network access control, including companies in the finance, healthcare, and government sectors. It can also be found in residential and academic settings.
NPS can be exploited by an attacker by enticing a user to click a malicious link, visit a compromised web site, or open a malicious file. An exploit can be delivered in a variety of ways, such as sending an email with a malicious attachment, posting a link on social media, or dropping a file on a user’s computer. Once executed, the exploit attempts to retrieve information by sending a packet on the RADIANS protocol to the NPS. A successful exploit results in the attacker receiving the information that was requested by the user.
The following are some scenarios in which this vulnerability can be exploited. - An attacker can send a malicious link to a user, tricking him/her into visiting it. - An attacker can drop a malicious file on a user’s computer, tricking him
VENDOR RESPONSE AND MITIGATION
- There are no known exploits in the wild. - A patch is available for CVE-2022-41097.
Operation and Mitigation
An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by crafting a link or file that will execute the exploit. The user should be notified of when an attempt was made to exploit the vulnerability and if it was successful. If the user has administrative privileges, he/she can mitigate the attack by configuring NPS to authenticate users on RADIUS protocol instead of HTTP. If the user can’t change this setting, he/she could request an audit from their network administrator.
Useful links:
NPS - https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/network-access-control-systems-nanacvs/nps
RADIUS - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Remote_Authentication_Diameter
How Does This Vulnerability Make an Attack Possible?
If an attacker sends a malicious link to a user, the exploit executes when the user clicks on the link. The exploit attempts to retrieve information by sending a packet on the RADIUS protocol to the NPS. A successful exploit results in the attacker receiving the information that was requested by the user.
- An attacker can also drop a malicious file on a user’s computer, tricking him/her into opening it and running the exploit.
- Another way an attacker could use this vulnerability is by sending an email with a malicious attachment to an authorized user of your network.
An attack would be possible if: * The attacker wants to exfiltrate personally identifiable information from your system * The attacker wants to create access for himself/herself or others
To prevent exploits from being successful, you should always follow best practices for configuring your systems and limit privileges and permissions for operating systems, services, and users. You should also be sure that you are using strong passwords and two-factor authentication options.
Overview of the NPS Vulnerability
NPS is a web-based authentication server that can be used by administrators to control access to a network. By default, it is installed on the majority of Linux, Microsoft Windows, and Apple OS X systems. NPS is used in various industries for network access control, including companies in the finance, healthcare, and government sectors. It can also be found in residential and academic settings.
NPS can be exploited by an attacker by enticing a user to click a malicious link, visit a compromised web site, or open a malicious file. An exploit can be delivered in a variety of ways, such as sending an email with a malicious attachment, posting a link on social media, or dropping a file on a user’s computer. Once executed, the exploit attempts to retrieve information by sending specific packets on the RADIANS protocol to the NPS service. A successful exploit results in the attacker receiving the information that was requested by the user.
The following are some scenarios in which this vulnerability can be exploited: - An attacker can send a malicious link to a user who comes across it online; this links prompts him/her into visiting it (the attack is successful). - An attacker could drop an un-signed malicious file onto someone else's computer; this then prompts them into opening it (the attack will succeed).
Timeline
Published on: 11/09/2022 22:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/10/2022 00:33:00 UTC