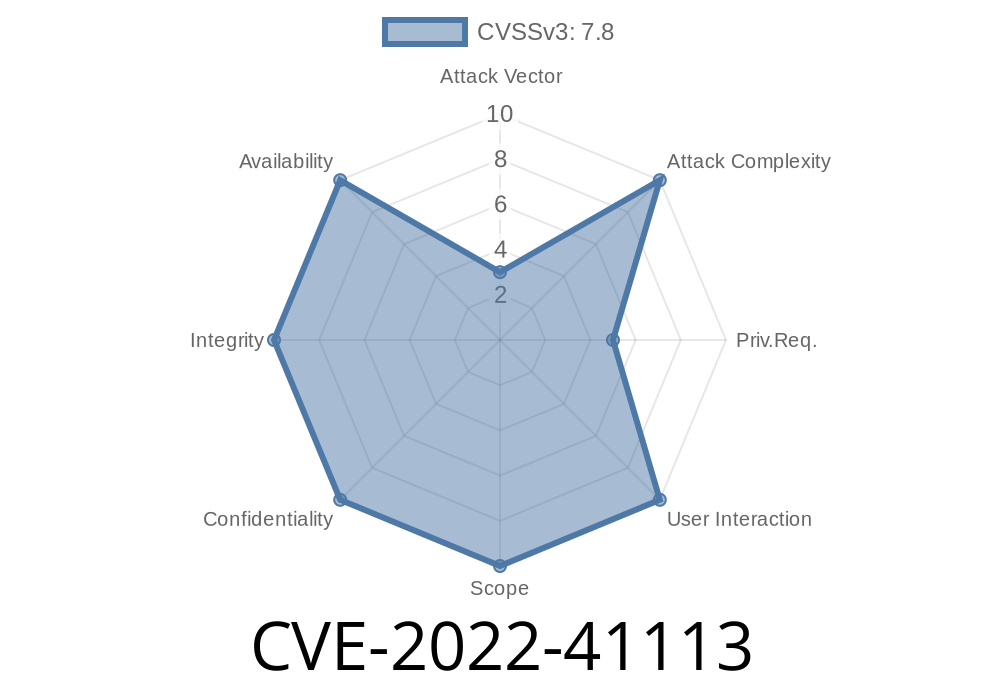
The Win32K kernel subsystem is the component of Windows operating systems that manages components that run on the same operating system as Windows, as well as on other computers.
A newly discovered vulnerability in the Win32K subsystem can be exploited by attackers to take advantage of elevated privileges on targeted systems. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to launch man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, obtain sensitive information, create denial-of-service (DoS) conditions, and execute arbitrary code on a target system.
The Win32k subsystem runs on top of the Kernel component, and is essential to the operation of the operating system. The Win32k subsystem handles input/output operations for Windows user-mode applications, and provides support for several Windows components, such as the Networking component, the Cryptography component, the Plug and Play component, and the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) component.
In order for applications to interact with Windows, the Win32k subsystem also provides support for several Windows components, such as the Networking component, the Cryptography component, and the Plug and Play component.
The Win32k subsystem is also used by several Windows components, such as the Networking component, the Cryptography component, and the Plug and Play component.
An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code under the context of the Win32k kernel subsystem.
Windows Version and Service Pack
The vulnerability affects all supported versions of Windows, including Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8.1, and 10.
An update to address this vulnerability is expected in March 2019 with the release of the next monthly service pack for Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019.
Vulnerability overview
The vulnerability is a local privilege escalation issue in the Win32k subsystem, which allows attackers to take control of the process running in the subsystem.
By exploiting this issue, attackers can escalate their privileges and execute code under the context of the Win32k kernel. This could lead to arbitrary code execution on a target system.
An attacker must first gain access to an affected system, then leverage this vulnerability to elevate their privileges and execute code under the context of the Win32k kernel.
Applying OS updates for vulnerable systems is recommended to remediate this flaw.
Win32k Information Disclosure Vulnerability
The Win32k kernel subsystem is the component of Windows operating systems that manages components that run on the same operating system as Windows, as well as on other computers.
A newly discovered vulnerability in the Win32k subsystem can be exploited by attackers to take advantage of elevated privileges on targeted systems. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to launch man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, obtain sensitive information, create denial-of-service (DoS) conditions, and execute arbitrary code on a target system.
The Win32k subsystem runs on top of the Kernel component, and is essential to the operation of the operating system. The Win32k subsystem handles input/output operations for Windows user-mode applications, and provides support for several Windows components, such as the Networking component, the Cryptography component, the Plug and Play component, and the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) component.
In order to interact with these components in order to use them in your application, it is vital that you are using an authenticated connection with them so they can trust you.
In order to do this securely via an authenticated connection with these components you need to use Kerberos authentication and mutual authentication with Kerberos tickets if possible. This means that you must also be using certificates or SSL/TLS when interacting with these components so they can trust your end point certificate/SSL/TLS endpoint as well.
If you cannot use SSL/TLS then another secure
Timeline
Published on: 11/09/2022 22:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/10/2022 00:33:00 UTC