This vulnerability is due to a lack of input validation in the web front-end in Windows when handling specially crafted web requests, which can be exploited to execute malicious code on the remote host.
An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by sending a malicious request to an affected Windows server when the server is configured to allow remote code execution. This can be accomplished via a malicious website, or by sending the request over a network that runs a Windows server.
CVE-2023-41110 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server that can be exploited by sending a malicious message over Exchange Server. This can be accomplished by sending an email message with an attached malicious Microsoft Word document, an Outlook message with an attached malicious Microsoft Word document, an Outlook email message with a malicious Microsoft Word document, or an Outlook meeting invitation with a malicious Microsoft PowerPoint document. CVE-2024-41112 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server that can be exploited by sending a malicious message over Exchange Server. This can be accomplished by sending an email message with an attached malicious Microsoft Word document, an Outlook message with an attached malicious Microsoft Word document, an Outlook email message with a malicious Microsoft Word document, or an Outlook meeting invitation with a malicious Microsoft PowerPoint document
Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities
The following table provides an overview of the remote code execution vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange Server that are mentioned in the blog post and their respective CVEs.
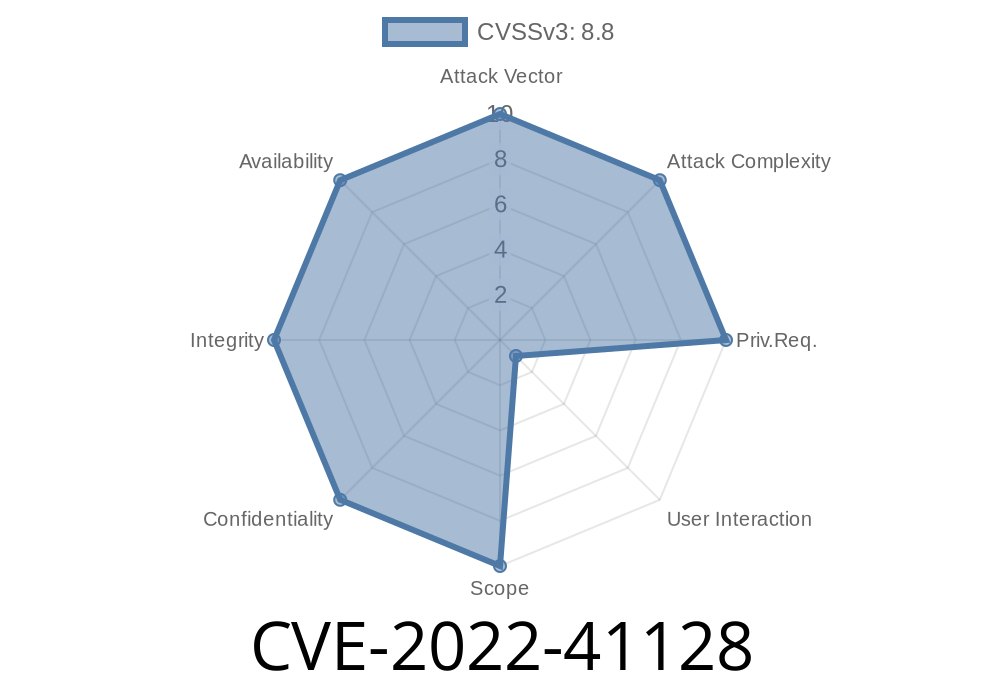
CVE-2022-41128
CVE-2023-41110
CVE-2024-41112
Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
A vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server can allow remote code execution on a Windows Server. Microsoft Exchange Server is an email server that provides messaging services for enterprises and individuals. This vulnerability exists due to a lack of input validation in the web front-end when handling specially crafted web requests. An attacker may exploit this vulnerability by sending a malicious request to an affected server when the server is configured to allow remote code execution. This can be accomplished via a malicious website, or by sending the request over a network that runs the Exchange Server variant of Windows.
An attacker exploiting this vulnerability may execute arbitrary code on the remote host without authentication required, or take complete control of the system without authentication required, which could lead to unauthorized actions such as stealing sensitive information from the system or disrupting its operation.
How do I know if I am vulnerable?
As of this time, there is no known way to detect whether an organization is vulnerable.
Microsoft Exchange Server Vulnerability
Microsoft Exchange Server is an email system that allows users to exchange messages, calendar events, tasks, and other data. It is typically deployed as part of a Microsoft Exchange Server Enterprise deployment. This vulnerability is due to a lack of input validation in the web front-end in Windows when handling specially crafted web requests, which can be exploited to execute malicious code on the remote host.
Timeline
Published on: 11/09/2022 22:15:00 UTC