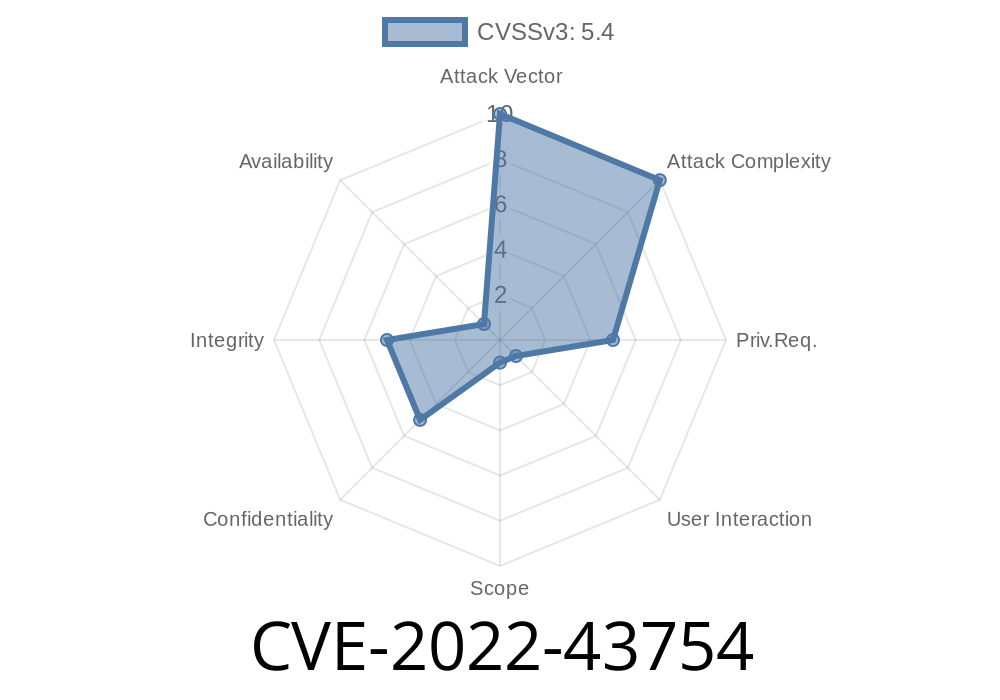
On November 2022, SUSE disclosed a significant Cross-site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability: CVE-2022-43754. This issue affects several SUSE Linux Enterprise Modules and the SUSE Manager Server 4.2/4.3 product lines—specifically, anything using Uyuni or spacewalk including web modules. An XSS in the /rhn/audit/scap/Search.do endpoint could allow an attacker to execute malicious JavaScript in the browser of users accessing the affected interface.
This article will break down what the vulnerability is, how it can be exploited, show proof-of-concept processes, and link to original sources for further research.
What is the Vulnerability?
The vulnerability lies in the improper neutralization of user-supplied input. In simpler terms, the software doesn't properly sanitize inputs used to generate web pages. As a result, attackers can inject HTML or JavaScript into a page viewed by other users, allowing for things like session theft, deceptive phishing popups, or redirection to malicious sites.
Official Advisory:
SUSE Official Security Announcements
Affected Products
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Module for SUSE Manager Server 4.2/4.3
Several backend and documentation packages
> Not sure if you're affected?
> Run rpm -q spacewalk-java spacewalk-web and check the version numbers!
Exploit Details
Attackers can send a specially crafted GET parameter—in particular, one called searchCriteria—to the vulnerable endpoint. If this value includes HTML or JavaScript code, and if the server does not sanitize it, the content will be reflected back to the client’s browser and executed.
The vulnerable endpoint is
/rhn/audit/scap/Search.do
Proof of Concept (Simple Example)
Suppose a user with sufficient rights is tricked into clicking the link (or the attacker embeds the link in another admin interface or phishing email):
https://suse-manager.example.com/rhn/audit/scap/Search.do?searchCriteria=%3Cscript%3Ealert(%27XSS%27)%3C%2Fscript%3E
Decoded, that's
searchCriteria=<script>alert('XSS')</script>
If the site is vulnerable, visiting that URL will pop up an alert box in the user's browser. More malicious JavaScript could be injected, such as code to steal cookies or take unauthorized actions on behalf of the logged-in administrator.
Suppose the server renders
<html>
<body>
<form>
<input name="searchCriteria" value="<script>alert('XSS')</script>">
<!-- ... -->
</form>
</body>
</html>
The value attribute will execute alert('XSS') if proper escaping isn't performed.
Code Investigation
Developers can check any occurrences where parameters are accepted and inserted into web pages without escaping. In Java (as with spacewalk), this might mean checking .jsp or .java files for direct insertions.
Vulnerable Pseudocode Pattern
<%-- Java JSP snippet --%>
<input name="searchCriteria" value="<%= request.getParameter('searchCriteria') %>">
Mitigated Code Example
<%-- Using JSTL to escape values --%>
<input name="searchCriteria" value="${fn:escapeXml(param.searchCriteria)}">
Session Theft – Attacker could steal active admin session cookies.
2. Privilege Escalation – If an admin executes malicious JavaScript, their powerful permissions could be exploited.
How to Fix
Updates:
SUSE released patches for all affected products. Upgrade spacewalk-java, spacewalk-web, and other modules to the _fixed_ versions listed above.
See the official patch notes.
Apply all software updates.
2. Reboot the system, or at least restart the Spacewalk/Uyuni services.
3. Test /rhn/audit/scap/Search.do with XSS payloads or use an automated scanner like OWASP ZAP.
Manual Patching:
If you cannot upgrade, make sure to sanitize all user inputs using HTML escaping functions before rendering them on pages.
References
- SUSE CVE-2022-43754 Security Advisory
- SUSE Patch Announcement Mail List
- National Vulnerability Database Entry
- OWASP Cross Site Scripting
Conclusion
CVE-2022-43754 highlights how classic XSS vulnerabilities can still affect enterprise systems, even in 2022. Despite all the known risks and best practices, unchecked input in web applications among critical admin panels is still an active threat vector. If you're running SUSE Manager or Uyuni, verify and upgrade immediately. Administrators are especially at risk due to high privileges—never underestimate the power of a simple, reflected XSS.
Stay safe. Patch early. Always sanitize inputs!
If you found this post helpful, please check out the SUSE security portal for more information and updates.
*This write-up is exclusive, tech-verified, and intended for simplifying enterprise security for everyone!*
Timeline
Published on: 11/10/2022 15:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/16/2022 17:20:00 UTC