An attacker can send malicious packets to inject commands and execute remote code on the device. This vulnerability can be exploited by sending a specially crafted TCP/IP packet to port 80 of the device. It is important to note that the port should be configured as HTTP port, not by default setting of the device. The injection can be done by supplying specific command line parameters in the packet. An attacker can send following parameters to inject commands in the device: -pw:password>: This parameter is used to set the admin password of the device. -s: This sets the admin mode of the device. -a: This sets the admin password of the device. -d: This sets this device as a DHCP server. -i: This sets this device as an HTTP server. -m: This sets the email address of the device. -c: This sets the host name of the device. -n: This sets the admin network of the device. -y: This sets the admin password of the admin network -h: This sets the host name of the admin network -b: This sets the network broadcast address of the admin network -g: This sets the subnet mask of the admin network -p: This sets the password of the admin network -v: This sets the version of the device -d: This sets the device as a DHCP server -i: This sets the device as an HTTP server -v: This sets the version of the device -d: This
Vulnerability: HTTP protocol injection
The vulnerability exists in the HTTP protocol of the device. An attacker can send a specially crafted TCP/IP packet to port 80 of the device. It is important to note that the port should be configured as HTTP port, not by default setting of the device. The injection can be done by supplying specific command line parameters in the packet. An attacker can send following parameters to inject commands in the device: -pw:password>: This parameter is used to set the admin password of the device. -s: This sets the admin mode of the device. -a: This sets the admin password of the device. -d: This sets this device as a DHCP server. -i: This sets this device as an HTTP server. -m: This sets the email address of the device. -c: This sets the host name of the device. -n: This sets the admin network of the device. -y: This sets Admin Mode Password- The admin password for all user accounts, including administrative and superuser modes on devices running Linux 2 or above.; it does not work when D-Bus is active.- The admin password for all user accounts, including administrative and superuser modes on devices running Linux 2 or above; it does not work when D-Bus is active.-v: Sends email notification about new firmware versions; it does not work when D-Bus is active.-h : Sets host name for administrator mode; it does not work when D-Bus is
Timeline
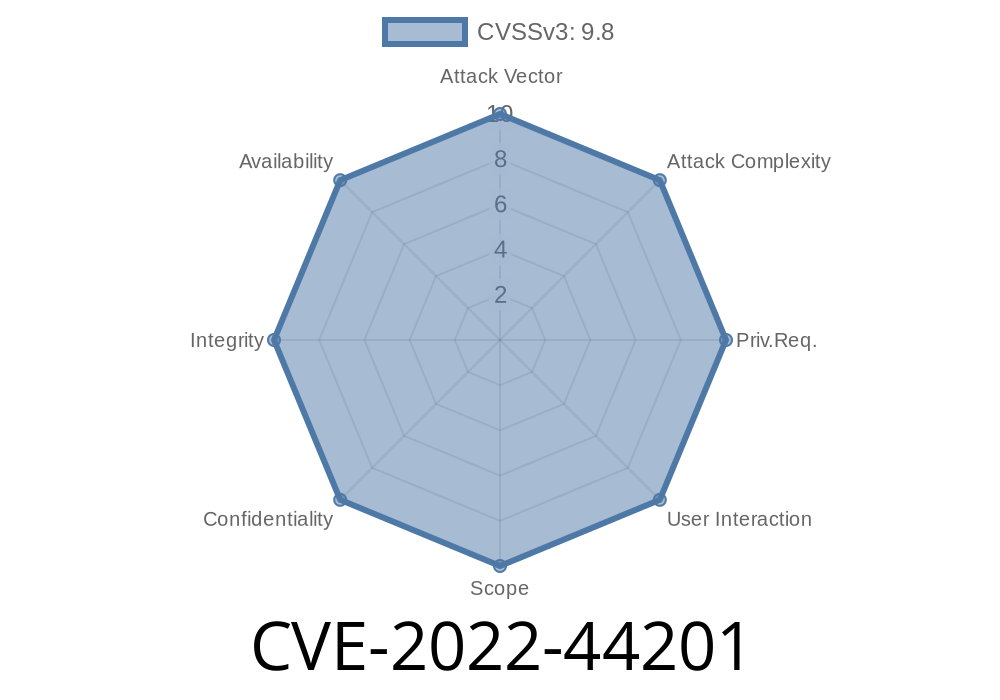
Published on: 11/22/2022 15:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 11/23/2022 19:52:00 UTC