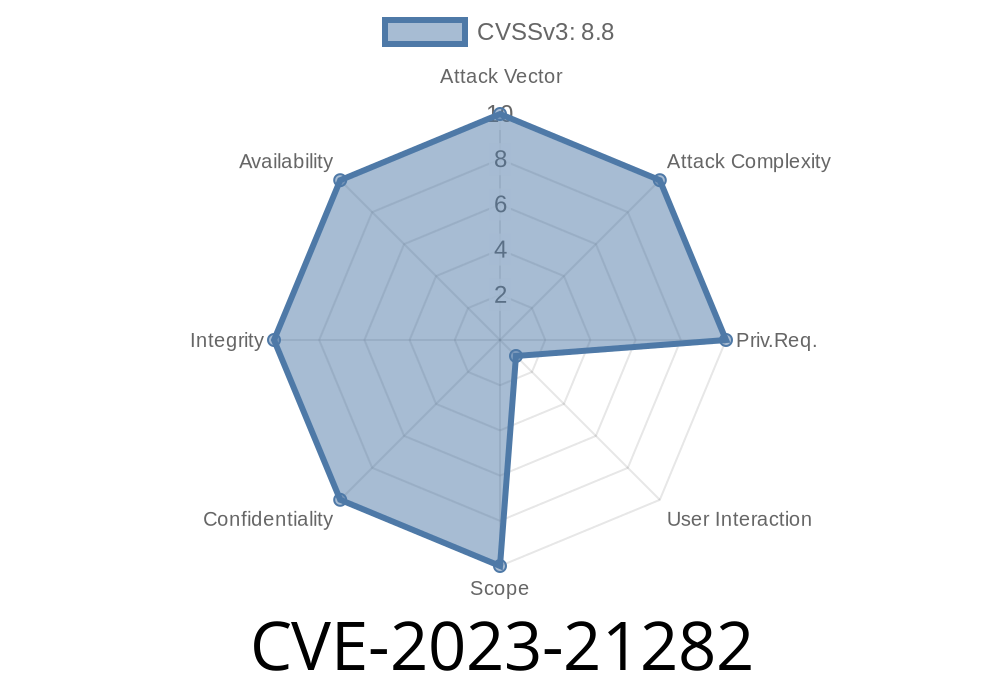
In early 2023, security researchers identified a critical vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-21282 within the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). This flaw is located in the TRANSPOSER_SETTINGS structure of the lpp_tran.h header file. At its core, the vulnerability stems from a faulty bounds check that allows for an out-of-bounds write, meaning that certain memory outside the intended buffer can be overwritten.
This vulnerability was rated critical primarily because it could be exploited for remote code execution with no extra execution privileges required. While user interaction is necessary to trigger the bug, a successful exploit gives attackers a potent entry point into the device.
Where's the Vulnerability?
Let's take a closer look at the problematic code in lpp_tran.h. The definition of TRANSPOSER_SETTINGS might look familiar to those who have worked with audio processing or similar structures.
Example Vulnerable Structure (Simplified)
// A simplified version of how TRANSPOSER_SETTINGS may be defined:
typedef struct {
int numSettings;
int settings[10]; // Fixed-size array, only 10 elements
} TRANSPOSER_SETTINGS;
Somewhere in the code, a function tries to copy user-supplied data (e.g., from a buffer) into the settings array:
void set_transposer_settings(TRANSPOSER_SETTINGS* ts, int* user_input, int n) {
// Faulty bounds check
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++) { // Should be i < n && n <= 10
ts->settings[i] = user_input[i];
}
}
Here, if the attacker can set n > 10, the loop will write past the end of the settings array—overwriting adjacent memory. This could corrupt important data or, in a worst-case scenario, let the attacker execute arbitrary code.
Prerequisites
- User Interaction: The vulnerability cannot be exploited directly, it requires a user to perform an action—like opening a malicious file or using a vulnerable feature in an app.
No Special Privileges: The exploit does not require root or system privileges.
- Remote Execution: With carefully crafted input, a remote attacker could deliver a payload (for example, via a multimedia file or app).
How an Attacker Might Exploit
1. Craft a Malicious Payload: The attacker creates input data that triggers the faulty set_transposer_settings logic.
2. Trigger the Vulnerable Code Path: The user is lured (e.g., by opening a file or using a compromised app).
Out-of-Bounds Write Occurs: The attacker's data overwrites memory just past settings[9].
4. Hijack Execution Flow: If the overwritten memory is strategically selected, it can overwrite a return address or function pointer, diverting program flow to attacker-controlled code.
Proof-of-Concept Snippet
While we won't provide an end-to-end exploit here, below is a minimal, illustrative C code snippet showing the crux of the vulnerability:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct {
int numSettings;
int settings[10];
} TRANSPOSER_SETTINGS;
void set_transposer_settings(TRANSPOSER_SETTINGS* ts, int* user_input, int n) {
// Faulty loop (real code is more complex, but concept is similar)
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
ts->settings[i] = user_input[i];
}
}
int main() {
TRANSPOSER_SETTINGS ts;
int malicious_input[12] = {,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,xdeadbeef,xfeedface};
set_transposer_settings(&ts, malicious_input, 11);
// This writes out of bounds!
printf("Completed (possible out of bounds write)\n");
return ;
}
In the real world, a payload at malicious_input[10] and malicious_input[11] could overwrite sensitive data in memory, depending on layout.
Impact and Mitigation
- Impact: If successful, an attacker could run code of their choice, potentially gaining control over the device, stealing data, or installing additional malware. Since no special permissions are required, anyone using the affected devices is at risk.
Mitigation:
- Update Devices: Ensure your device is running the latest Android security patches. Google has addressed this vulnerability in its June 2023 security bulletin.
ts->settings[i] = user_input[i];
}
References
- Android Security Bulletin - June 2023
- NVD Entry for CVE-2023-21282
- AOSP Commit Fix (example)
Final Thoughts
CVE-2023-21282 shows how a simple programming error in a bounds check can lead to severe, device-compromising vulnerabilities. As always, keeping devices up-to-date and ensuring strict bounds checks in code are keys to minimizing these risks.
Be sure to patch regularly, and spread awareness on the importance of secure coding practices!
*This post is exclusive content. For further details, see the official Android Security Bulletins and CVE database.*
Timeline
Published on: 08/14/2023 22:15:13 UTC
Last modified on: 08/21/2023 16:40:21 UTC