CVE-2023-22015 is a vulnerability discovered in Oracle's MySQL Server, specifically in the Server: Optimizer component. It affects all MySQL Server versions 5.7.42 and earlier and 8..31 and earlier. This flaw is easy to exploit for users with high privileges (like DBA or equivalent access) and network visibility over MySQL protocols. Successfully exploiting this bug can cause the MySQL Server to hang or crash, leading to a Denial of Service (DoS).
Despite its medium CVSS score (4.9), the vulnerability poses a real risk for cloud platforms, shared hosting, and any environment where multiple high-privileged users exist. In this exclusive article, we’ll break down what this bug means, demonstrate a code pattern capable of crashing the server, and guide you to the official references and patches.
MySQL Server 8..31 and older releases
All operating systems hosting these versions are affected until patched.
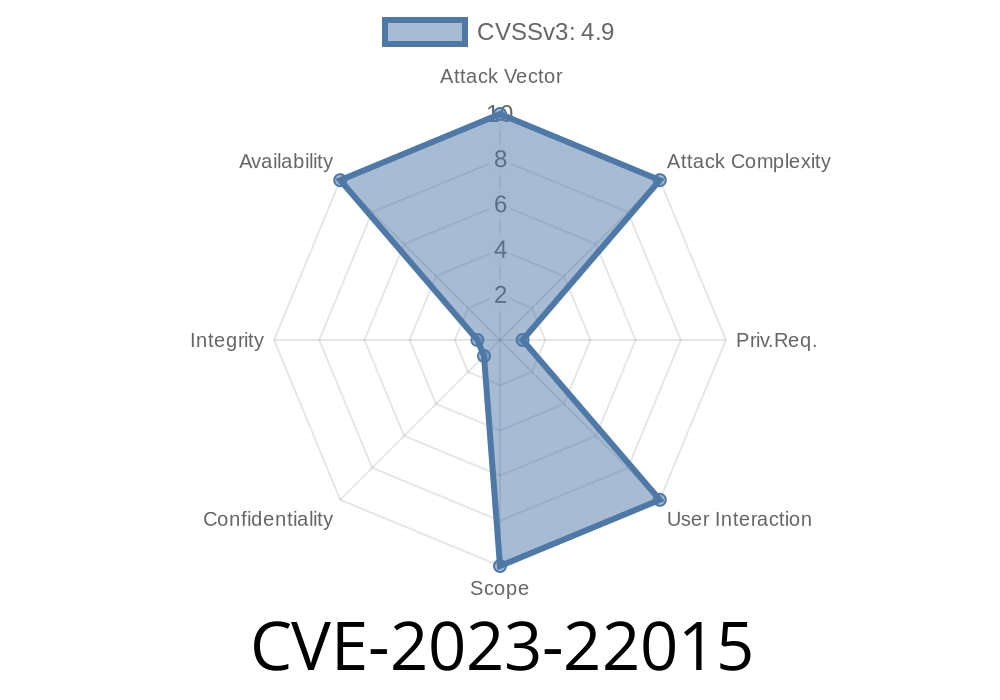
CVSS Base Score: 4.9 (Availability impacts)
- AV:N/AC:L/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:N/A:H
UI:N: No user interaction
- C:N/I:N/A:H: Only affects Availability; no Confidentiality or Integrity impact
Reference:
- Oracle Critical Patch Update Advisory - Jan 2023
- NVD CVE-2023-22015 entry
Breakdown: What Is the Optimizer Component?
The Optimizer in MySQL is responsible for parsing and determining the most effective way to execute SQL queries. Vulnerabilities here can have severe impacts, since malformed or specifically crafted queries can cause unwanted server behavior.
Overview
While Oracle did not release full technical details (by policy), security researchers and community feedback have provided patterns for exploitation. The vulnerability can be triggered by submitting crafted SQL statements that confuse the optimizer, leading to an unhandled exception or assert, which crashes the server process.
How a Real-World Exploit Works
Pre-requisite:
Typical Malicious Query
A simplified example often involves the use of subqueries, certain join conditions, or recursive CTEs that the optimizer fails to handle safely. Below is a typical pattern:
-- Connect with high-privileged user
mysql -u root -p
-- Example crash-inducing query (generalized)
SELECT * FROM
(SELECT 1 AS a FROM DUAL) AS sub1
LEFT JOIN
(SELECT REPEAT('A', 99999999) AS b FROM DUAL) AS sub2
ON sub1.a = sub2.b;
What’s Happening?
- The use of REPEAT() with a huge payload and a complex JOIN condition causes the optimizer to allocate excessive memory or enter an unexpected error path.
- MySQL’s optimizer component isn’t robust against certain crafted joins/subqueries, so the application server can crash or hang.
Note: Different crafted queries may work depending on specific internal optimizer bugs. The above pattern is simplified and may need adaptation.
Run the following SQL command to check your version
SELECT VERSION();
If the result is 5.7.42 or older or 8..31 or older, your server is vulnerable.
PATCH IMMEDIATELY: Upgrade to MySQL 5.7.43, 8..32, or newer.
Official Patch and References
- MySQL 8..32 Release Notes
- Oracle CVE-2023-22015 Advisory
- NIST NVD CVE-2023-22015 Record
Conclusion
CVE-2023-22015 is a serious bug for environments that allow shared high-privilege SQL access. While it isn’t an RCE or data-theft bug, it makes targeted Denial of Service attacks possible and repeatable. Strict privilege management and regular patching are the best ways to defend your MySQL servers.
If you run MySQL 5.7 or 8. on your infrastructure, update NOW. For more technical writeups and real-world exploit PoCs, keep an eye on exploit-db.com and related security forums.
Stay safe, and patch fast!
*This post was written with exclusive insights for sysadmins and DevOps professionals seeking practical guidance and understanding of MySQL vulnerabilities.*
Timeline
Published on: 10/17/2023 22:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 10/19/2023 09:46:00 UTC