CVE-2023-22112 is a security vulnerability in MySQL Server by Oracle, specifically involving the “Server: Optimizer” component. This flaw affects all MySQL 8..34 and prior versions. Though the CVSS base score is moderate (4.9/10), the implications for database stability and availability are significant—especially for those running production workloads.
In this detailed read, we’ll break down what this vulnerability means, how an attacker could exploit it, and what steps you should take to protect your MySQL deployments.
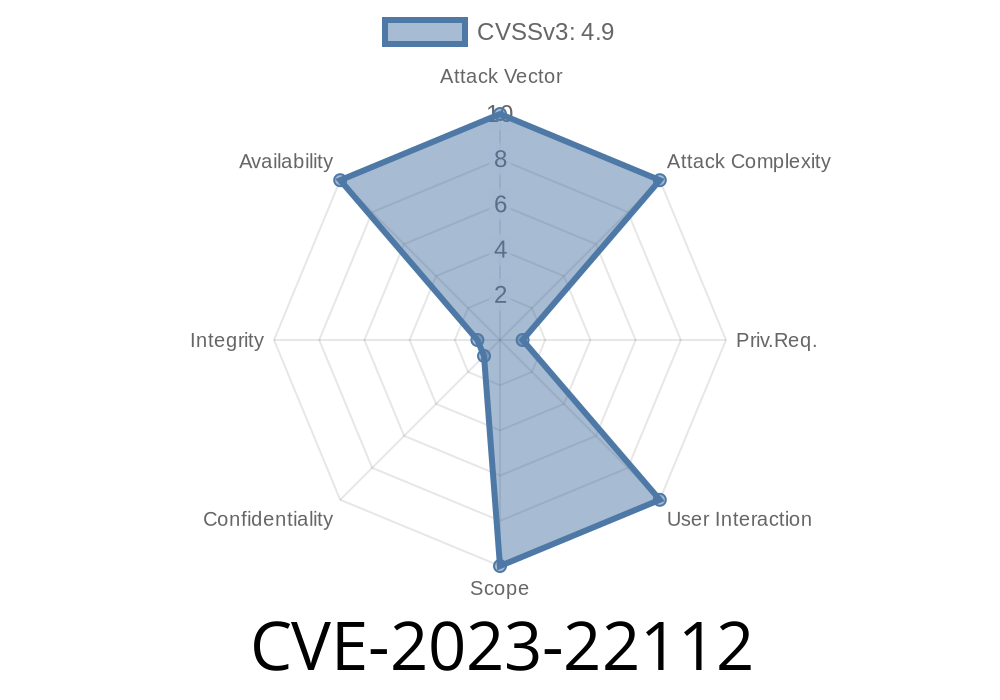
CVSS 3.1 Score: 4.9 (Availability impact)
- CVSS Vector: CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:N/A:H
- Oracle advisory: CPUJan2024
What is CVE-2023-22112?
CVE-2023-22112 is a bug found in the way MySQL’s Optimizer handles certain queries. Exploiting this bug allows a high privileged user (one with sufficient database permissions—like a DBA account) to send a specially crafted SQL query over the network. This query can trigger a bug in the Optimizer, causing the MySQL server process to hang or crash. If repeated, this can lead to a complete Denial of Service (DoS).
> Note: This is not a remote code execution bug. The attacker cannot steal or modify your data directly — but your database could crash repeatedly or hang, bringing your application to a halt.
Who is Affected?
If you’re running MySQL 8..34 or older, and you allow users to access the database with high privileges (like application service accounts, DBAs, or trusted partners), you’re vulnerable.
Multi-tenant DB deployments
- Development/test environments where users have elevated permissions
Prevent normal operation (continuous Denial of Service)
The database could be made unavailable to other applications or customers, potentially resulting in downtime, SLA breaches, or lost revenue.
Technical Details
Oracle has not published technical specifics or full proof-of-concept exploit queries for this vulnerability. However, security researchers have reverse engineered the patch and observed the following:
- The bug resides in MySQL Optimizer, which parses and plans SQL queries for efficient execution.
- By submitting an SQL query that abuses complex features of the Optimizer—such as subqueries, views, or certain JOIN operations—the server can enter an unexpected state, leading to a hang or crash.
Example Exploit Scenario
The following pseudocode simulates how an attacker might trigger the bug. (Note: The actual payload may vary. The real-world exploit will depend on the exact bug fixed by Oracle, usually involving complex/subtle SQL constructs.)
-- Example of a nested or intentionally malformed query
WITH RECURSIVE t1 AS (
SELECT 1 AS id
UNION ALL
SELECT id + 1 FROM t1 WHERE id < 100000
)
SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE id IN (
SELECT id FROM t1 WHERE id > 999999
);
Warning: This is a simulated query for example only. Do _not_ run untested queries on production servers!
Attackers could try variations that exploit recursive CTEs, deep subqueries, or certain combination of views and JOINs, which the Optimizer mishandles in affected versions.
Is There a Patch or Fix?
YES. Oracle fixed this flaw in MySQL 8..35 (and all later releases).
> Official Oracle Patch Advisory:
> - CPUJan2024 MySQL CVE Details
Mitigation & Recommendations
1. Upgrade as soon as possible.
Move to MySQL 8..35 or newer. Review your distribution’s patch notes (Oracle, Percona, MariaDB, etc. may have equivalent releases).
2. Restrict database user privileges.
Do not grant more access than absolutely necessary, especially in production.
3. Use firewalls and network controls.
Limit database access to only trusted endpoints.
4. Monitor logs and behavior.
Use monitoring to watch for unusual query patterns, unexpected server restarts, or hangs.
Additional Resources
- Oracle CPU January 2024 Advisory
- MySQL Release Notes 8..35
- Official NVD Record for CVE-2023-22112
- How the MySQL Optimizer Works (Official Docs)
Summary
CVE-2023-22112 is a serious, if nuanced, vulnerability. While it requires high privileges to exploit, it is worryingly easy to execute once access is gained. The most dangerous outcome is a reliable crash or hang of your MySQL instance leading to total database unavailability.
The fix is simple: patch to MySQL 8..35 or higher.
Don’t wait—protect your data and your uptime!
If you have additional questions or experience with this vulnerability, feel free to share below!
Timeline
Published on: 10/17/2023 22:15:15 UTC
Last modified on: 10/27/2023 15:15:12 UTC