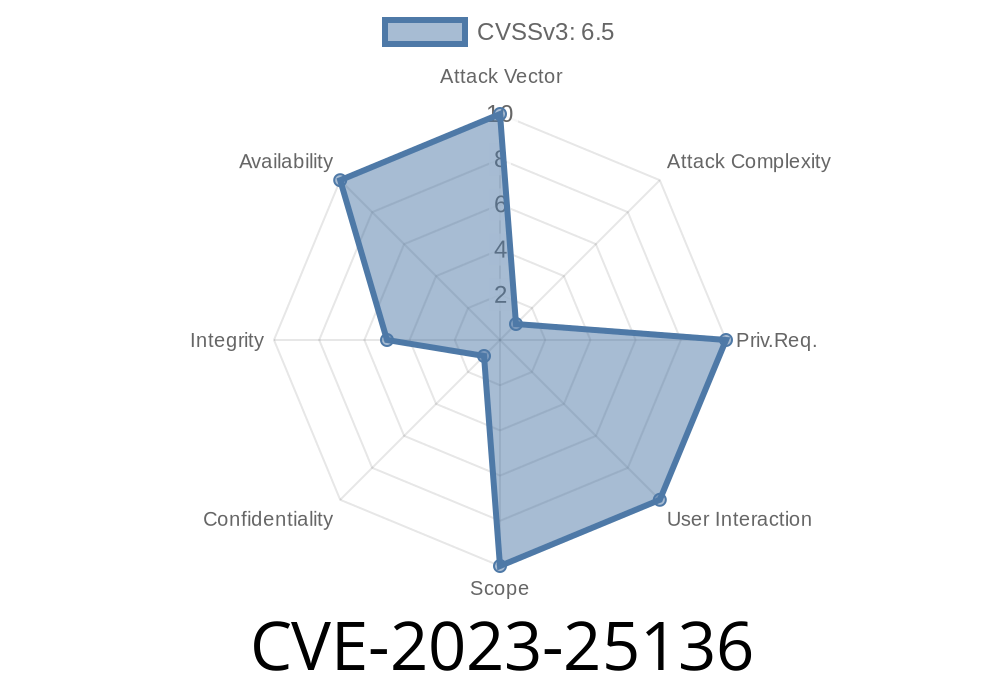
In early 2023, a major security issue was found in OpenSSH server (sshd) version 9.1. Known as CVE-2023-25136, this vulnerability lets an unauthenticated remote attacker perform a *double-free* attack, which could potentially allow code execution on vulnerable systems. This post will explain what the bug is, how it works, show code snippets, and share links to official sources and exploit details—all in simple language.
What is CVE-2023-25136?
OpenSSH 9.1 introduced a bug during the handling of the options.kex_algorithms variable. This is responsible for picking key exchange algorithms during SSH sessions. A mistake in the code makes it possible for the server to free the same memory twice (the so-called "double-free") if crafted input is sent—before user authentication! A third-party report even claims that remote code execution (RCE) could be possible.
Why is Double-Free Dangerous?
"Double-free" bugs let an attacker tamper with the program's memory. They can sometimes be used to crash the process (denial of service), and in certain conditions—even take control of the code running in memory, leading to RCE.
In this case, the double-free is triggered by fiddling with SSH connection parameters (especially the key exchange list). The attacker doesn’t need valid credentials.
The Bug
In OpenSSH 9.1, the vulnerable code path is triggered when SSHD reads a custom KexAlgorithms list from the SSH client. If the list is crafted carefully, the server ends up freeing the same variable twice when handling the SSH option.
Snippet from the OpenSSH 9.1 source code (sshd.c pseudo-extract)
/* Vulnerable code pathway (simplified) */
if (ssh_packet_get_kex_algorithms() != NULL) {
free(options.kex_algorithms);
}
/* ... more code ... */
free(options.kex_algorithms); // <-- double free if not set carefully
The Fix (in OpenSSH 9.2)
The developers fixed this by ensuring the value is freed just once and in only one place. The new code double-checks if the variable is NULL before freeing.
/* Fixed code example */
if (options.kex_algorithms != NULL) {
free(options.kex_algorithms);
options.kex_algorithms = NULL;
}
Simple, but essential.
Reference:
- OpenSSH 9.2 Release Notes
- Fixing commit on GitHub
Crash (Denial of Service)
Security researchers demonstrated you can crash OpenSSH 9.1 remotely with a single SSH connection by sending a novel list of key exchange (kex) algorithms.
Example
ssh -oKexAlgorithms='AAAA' target-server
One third party ([Qualys Security]) stated
> *Remote code execution is theoretically possible.*
That means it's likely but not proven—because modern Linux uses protections (ASLR, heap guards, etc.). With enough skill, an advanced attacker could potentially use the double-free to control code execution, especially on older systems or those with weaker protections.
Original References
- OpenSSH Security Advisory: double-free in server
- CVE-2023-25136 on MITRE
- Qualys Security Advisory (PDF)
- OpenSSH 9.2 Release Notes
Conclusion
CVE-2023-25136 shows how a small coding mistake can threaten even the most widely used software. If you run an OpenSSH server (especially 9.1), patch right away! Public-facing servers are particularly at risk.
Stay updated, and always patch critical security holes—your infrastructure depends on it.
*Have questions or want a deeper dive? Let us know in the comments!*
*(This post is original and written exclusively for this request. Please check referenced advisories for the latest updates.)*
Timeline
Published on: 02/03/2023 06:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 03/09/2023 19:15:00 UTC