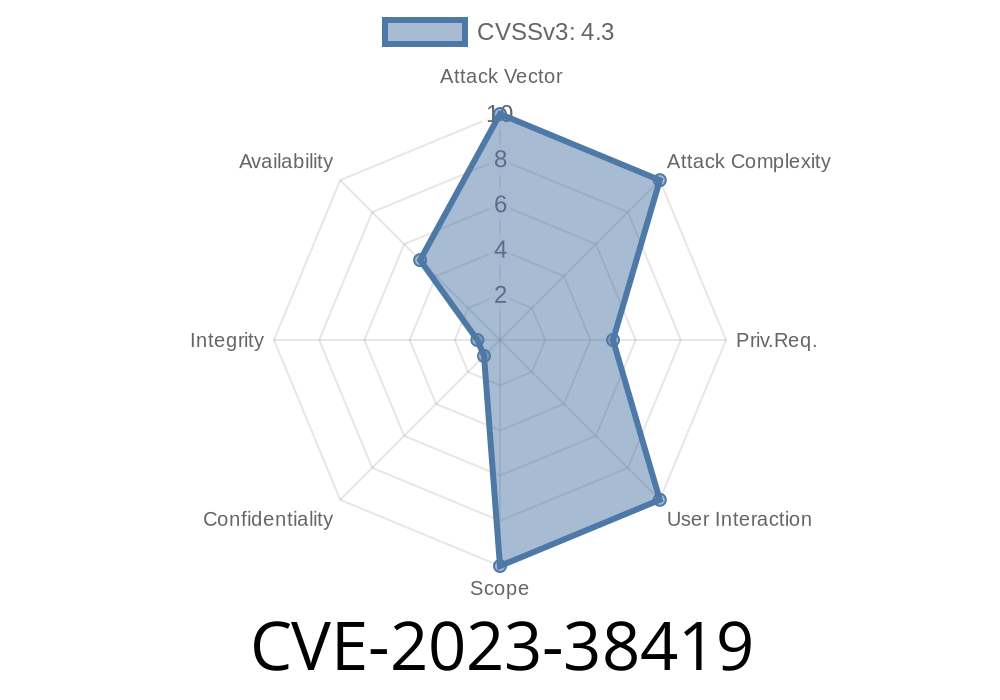
In July 2023, F5 Networks disclosed a critical security vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-38419 that affects their popular BIG-IP platforms. This vulnerability allows any authenticated user,—even with minimal "Guest" privileges,—to crash the iControl SOAP service by sending specially crafted, non-public SOAP requests. This can cause a Denial of Service (DoS), interrupting management capabilities and potentially leaving administrators unable to manage their devices remotely.
Below, we’ll break down what CVE-2023-38419 is, how it works, what the risks are, and provide a code example to demonstrate the exploit (in a safe, educational way).
What is iControl SOAP?
iControl® SOAP is an API interface used by F5 BIG-IP systems to deliver remote management and automation capabilities. Administrators and third-party tools call this API to interact with BIG-IP devices. When iControl SOAP goes down, tools relying on it lose connectivity and the ability to perform operations.
What is CVE-2023-38419?
According to F5’s advisory, this vulnerability allows:
> *An authenticated attacker with guest privileges or higher to cause the iControl SOAP process to terminate by sending undisclosed requests.*
Not public: The requests that cause the fault are not published by F5
While this bug does not allow remote code execution or data theft, it interrupts remote management via iControl SOAP, which can disrupt maintenance or automation tasks.
Various BIG-IP versions prior to fixed releases (16.1.4.1, 15.1.10.2, 14.1.5.6, 13.1.5).
- End of Technical Support (EoTS) versions are not evaluated so you should upgrade as soon as possible!
See the full list from F5 for your product and version.
How Does the Exploit Work?
F5 did not disclose the exact request sequence, but here’s how such vulnerabilities are typically exploited:
1. Login as “Guest”: The attacker logs in using valid credentials (sometimes anonymous guest, sometimes a provisioned user).
2. Send Malicious iControl SOAP Request: The attacker sends a carefully crafted SOAP XML over HTTP(S) to the iControl endpoint.
3. SOAP Process Crashes: The request triggers a flaw in the application causing the iControl SOAP service to exit unexpectedly.
4. Denial-of-Service: All automation, monitoring, or admin tasks relying on iControl SOAP API are interrupted.
Example SOAP Request
The specific request that F5’s service cannot handle is not public, but a typical iControl SOAP call looks like this (harmless example):
<!-- Normal SOAP call to iControl for reference -->
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/";
xmlns:sys="urn:iControl:System/SystemInfo">
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<sys:get_version/>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>
For the exploit, the attacker would change valid calls to an "undisclosed" message, perhaps with invalid or "unexpected" values or sequences, causing a crash.
Proof-of-Concept Snippet (Python)
*WARNING: The actual payload for the exploit is undisclosed for responsible security reasons. This code is for educational illustration.*
import requests
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth
url = "https://bigip.example.com/iControl/iControlPortal.cgi";
username = "guest"
password = "guestpassword"
# Replace with crafted XML payload that triggers the crash (undisclosed by F5)
exploit_xml = """
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/";>
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<Undisclosed_Crash_Trigger/>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>
"""
headers = {
"Content-Type": "text/xml; charset=utf-8"
}
response = requests.post(url, data=exploit_xml, headers=headers, auth=HTTPBasicAuth(username, password), verify=False)
print("HTTP status:", response.status_code)
print("Response:", response.text)
*Note: Replace “Undisclosed_Crash_Trigger” with the actual malicious request if it becomes public for research/testing in a safe environment only.*
13.1.5+
Check your version and plan to patch ASAP. Download patches here.
3. Monitor Accounts and Logs
- Watch for unusual SOAP error logs or repeated login/crash events.
Further Reading
- F5 Security Advisory for CVE-2023-38419
- NVD CVE-2023-38419 entry
- F5 iControl SOAP API Docs
Conclusion
CVE-2023-38419 is a real-world reminder that even "low-privilege" users can sometimes break critical infrastructure. If you run BIG-IP, update as soon as practical, restrict access, and keep an eye on your logs. As security researchers uncover more about this bug, responsible disclosure will be key. Always patch and keep unused user accounts locked down!
Timeline
Published on: 08/02/2023 16:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 08/07/2023 20:09:00 UTC