---
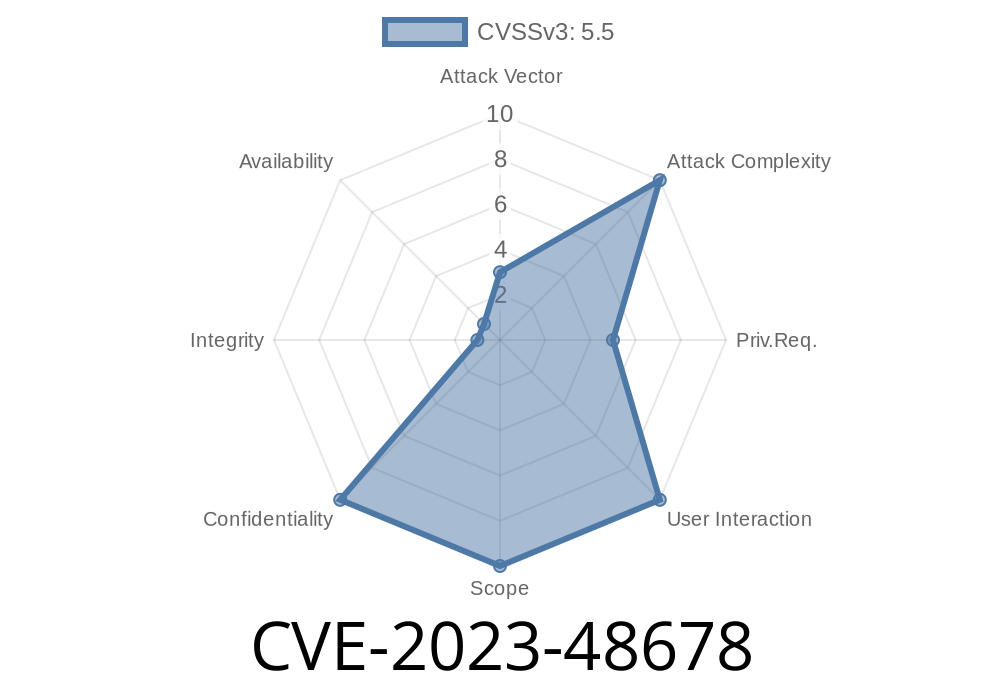
CVE-2023-48678 is a high-risk security vulnerability discovered in Acronis Cyber Protect 16 (Linux and Windows versions) that existed before build 37391. This flaw can lead to sensitive information disclosure due to weak or incorrect folder permissions. In this article, we'll dive into the details of the vulnerability, how an attacker could exploit it, some code snippets to demonstrate the issue, and reference links for further reading.
What Is CVE-2023-48678?
Acronis Cyber Protect is a widely-used backup and security solution designed for enterprise environments. The vulnerability CVE-2023-48678 refers to inappropriate permissions given to certain folders during installation or upgrade. Because of this, unauthorized users—whether on the same machine or on a network—could access sensitive files, read confidential data, and potentially escalate their privileges.
Below are more details on how this vulnerability works, how it can be exploited, and how you can check if you’re affected.
How Does the Vulnerability Work?
When Acronis Cyber Protect 16 (before build 37391) is installed, some crucial folders are assigned overly broad permissions. This means that regular (non-admin) users on the same system, or potentially even remote users if the folder is shared, may be able to access sensitive files that should be restricted.
Affected Environments
- Windows: The default installation grants users unnecessary READ access to program files and configuration directories, such as C:\Program Files\Acronis\.
- Linux: Similarly, folders like /opt/acronis/ or /var/lib/acronis/ may be readable by users who should not have access.
Example 1: Checking NTFS Permissions on Windows
You can use the icacls utility to view permissions. On a vulnerable system, you might see something like this:
icacls "C:\Program Files\Acronis\"
Bad Output Example
C:\Program Files\Acronis\ Everyone:(OI)(CI)(RX)
In this case, Everyone has "Read and Execute" access, which should only be given to Administrators.
You can use the ls -ld command to check directory permissions
ls -ld /opt/acronis/
Bad Output Example
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Jan 01 10:00 /opt/acronis/
Here, others (the last 'x') can browse the directory, which may contain sensitive files.
Suppose a config file with database credentials is world-readable
cat /opt/acronis/conf/job.cfg
If that’s readable by all users, any local user can fetch confidential information
[database]
host=192.168.1.99
user=backup_user
password=SuperSecret123!
Attackers could then use these credentials to connect to critical infrastructure!
Patching & Mitigation
Acronis fixed this issue in build 37391 and later. Upgrading to this build is strongly recommended.
Upgrade your software:
Download & apply the latest build from Acronis Cyber Protect Downloads.
`shell
icacls "C:\Program Files\Acronis" /inheritance:r /grant Administrators:F /remove Users Everyone
`bash
chmod -R 750 /opt/acronis/
chown -R root:backup-admin /opt/acronis/
References
- Acronis Cyber Protect 16 Release Notes
- National Vulnerability Database - CVE-2023-48678
- Security Advisory: CVE-2023-48678
Conclusion
CVE-2023-48678 is a reminder that folder and file permissions are a crucial element of security for backup and security appliances. If you’re using Acronis Cyber Protect 16, upgrade ASAP, verify your file permissions, and stay vigilant. Leaking any kind of sensitive information—even backup logs—can open the door for more serious attacks. Always keep your software current and tighten up your file system permissions!
*Stay secure. Update, audit, and protect your assets.*
Timeline
Published on: 02/27/2024 17:15:10 UTC
Last modified on: 02/28/2024 14:07:00 UTC