- Product: cecilapp/cecil (Static Site Generator)
Affected versions: Before 7.47.1
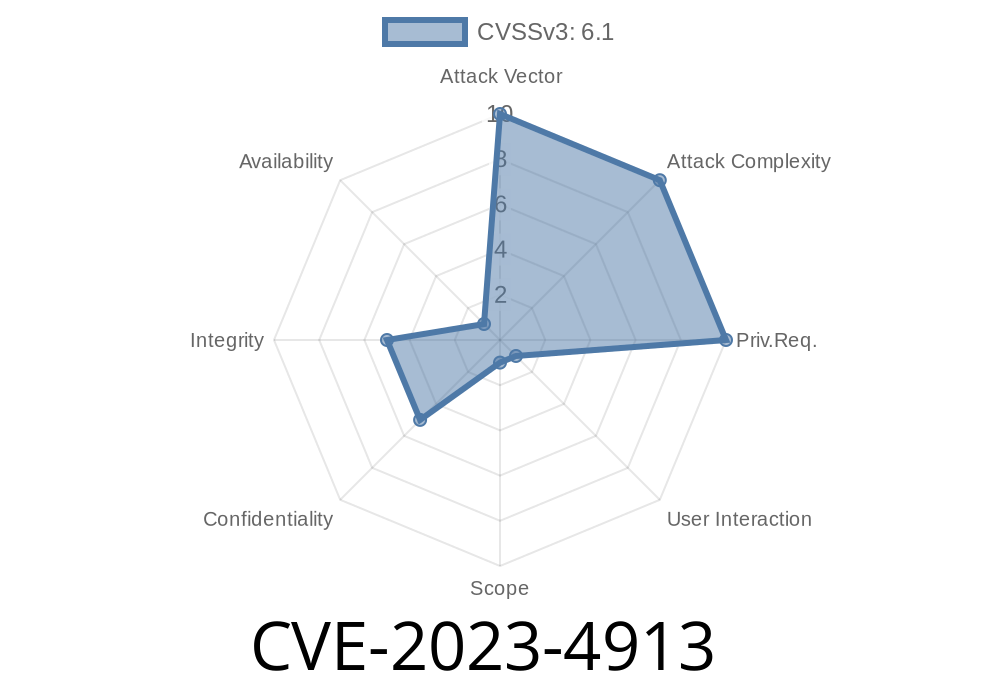
- CVE: CVE-2023-4913
What is Cecil?
Cecil is an open-source static site generator written in PHP. Used by individuals and organizations to publish fast, secure, and modern static websites from Markdown files and templates. You can find the source code on GitHub.
What is Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)?
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a security bug where attackers inject malicious code (usually JavaScript) into web pages, which then runs in the browsers of users who visit those pages. This can lead to stolen cookies, stolen sessions, redirects, or even malware downloads.
Reflected XSS: Payload is part of the request and reflected by the server in the response.
- Stored XSS: Payload saved on the server (e.g., in a comment) and delivered to any user visiting the page.
- DOM-based XSS: Payload is triggered in the browser through the DOM, not directly handled by the server.
In this case, CVE-2023-4913 is a reflected XSS.
## Technical Details: How Was cecilapp/cecil Vulnerable?
In versions before 7.47.1, the cecilapp/cecil project did not properly sanitize user-supplied data in certain HTTP request parameters. When accessed in "serve" mode (the built-in development web server), user input provided in the query string (like ?param=...) could be reflected back in rendered HTML without any encoding or sanitization.
This means if an attacker submits a crafted URL with malicious JavaScript code, it gets reflected and executed in the browser of anyone who clicks the link!
Let’s illustrate the issue using simplified PHP code, as used by Cecil’s development server
<?php
// This is a simplified example, not actual Cecil code
if (isset($_GET['q'])) {
$query = $_GET['q'];
// Vulnerable: Directly outputs user input into HTML
echo "<div>Search results for: $query</div>";
}
?>
What’s wrong?
- It outputs user input directly into HTML without escaping special characters, allowing attackers to inject HTML/JavaScript.
Suppose the Cecile dev server is running, and a user visits the following malicious link
http://localhost:808/?q=<script>alert('XSS')</script>;
What happens
1. The server receives q=<script>alert('XSS')</script>
`html
Search results for:
`sh
vendor/bin/cecil serve
`
http://localhost:808/?q=
The Official Fix
Version 7.47.1 of Cecil includes a patch that escapes or strips possible script tags or dangerous characters in user-supplied input.
Sanitizing User Input Example
if (isset($_GET['q'])) {
// Protects against XSS by escaping HTML special chars
$query = htmlspecialchars($_GET['q'], ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
echo "<div>Search results for: $query</div>";
}
Upgrade to Cecil 7.47.1 or later:
Always escape user input when reflecting it back in responses.
- Run dev services in safe/local environments.
More Reading and References
- Cecil Security Advisory: GHSA-qh7v-h5fc-jwq2
- Official CVE Entry (CVE-2023-4913)
- Reflected XSS – OWASP Guide
- Sanitizing Output in PHP
Closing Thoughts
While this XSS issue (CVE-2023-4913) was specific to Cecil’s dev server before 7.47.1, it’s a common problem whenever web apps reflect user input back into HTML without sanitization. Keep your frameworks up to date, sanitize all user input, and stay vigilant for web security advisories.
If you maintain a static site generator, development framework, or any web software, always encode output – not just for now, but as a habit!
Was this useful?
Let us know in the comments, or share new vulnerabilities in the open source ecosystem!
*Written exclusively for your security reading by AI, June 2024.*
Timeline
Published on: 09/12/2023 15:15:00 UTC
Last modified on: 09/14/2023 00:44:00 UTC