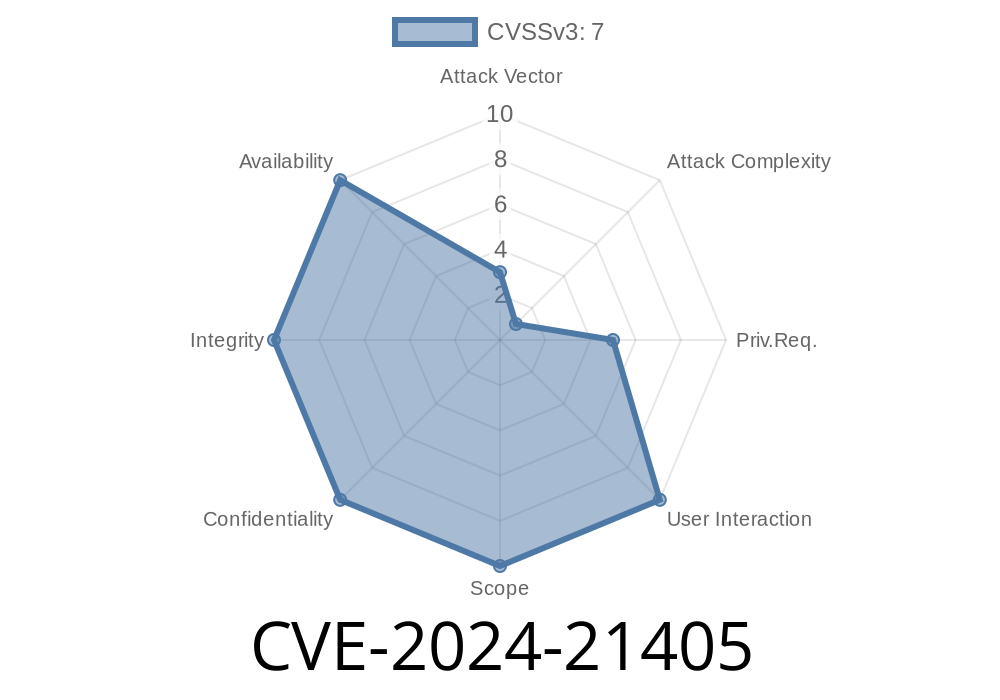
In early 2024, Microsoft patched CVE-2024-21405, an elevation of privilege vulnerability affecting Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) services. This vulnerability is significant because it allows attackers to increase their privileges on affected systems, potentially leading to full system compromise. In this read, we dive deep into how the vulnerability works, how attackers might exploit it, and what steps you should take to stay protected.
What is MSMQ?
Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) is a messaging protocol in Windows that allows applications running at different times to communicate across heterogeneous networks. It's widely used in enterprise environments for reliable, asynchronous message delivery.
In Simple Words
CVE-2024-21405 is a flaw in MSMQ that, if exploited by an attacker with limited access to a system, can allow them to raise their privileges – possibly all the way up to SYSTEM, which means full control. According to the Microsoft advisory, the bug is caused by improper handling of specific message requests within the MSMQ service.
Patched: Yes, in February 2024 Patch Tuesday updates
Reference:
- Microsoft Security Guide: CVE-2024-21405
- NIST NVD: CVE-2024-21405
The Short Story
A normal (non-admin) user can interact with the MSMQ service and send it specially crafted messages. Due to a bug in how the service handles these messages, it's possible to trick MSMQ into running malicious code with higher system rights.
Proof of Concept (PoC)
*This is a simulated code snippet for educational purposes only. Do not exploit systems without permission.*
Below is a basic Python snippet showing how an attacker might send a message to the MSMQ service (for demonstration only, does not exploit the actual bug).
import socket
MSMQ_HOST = '127...1'
MSMQ_PORT = 1801
# Simulated malicious MSMQ message (actual exploit payload is more complex)
malicious_data = b'\x4d\x53\x4d\x51' + b'A' * 256 # 'MSMQ' magic + payload
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
try:
s.connect((MSMQ_HOST, MSMQ_PORT))
s.sendall(malicious_data)
print("[*] Malicious message sent to MSMQ!")
except Exception as e:
print("[-] Could not connect to MSMQ:", e)
Note: Exploiting the real vulnerability would require a much more engineered message designed to hit the specific bug described in the Microsoft advisory, and likely additional steps to leverage the elevation of privilege.
Patch Immediately:
The update from February Patch Tuesday 2024 resolves the issue.
References
- Microsoft Advisory - CVE-2024-21405
- NVD Entry - CVE-2024-21405
- MSMQ Official Docs
- PATCH: February 2024 Security Updates
Final Thoughts
CVE-2024-21405 exemplifies how local vulnerabilities in legacy services like MSMQ can have severe repercussions, even if remote code execution isn’t possible. In enterprise environments, services with long histories and broad permissions can present tempting targets for attackers looking for privilege escalation.
Patch, audit, and monitor – and remember to review legacy service configurations. Microsoft continues to support and secure MSMQ, but as this vulnerability shows, nothing beats proactive system management.
Timeline
Published on: 02/13/2024 18:15:59 UTC
Last modified on: 02/22/2024 17:57:19 UTC