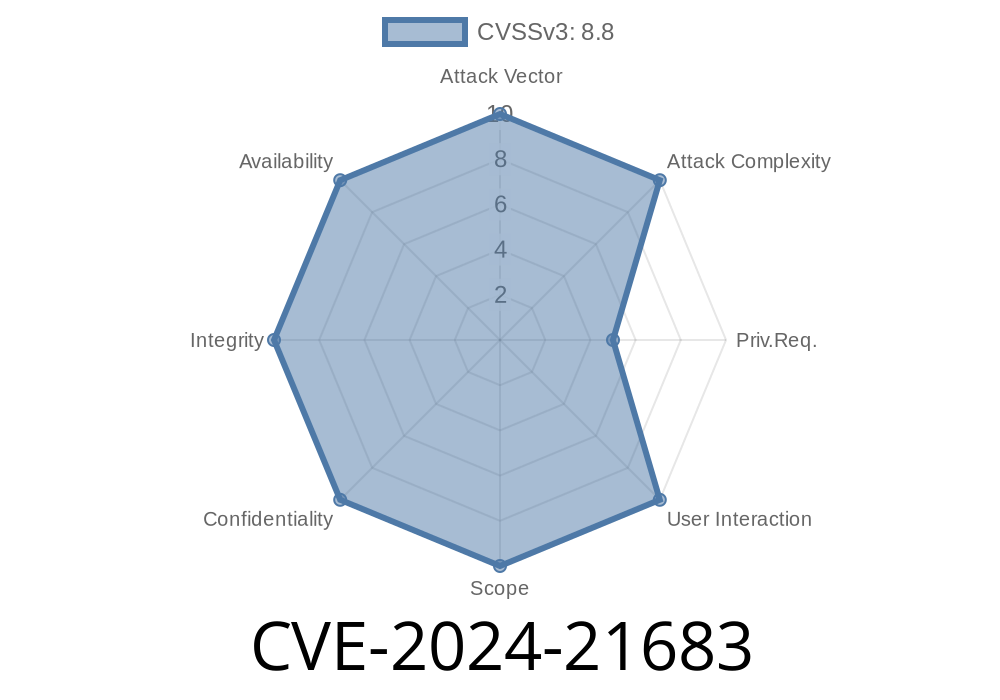
Confluence, Atlassian’s popular collaboration software for enterprises, has been hit with yet another serious security threat: CVE-2024-21683, a Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability. This bug was introduced in version 5.2 of Confluence Data Center and Server, and it comes with a CVSS Score of 8.3—that’s high, meaning the risk is very real.
In this detailed (and easy to understand) post, we’ll walk through the basics, include a code example, exploit details, official links, and what to do next. If you know your company runs Confluence, keep reading.
What is CVE-2024-21683?
CVE-2024-21683 is a Remote Code Execution hole, discovered internally by Atlassian, that allows an authenticated attacker to run any code they want on the server. That means if someone has a username and password on your Confluence instance, they could completely take it over.
Availability: Whole servers could be stopped or wiped.
- No User Interaction Required: All the attacker needs is an account. They don’t need to trick an admin or get anyone to click a link.
Where did it come from?
- Affected Versions: Introduced in Confluence Data Center and Server version 5.2 and all later releases up to the patched versions.
How Does the Exploit Work?
While Atlassian hasn’t published detailed exploit code (for obvious reasons), information in security circles, PoCs, and patch logs show this exploit usually leverages a specific endpoint or function that processes user-supplied input unsafely. By manipulating this input, an attacker can inject malicious code that the server processes.
Simulated Exploit Snippet
Below is a simplified Python snippet demonstrating how an attacker might exploit affected Confluence servers that don’t have the patch installed. Remember: THIS IS FOR EDUCATION AND DEFENSE TESTING ONLY.
import requests
# Replace with your target and credentials
confluence_url = 'https://your-confluence-site.com';
username = "testuser"
password = "password123"
# Hypothetical vulnerable REST endpoint
endpoint = f"{confluence_url}/rest/api/some-vulnerable-endpoint"
# Payload to execute a shell command (for demo, list directory)
payload = {
"input": "some-value; ls -la /;" # Injection via command separator
}
# Authenticate via HTTP Basic Auth
response = requests.post(endpoint, auth=(username, password), json=payload)
print("Server Response:")
print(response.text)
1. Upgrade Immediately
- Visit Atlassian Confluence Release Notes
- Download latest safe versions from the Download Archives.
If you cannot upgrade immediately, Atlassian recommends upgrading to a supported fixed version (see their release notes for exact versions).
References & More Info
- Atlassian Confluence Release Notes
- Confluence Download Archives (patch/fixed versions)
- Official Atlassian Security Advisories
- NVD Entry for CVE-2024-21683 *(if published)*
Final Thoughts
Vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-21683 show how even “trusted” internal tools can become immense liabilities. If your business runs Confluence Data Center or Server, don’t wait—patch now, monitor your systems, and keep your software up to date. If you have any doubts or spotted anything suspicious, consult with your IT or security team immediately.
Timeline
Published on: 05/21/2024 23:15:07 UTC
Last modified on: 06/04/2024 14:30:30 UTC